Feb 15, 2013 | News
The ICJ today expressed its great concern at reports that the police in Zimbabwe have carried out what appears to be an unjustifiable raid against human rights defenders, Zimbabwe Peace Project (ZPP).
On 11 February 2013, police reportedly raided the offices of ZPP, a non-profit organization comprising of non-governmental organizations (NGO) and church-based organizations, and confiscated mobile phones, wind up radios, files with donor information, political violence reports and DVDs.
“The continuous attacks against NGOs by law enforcement agencies clearly shows that there are systematic assaults on human rights defenders which are closing the democratic space within which human rights defenders operate”, said Martin Masiga, Deputy Director of the ICJ Africa Regional Program. “It appears that the police are trying to discourage human rights defenders from engage with citizens of Zimbabwe to exchange information concerning their rights and freedoms, as the country heads for a referendum and election during the course of the current year”.
The police undertook the raid pursuant to a search warrant issued by the Superintendent of the C.I.D Law and Order Division of the Zimbabwe Republic Police (ZRP).
The search warranted stated that there were reasonable grounds to believe that ZPP had committed offences in terms of the Criminal Law (Codification and Reform) Act, the Immigration Act, and the Customs and Excise Act.
On the same evening eight police officers were discovered by the security team that provides rapid response for the ZPP at the ZPP premises, after an alarm had been tripped.
The police officers demanded to gain access into the office of ZPP Director, Jestina Mukoko. However the office was locked and they could not enter. These officers did not have a search warrant.
The ICJ welcomes the statement of the Co-Minister of Home Affairs, the honourable Theresa Makone, which says that the Cabinet is concerned “over the overzealousness of some police officers”, and that the police “must follow the basic principle of policing” which is to investigate “to arrest rather than arresting to investigate”.
The ICJ urges the Zimbabwean government to ensure that it protects human rights defenders in accordance to United Nations Human Rights Defenders Declaration, endorsed by all the States including Zimbabwe.
The ICJ further urges the Zimbabwean government to stand by its commitments to the Zimbabwean Constitution, the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which it is a state party. These instruments expressly guarantee the right to the freedom of opinion, expression and association.
Lastly, the ICJ further urges the police in Zimbabwe to conduct impartial investigations into allegations of violations of human rights, to hold accountable those responsible for human rights abuse and to protect human rights defenders and NGOs that work for the protection of human rights in Zimbabwe.
Contact:
Martin Okumu-Masiga, Deputy Director of the ICJ Africa Regional Programme, t: +27110248268; e-mail: martin.okumu-masiga@icj.org

Feb 15, 2013
 The ICJ wrote to the Nigerian President Goodluck Jonathan to call his attention to the ruling by the Court of Justice of the Economic Community of West African States in the case SERAP vs The Federal republic of Nigeria.
The ICJ wrote to the Nigerian President Goodluck Jonathan to call his attention to the ruling by the Court of Justice of the Economic Community of West African States in the case SERAP vs The Federal republic of Nigeria.
In this case the ECOWAS Court recently ruled that Nigeria had violated its obligations under the Article 24 of the African Charter on Human Rights and People’s Rights, which provides: “All peoples shall have the right to a general satisfactory environment favourable to their development”.
The case concerns activities by oil companies operating in the Niger Delta, whose operations were identified as the cause of severe pollution of water, land and the general environment where people of the Niger Delta live.
The ICJ is asking the Nigerian President to ensure the enforcement of the ruling by the competent authorities in the Niger Delta and the Federal Government.
Nigeria-ICJ letter to President-advocacy-2012 (full text of the letter in pdf)

Jan 17, 2013 | News
 The ICJ expresses great concern over the recent pattern of attacks on human rights defenders in Zimbabwe by the Law and Order Section of the Zimbabwe Republic Police (ZRP).
The ICJ expresses great concern over the recent pattern of attacks on human rights defenders in Zimbabwe by the Law and Order Section of the Zimbabwe Republic Police (ZRP).
The ICJ says the systematic assault on human rights defenders has taken the form of arbitrary arrests of human rights practitioners, unjustifiable raids on their offices and interference with their meetings amongst other forms of harassment.
Such attacks have been a continuous source of international concern, including when raised by United Nations Human Rights Council in its Universal Periodic Review of Zimbabwe in 2011.
There has been a failure on the part of the Zimbabwe judiciary to exercise its responsibility of judicial oversight over these abuses, the ICJ adds.
“Government officials including the ZRP are using repressive laws to harass and intimidate human rights defenders and NGOs with the aim of causing them to abandon their work in promoting and defending human rights in Zimbabwe,” said Martin Masiga, Deputy Director of the Africa Regional Programme of the ICJ. “It is deplorable that the government has contrived to fabricate charges against its own citizens to discredit, delegitimize and frustrate their lawful civic activities.”
The ICJ underscores the reports of the arrest of Zimbabwe Human Rights Association (ZimRights) Director Okay Machisa (photo) on Monday, 14 January 2013 in Harare on charges of allegedly “conspiring to commit voter registration fraud and publishing or communicating falsehoods”.
The magistrate in this matter denied bail for reasons inconsistent with international fair trial standards and which appeared to be politically motivated.
The arrest of Okay Machisa follows the detention of his deputy, Leo Chamahwinya and three other staff members of ZimRights in December 2012 on the same charges.
These arrests occurred just a few weeks after ZimRights [publicly] denounced the trend of increasing police brutality across Zimbabwe and called for urgent action by competent authorities to address these human rights violations.
The Zimbabwean Constitution, the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which Zimbabwe is a state party, guarantees the right to the freedom of opinion, expression and association.
The UN Declaration on Human Rights Defenders, which articulates universal standards for the protection of those working to protect human rights, affirms that “everyone has the right, individually and in association with others, to promote and to strive for the protection and realization of human rights and fundamental freedoms at the national and international levels “.
Accordingly, Zimbabwe has a legal obligation to protect those persons and organisations that strive for the protection and promotion of human rights.
Zimbabwe reportedly will hold national elections in 2013, the first since the formation of the Government of National Unity following the tragic events of the 2008 national election.
The ICJ insists it is essential for the people of Zimbabwe and for the advancement of Zimbabwe in the arena of constitutional democracy that State officials exercise their responsibility to protect human rights activists instead of attacking them.
The ICJ urges the Government of Zimbabwe to respect regional and international human rights standards, and to call upon its law enforcement agencies to cease the harassment and intimidation of HRDs in Zimbabwe.
The ICJ calls on the Zimbabwean judiciary to exercise its responsibility to uphold international fair trial standards and the constitutional provisions of Zimbabwe in adjudicating the matters relating to human rights defenders, including the officials of ZimRights.
Contact:
Martin Okumu-Masiga, Deputy Director of the ICJ Africa Regional Programme, t: +27110248268; e-mail: martin.okumu-masiga(at)icj.org

Dec 6, 2012 | News
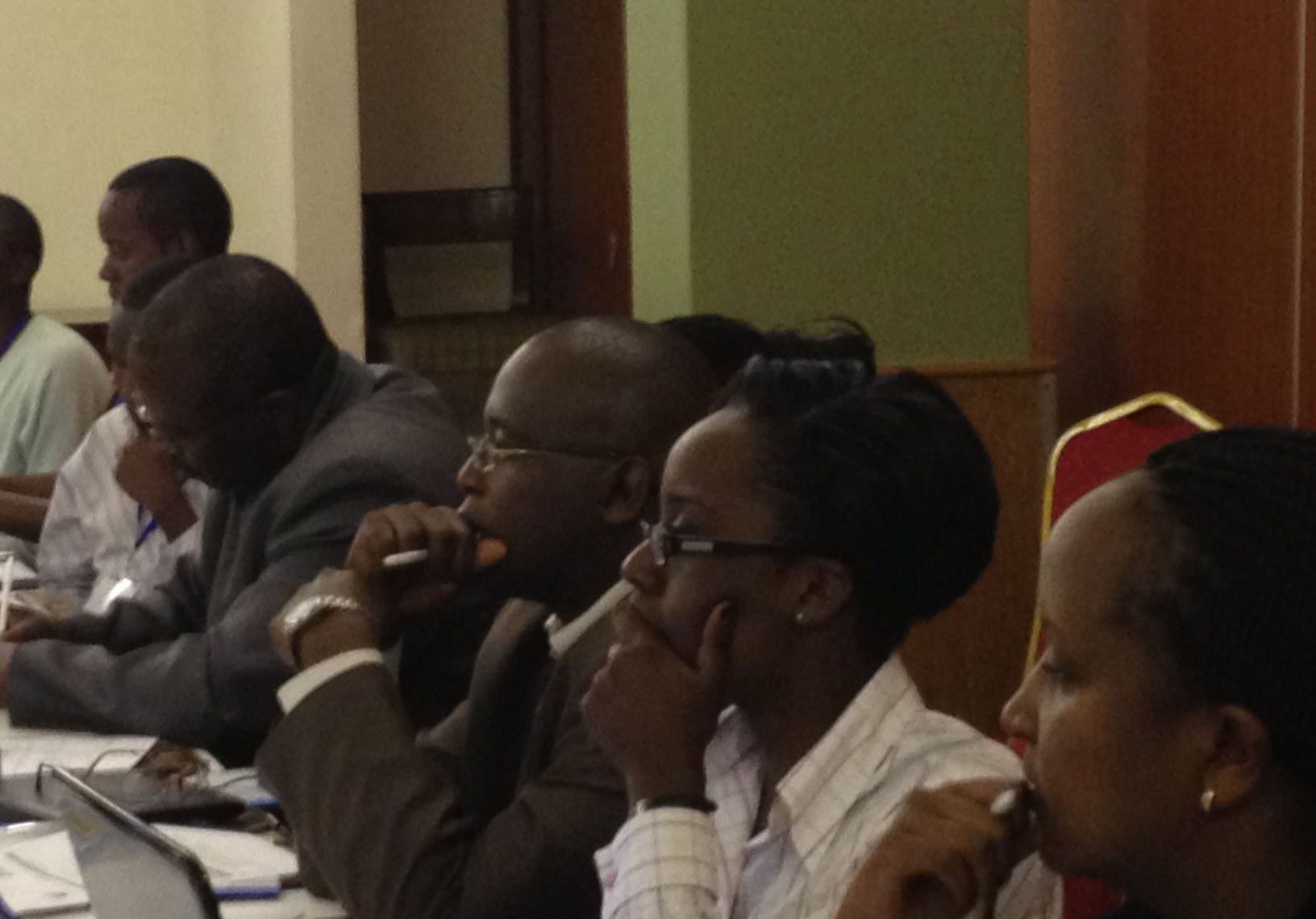 On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.
On 6 December 2012, the ICJ and ICJ-Kenya convened a roundtable entitled “LGBT Human Rights” in Nairobi.
The event brought together members of the Kenyan bar with LGBT human rights activists for a full discussion of criminal and constitutional law and international human rights standards, as well as possibilities for reform through either judicial or parliamentary processes.
The event was opened by Lawrence Mute, a former national human rights commissioner, signatory of the Yogyakarta Principles, and winner of ICJ-Kenya’s Jurist of the Year award.
Nov 30, 2012 | News
The ICJ condemns the reintroduction of Anti-Homosexuality Bill in the Ugandan Parliament. The bill has passed out of committee and is expected to come to a floor vote in early December.
According to reports from civil society organizations in Uganda, the bill still contains the death penalty for acts of “aggravated homosexuality.”
In addition, the Anti-Homosexuality Bill criminalizes the promotion of homosexuality, which is defined to include all advocacy activities.
“Adopting the Anti-Homosexuality Bill would be a serious threat to the human rights and human dignity of LGBT individuals and organizations,” said Alli Jernow, Senior Legal Adviser at the ICJ. “Under the Bill, not only might someone face life in prison or the death penalty for being gay, but human rights defenders would also be prevented from speaking out to challenge the law.”
Under the Bill, anyone in authority, such as a teacher or medical professional, who fails to report an offence to law enforcement within twenty-four hours, is liable to three years’ imprisonment.
The ICJ says the bill is dangerous and deadly and urges Parliament to reject it.
Parliament must also reaffirm the rights to non-discrimination, privacy, freedom of expression and freedom of association for all Ugandans, the ICJ adds.
The Anti-Homosexuality Bill has already been used to justify a general clampdown on civil society in Uganda.
Meetings and workshops have been disrupted and advocacy groups working on human rights have been threatened.
In February 2012, the Minister of State for Ethics and Integrity, Simon Lokodo, shut down a capacity-building session for LGBT activists organized by Freedom and Roam Uganda (FARUG) at a hotel in Entebbe and threatened to arrest FARUG’s executive director Kasha Jacqueline Nabagesera (picture above).
In June 2012, police raided a workshop for East African LGBT human rights defenders that had been organized by the East and Horn of Africa Human Rights Defenders Project and they detained participants for several hours.
Minister Lokodo also told the press that he was going to ban 38 organizations that were “sympathetic to LGBT people.”
“If adopted, the bill would clearly violate the human rights of all Ugandans,” Jernow added.
International human rights law, including treaties to which Uganda is a party, prohibit the criminalization of same-sex sexual conduct and forbid the imposition of the death penalty for non-violent conduct, including sexual relations between consenting adults.
International human rights law also guarantees the right of everyone, regardless of sexual orientation or gender identity, to freedom of expression, association and peaceful assembly.
Contact:
Alli Jernow, ICJ Senior Legal Advisor, t + 41 22 979 3823 ; e-mail: alison.jernow(at)icj.org