Feb 17, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has urged expert members of the UN Human Rights Council Advisory Committee to focus on the most direct and acute human rights issues, including a human-rights based approach to victims of terrorism, as the Committee prepares a report on “effects of terrorism on all human rights”.
In an oral statement to the Advisory Committee’s ongoing 24th session in Geneva, the ICJ expressed grave concern about the content of the latest draft of the report, and the potential negative consequences for human rights protection of the report in its current form, and urged the Advisory Committee:
- To substantially revise and refocus the report to include a clear recommendation to the Council that the exclusive focus of the Council’s work should remain on the most acute issues from a human rights perspective: violations in countering terrorism and a human-rights based approach to victims of terrorism, along the lines already established by successive holders of the Special Rapporteur mandate.
- To recommend against the Council entering into more diffuse macroeconomic issues such as diverting foreign direct investment, reducing capital inflows, destroying infrastructure, limiting foreign trade, disturbing financial markets, and negatively affecting certain economic sectors and impeding economic growth.
- To avoid making recommendations that simply repeat already-existing obligations or commitments to counter terrorism under various UN or other instruments.
- To affirm that the existing and longstanding normative and institutional framework on counter-terrorism and human rights is already sufficient to address relevant impacts of terrorism from a human rights perspective.
Prior to the session, the ICJ together with other NGOs had filed a written statement alerting the Advisory Committee to the highly sensitive context into which its report would be delivered at the Council, and urging the Committee to guard against its work being instrumentalized by Egypt and other States who seek to distort, distract and divert the limited resources and attention of the Council and its Special Rapporteur, away from the longstanding focus, achieved by years of Mexican leadership with consensus support of the Council, on human rights in countering terrorism, and the human rights of victims of terrorism.
The Advisory Committee’s report was requested by a 2017 resolution led by Egypt, which was not a matter of consensus, and is being drafted by a former Ambassador of Egypt who is now a member of the Committee.
Earlier at the session, several States including the EU, Switzerland, and Mexico had expressed concern or otherwise questioned particular aspects of the current draft of the report, and urged the Committee to substantially review and revise the draft. Egypt, China, Russia and several other States expressed satisfaction with the draft and urged the Committee to quickly finalize the report and send it to the Council.
The Advisory Committee report is due to be presented to and considered at the September 2020 session of the Human Rights Council, although some Committee members expressed the wish to finalize the report at the current Committee session.

Feb 17, 2020
Today the ICJ published a guide on Corporate Accountability for Abuses of Economic, Social & Cultural Rights in Conflict and Transition.
Around the world, businesses frequently operate in areas or regions in which armed conflict, internal disturbances or upheaval, severe authoritarianism, or other crises are either continuing or have recently ceased.
It is now common for societies seeking to move past such periods to employ transitional justice processes and mechanisms in efforts to build constitutional democracies grounded in the rule of law, protection of human rights and the fair administration of justice.
At times businesses are involved, either directly or in complicity with State agents, armed groups or other actors, in human rights violations or abuses, which occur during or after such conflicts or authoritarian settings.
These abuses may be of civil and political rights but they also often implicate economic, social and cultural rights. Failure to properly consider abuses of economic, social and cultural rights in transitional justice processes, including those caused or contributed to by businesses, can render their outcomes less effective and unsustainable.
All transitional justice processes and mechanisms must be grounded in the principles of international law.
This guide therefore sets out the core principles of international human rights law relating to: Transitional Justice; Economic, Social and Cultural Rights and Business and Human Rights, clearly describing how these three sets of principles interact and coalesce.
This guide will therefore be particular useful to transitional justice practitioners in ensuring that the design and implementation of transitional justice processes and mechanisms are fully consistent with international human rights law.
It also provides guidance to businesses in considering how to ensure compliance with international human rights law when they are operating in situations where conflict is occurring, likely to occur or recently has occurred.
In addition, because of their severe vulnerability of children to rights violations in such contexts, the guide includes a specific chapter focuses on corporate accountability for abuses of children’s rights in conflict settings.
The guide draws on examples of best practice throughout and includes case studies and examples from a wide range of countries including: Argentina; Colombia; East-Timor; Mauritius; Myanmar; Liberia; South Africa; Sierra Leone; Uganda and Tunisia.
Read also
The guide is best read with the following ICJ publications:
The ICJ’s Practitioners Guide on The Right to a Remedy and Reparation for Gross Human Rights Violations; the ICJ’s Practitioners Guide on Adjudicating Economic, Social and Cultural Rights at National Level; The ICJ & Child Rights International Network’s Practical Guide for Non-Governmental Organizations on how to use the United Nations Committee on the Rights of the Child’s General Comment No. 16; and the ICJ and UNICEF’s Practical Guide for States on how to implement the United Nations Committee on the Rights of the Child’s General Comment no. 16.
Download
Universal-ESCR accountability guide-Publications-Reports-Thematic report-2020-ENG (the full guide, in PDF)
Universal-ESCR accountability guide summary-Publications-Reports-Thematic report-2020-ENG (the executive summary and overview, in PDF)

Jan 16, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has submitted information and recommendations for the upcoming review of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy, emphasising the need to strengthen the role of human rights in the framework and implementation of the strategy.
The submission was prepared in response to a call for civil society input, from the UN Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT).
It summarizes recent ICJ activities relevant to implementation of the strategy, and urges among other things:
- removal of impediments to civil society participation in certain UN or other global policy-making processes;
- recognition that not only is violation of human rights in the context of countering terrorism, whether through arbitrary application or deliberate abuse, in itself unlawful and unacceptable, it also undermines the credibility and effectiveness of the struggle against terrorism;
- better recognition and implementation of the human rights of victims of terrorism;
- mainstreaming of human rights throughout the text and implementation measures for the Strategy as a whole;
- establishment of an independent human rights oversight entity within the UN counter-terrorism architecture;
- creation of a Civil Society Unit within UNOCT;
- increased resources for the UN Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms while countering terrorism;
- increased engagement of the UN counter-terrorism architecture with OHCHR and with other UN Special Procedures;
- benchmarks and indicators for assessing States’ compliance with human rights obligations in implementation of the GCTS.
The complete submission can be downloaded in PDF format here: UN-Advocacy-GCTStrategy-2019
For more information contact un(a)icj.org

Dec 15, 2019 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has urged the UN Special Rapporteur on Independence of Judges and Lawyers to ensure that his upcoming report on challenges to the independence of prosecutors, fully addresses abuse of prosecution powers to target human rights defenders, political opponents or others, or giving rise to a more general and systemic lack of fair trial for accused persons, or entrenching impunity of State perpetrators of human rights violations, as among the dominant contemporary challenges to prosecutorial independence globally from a human rights perspective.
The Special Rapporteur has made clear his intention to address challenges to prosecutorial independence arising from transnational corruption and organized crime. While the ICJ certainly agrees that such interference can and does have impacts on human rights, to varying extents around the world, the ICJ submission also highlights and documents that threats to prosecutorial independence emanating from the prosecutor’s own Executive government should be seen to be of at least equal concern from a human rights perspective, globally, and should be fully addressed in any report on “contemporary challenges of prosecutorial independence” from a human rights perspective.
The ICJ’s submission can be downloaded in PDF format here: UN-Advocacy-SRIJLProsecutors-2019
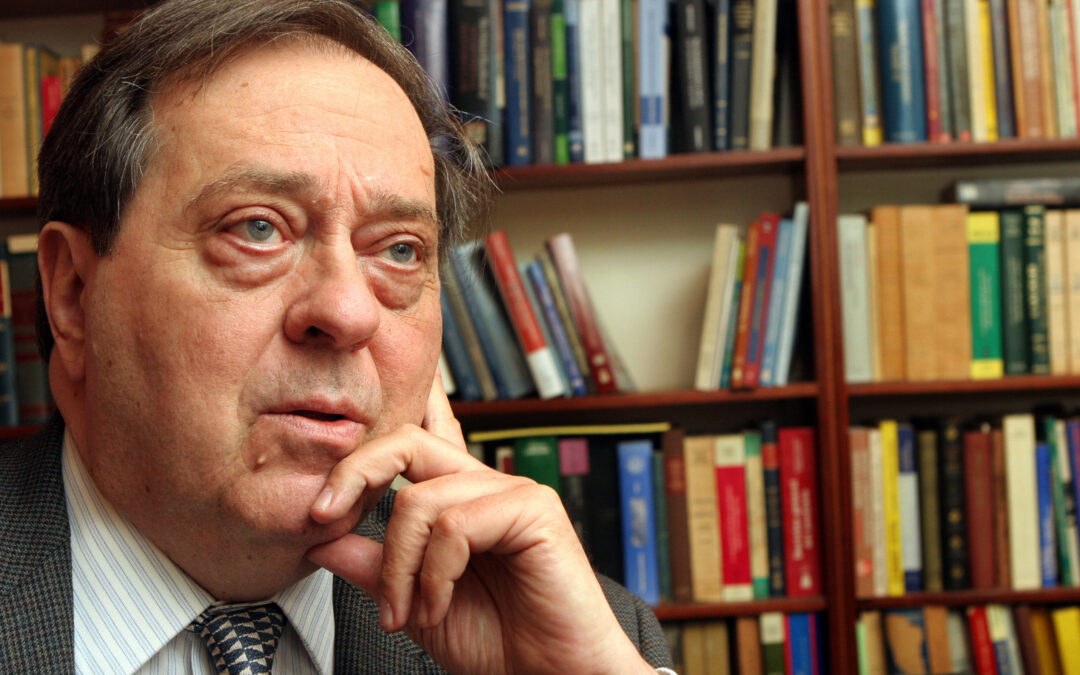

Dec 10, 2019 | News
The ICJ mourns the loss of Professor Pedro Nikken, former President and Commissioner of the ICJ. Prof Nikken was elected ICJ President in January 2011, succeeding Mary Robinson (2008-2010) and followed by Nigel Rodley (2012-2017).
“Pedro Nikken left a tremendous legacy of respect for the rule of law and defense of human rights in his homeland of Venezuela, across Latin America and around the world,” said Prof Robert Goldman, the ICJ’s President.
“ Like so many others, I have lost a cherished friend and mentor whose company I will greatly miss,” he added.
Prof Nikken was a former Judge (1979-1989) and President (1983-1985) of the Inter-American Court of Human Rights. He served as UN Independent Expert on El Salvador from 1992 to 1995 and from 1990-1992 he served as Legal Adviser to the UN Secretary-General on El Salvador’s peace process.
In 1995 he served as Special Envoy of the UN Secretary-General to Burundi. He is former Dean and Professor (emeritus) at the Law School of the Universidad Central de Venezuela.
He was also former President and Permanent Counselor of the InterAmerican Institute of Human Rights. He was a Member (Chair N° 9) of the Venezuelan National Academy of Political and Social Sciences.
“Prof Nikken helped drive the ICJ’s work in pursuit of justice and accountability, particularly through regional human rights systems such as the Inter American Court of Human Rights, even as various governments tried to weaken the process and evade responsibility,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ Secretary General.
“Pedro was indefatigable as a human rights defender and unsurpassed in the quality of his legal analysis, a rare combination of qualities that made him a role model for several generations of human rights lawyers around the world,” he added.
Pedro Nikken was born in Caracas, Venezuela in 1945. He graduated in 1968 from the Andres Bello Catholic University and obtained a diploma of higher studies in law at the Pentheon-Assas University (Paris II) and a doctorate in law from the University of Carabobo.