Jul 9, 2020 | Agendas, Events, News
The ICJ is holding an online discussion for lawyers and other representatives of civil society in Tajikistan on access to justice in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic. The discussion is held on 10 July 2020 from 14.00 to 17.00 Dushanbe Time (GMT + 5) on the GoToMeeting platform
The discussion aims to raise some of the main issues that lawyers face in providing legal representation both in and outside of courts.
The event will present an opportunity for practicing lawyers, NGOs and IGOs to discuss the recent challenges that the legal profession faced in Tajikistan as well as seek some of the solutions based on international law and best practices of other countries.
During the discussion, relevant international law and standards as well as comparative examples from the Central Asian countries and Azerbaijan will be discussed.
To participate in the discussions registration is required on the following link : https://forms.gle/QRywqBFPSxfR5eyk7
Working languages of the event are Russian and Tajik.
Contact:
Dilshod Juraev, t: +992 77 700 18 34 ; e: Dilshod.jurayev(a)icj.org
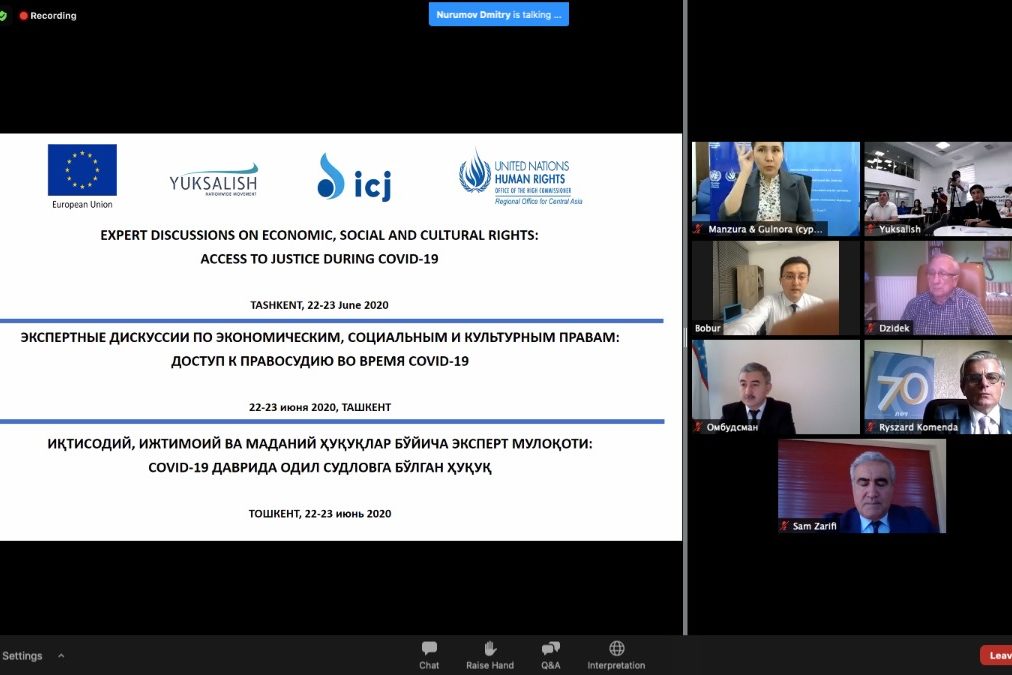
Jun 22, 2020 | News
Today, the ICJ, the Regional Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) for Central Asia and the Nationwide Movement “Yuksalish” are holding an Expert Discussion on the impact of COVID-19 on access to justice for economic, social and cultural rights (ESC rights) in Uzbekistan and comparative experiences from Europe and Central Asia.
The Fifth Expert Discussion, Access to justice in times of COVID-19, will address issues including access to a lawyer and access to court.
The event will present an opportunity to national and international experts, including lawyers, judges, members of UN human rights bodies, civil society, and other experts to debate questions of fundamental importance for ensuring access to justice and the protection of human rights in Uzbekistan.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has put new challenges before justice institutions around the world, including in Uzbekistan. These measures affected access to lawyers and courts judiciary therefore impeding full access to justice. This event will present an opportunity to discuss the solutions of States from around the globe about their responses to the pandemic. We believe that sharing experience among judges, lawyers and international experts from around the world will enrich the National debate and give an impulse for further development and the independence of the judiciary in Uzbekistan” said Akmal Burkhanov, Chairperson of the Nationwide movement “Yuksalish”.
“The pandemic became the so-called “maturity test” for the justice system and many of the urgent issues should be resolved in the light of the anti-COVID-19 measures taken. Therefore, I would also see the pandemic as an opportunity. The opportunity for transforming, changing for the better the functioning of traditional courts, provided that a high quality of justice and respect for individual rights are at the forefront of all changes,” pointed Eduards Stiprais, EU Ambassador to Uzbekistan.
Ryszard Komenda, Regional Representative of the UN Office for Human Rights for Central Asia quoted the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Michelle Bachelet, who stated that “in order to cope effectively with the pandemic states may need to introduce certain restrictions on the exercise of certain human rights, however, such restrictions need to be necessary, proportionate, and non-discriminatory”. Mr. Komenda noted that “the impact of the regulations on lockdown affected the day-to-day work of courts and lawyers. From the perspective of international human rights standards, it is crucial that the right of individuals to an operative and independent judicial system, in particular the right to an effective remedy, habeas corpus guarantees and access to a lawyer of one’s choosing are strictly adhered to”.
“Our fifth Expert Discussion on economic and social rights, is devoted to addressing the major problems people have in getting access to justice and defending their rights during the global COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sam Zarifi, the ICJ Secretary General.
“The ICJ has documented how around the world the pandemic has severely affected peoples’ right to health, to food, to water, to education and to sanitation, and we have also seen the additional difficulties facing people with lower income and access to the levers of power.”
“We aim to discuss how international law and national best practices can help the judiciary and legal system alleviate some of the human rights issues arising from Covid-19 in Uzbekistan, and maybe even build a more responsive and accountable system after the pandemic.”
Background:
The Expert Discussions on ESC rights aim to raise awareness about the implementation of international law and standards on ESC rights by the national justice system, to facilitate access to justice in relation to ESC rights and promote effective use of international law on ESC rights at the national level. Each Expert Discussion is attended by international and national experts.
The first discussion was held in September 2018 on international standards in labour rights. The second meeting, held in December 2018, concerned judicial application of the principle of non-discrimination; the third meeting, held in March 2019, was dedicated to the rights of people with disabilities, and the forth meeting, held in October 2020, discussed the right to adequate housing in Uzbekistan.
Uzbekistan ratified the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) in 1995.
The Expert Discussions are organized by the ICJ within the framework of the “Advancing Civil Society in Promoting economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) Standards in Uzbekistan (ACCESS)” Project funded by the EU through the European Instrument for Democracy and Human Rights (EIDHR).
Contact:
Dilfuza Kurolova, ICJ Legal consultant, t: +998 90 9050099 ; e: dilfuza.kurolova(a)icj.org
Agenda:
English version
Russian version
Uzbek version

Jun 4, 2020 | News
The ICJ today urged the country’s authorities to take immediate measures to fully reconstitute the Zimbabwe Human Rights Commission (ZHRC) after its operations were effectively suspended following the expiry of the terms of office of four of its Commissioners on 7 May 2020.
One Commissioner had already resigned in 2018 meaning that the ZHRC no longer has the constitutionally required quorum for it to make certain decisions that are fundamental to the protection of human rights in Zimbabwe.
“The inability by the ZHRC to fully execute its constitutional mandate has serious implications on the ability of individuals -in particular victims of human rights violations -to access justice,” said Arnold Tsunga, Director of the ICJ Africa Programme.
“The role of ZHRC, as Zimbabwe’s national human rights institution is critical in providing an avenue for redress to victims of human rights violations and the general public,” he added.
Zimbabwe has been witnessing an escalation of human rights violations requiring investigation by a fully functioning and effective Commission.
This spate of human rights violations has had a disproportionate impact on the poor and economically vulnerable in the context of the Covid-19 lockdown measures.
There have been an increase in targeting of human rights defenders, civil society leaders and political opposition, which have included acts of enforced disappearance and torture and other ill-treatment.
The ICJ underlined that while redress for such violations required strong and independent judiciary as a guarantor of human rights, the role of fully functional ZHRC was critical to complement that of the judiciary.
The ICJ called upon the authorities in Zimbabwe, and in particular the Parliamentary Committee on Standing Rules and Orders, to act expeditiously to ensure that the vacant positions are filled without any further delay to enable the ZHRC effectively perform and discharge its constitutional mandate.
The ICJ said that failure by the responsible authorities to act expeditiously to fill the vacant positions violated the core values and principles the Constitution of Zimbabwe, in particular section 324 of the Constitution which provides that “all constitutional obligations must be performed diligently and without delay”.
In addition, the President to fill in any vacant position within three months of death or resignation of a Commissioner. The position of Commissioner Khombe became vacant on the 30 October 2018, and has not been filled to date.
Additional Information
The ZHRC is established as an independent institution under Chapter 12 of the Zimbabwe constitution with the general objective to “support and entrench human rights and democracy; to promote constitutionalism; to promote transparency and accountability in public institutions; to secure the observance of democratic values and principles by the State and all institutions and agencies of government, and government-controlled entities; and to ensure that injustices are remedied.”
On 26 May the Chairperson of the ZHRC, Dr. E.H Mugwadi, wrote a letter notifying “partners and stakeholders” of the retirement of four Commissioners, namely Dr Ellen Sithole (former Deputy Chairperson), Dr Joseph Kurebwa, Kwanele M. Jirira and Japhet Ndabeni-Ncube with effect from 7 May. The Chairperson noted that the retirement had left the Commission lacking the quorum to fulfil its constitutional obligations, particularly with respect to make policy resolutions and the adoption of monitoring and investigation reports. The Commission had also been unable to adopt Commission reports its activities.
International standards for effective and credible National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) are contained in the United Nations Principles relating to the Status of National Institutions (Paris Principles), which provide that NHRIs must be adequately resourced with sufficient institutional capacity to perform and discharge their responsibilities.
Contact:
Arnold Tsunga, ICJ Africa Director, t: +263 777 283 249; e-mail: arnold.tsunga(a)icj.org
Blessing Gorejena, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, t: +263 772 151 989, e-mail: Blessing.Gorejena(a)icj.org

Jun 3, 2020 | Advocacy, Cases, Legal submissions
The Council of Europe Committee of Ministers should issue a decision at its 4 June 2020 meeting directing Turkey to release the human rights defender Osman Kavala and drop all charges against him, the ICJ, Human Rights Watch and the Turkish Human Rights Litigation Support Project said today.
The three groups have submitted a detailed submission to the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe, which oversees enforcement of European Court of Human Rights judgments. The groups outlined how Turkey continues to violate Kavala’s rights by flouting a landmark judgment, that became final on May 11 requiring his immediate release.
“The European Court ruled that Kavala’s detention is unlawful, and their binding judgment requires Turkey to release him immediately,” said Emma Sinclair-Webb, Turkey director at Human Rights Watch. “The Committee of Ministers, at its June 4 meeting, should press Turkey to comply and issue a clear message that no Council of Europe member state should be silencing human rights defenders.”
The judgment is particularly significant because it is the first final ruling against Turkey in which the court determined that in interfering with an individual’s rights Turkey acted in bad faith and out of political motivations, violating Article 18 of the European Convention on Human Rights. The court said that by detaining Kavala since November 2017 and prosecuting him, the Turkish authorities had “pursued an ulterior purpose, namely to silence him as human rights defender.”
The European Court judgment in Kavala v. Turkey (Application no. 28749/18) found violations of Article 5(1) (right to liberty and security), Article 5(4) (right to a speedy decision on the lawfulness of detention), and the rarely used Article 18 (limitation on use of restrictions on rights) taken together with Article 5(1). It required Turkey to release Kavala and said that any continuation of his detention would prolong the violations and breach the obligation to abide by the judgment in accordance with Article 46(1) of the European Convention on Human Rights..
A court ordered Kavala’s detention on November 1, 2017 on bogus allegations that he used the 2013 Istanbul Gezi Park protests as a pretext for an attempted coup, and that he was involved in the July 15, 2016 attempted military coup. On February 18, 2020, Kavala and his eight co-defendants were acquitted on charges of “attempting to overthrow the government by force and violence” in the Gezi Park trial .
But Kavala was not released, and a court detained him again immediately on the charge of “attempting to overthrow the constitution by force and violence” because of an ongoing 2016 coup-related investigation against him. Turkey’s President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan had publicly criticized his acquittal just before he was detained again. Weeks later a court ordered his detention a second time on another charge (“espionage”) but relying on the same evidence and investigation file.
“The sequence of court orders prolonging his detention and the lack of objective deliberation as to the lawfulness of any deprivation of liberty indicates that decisions have been guided by political considerations and there has been a concerted official effort to prevent Kavala’s release,” said Róisín Pillay, Director of ICJ’s Europe and Central Asia Programme . “Since the European Court’s judgment, Turkey has continued to violate Kavala’s human rights.”
The targeted harassment in Turkey of rights defenders is part of a wider trend of arbitrary detentions and abusive prosecutions of journalists, elected politicians, lawyers, and other perceived government critics. This trend has been well-documented in many reports by the Council of Europe, the European Union, and human rights organizations.
“The campaign of persecution against Osman Kavala and the failure to release him and drop all charges have perpetuated a chilling environment for all human rights defenders in Turkey,” said Ayşe Bingöl Demir, Co-Director of the Turkish Human Rights Litigation Support Project.
The three organizations made detailed recommendations to the Committee of Ministers, urging it to:
- Call on the government of Turkey to ensure the immediate release of Osman Kavala as required by the European Court’s judgment, stressing that the judgment clearly applies to his ongoing detention and persecution;
- Place the Kavala v. Turkey judgment under “enhanced procedures” and treat it as a leading case under Article 18 of the European Convention;
- Recognize that Kavala’s continuing detention violates Article 46 of the convention, concerning the binding nature of final judgments of the European Court, and that a failure to release Kavala may trigger an Article 46(4) procedure (infringement proceedings);
- Emphasize to the Government of Turkey that Kavala’s release is of added urgency in the context of the Covid-19 pandemic, which increases the risk to his health in detention;
- Ask the Government of Turkey to drop all charges under which Kavala has been investigated and detained to silence him, in conformity with the court’s findings that his rights have been violated and that his exercise of rights to freedom of expression, assembly and association was wrongfully used as evidence to incriminate him.
The groups also identified the general measures that Turkey needs to take to carry out the judgment to end politically motivated detention and prosecution of human rights defenders and other perceived government critics. These measures focus on Turkey’s structural rule of law problems. They include executive control over Turkey’s judiciary and prosecutorial authorities, and the evidence of a clear pattern of direct political interference in court decisions through frequent public speeches by Turkey’s president and proxies. A pattern of criminalizing the exercise of convention-protected rights defines many of the cases against human rights defenders and other perceived government critics.
Turkey’s international partners, including the European Union, should make it clear that the full implementation of the court’s judgment in Osman Kavala’s case will be key in measuring the credibility of any government pledges for reform, the three groups said. Any justice reform and any human rights action plan would remain hollow until the reasons that unjustly led Kavala to prison are addressed and fixed.
Kavala_v_Turkey-Execution-JointSubmissionR9_2-ICJHRWTLP-LegalSubmission-2020-eng (downaload the submission)
Kavala_v_Turkey-Execution-JointSubmissionR9_2-ICJHRWTLP-LegalSubmission-2020-tur (download the submission in Turkish)
Türkiye: AİHM Kararı Sonrası Hak Savunucusu Serbest Bırakılsın
Avrupa Konseyi Bakanları Osman Kavala’nın tahliyesinde ısrar etmelidir
(Strazburg, 3 Haziran 2020) – İnsan Hakları İzleme Örgütü, Uluslararası Hukukçular Komisyonu ve Türkiye İnsan Hakları Davalarına Destek Projesi, Avrupa Konseyi Bakanlar Komitesinin 4 Haziran 2020 tarihli toplantısında Türkiye’yi insan hakları savunucusu Osman Kavala’nın serbest bırakılmasına ve ona yönelik tüm suçlamaların düşürülmesine yöneltecek bir karar alması gerektiğini belirttiler.
Bu üç grup, Avrupa İnsan Hakları Mahkemesi kararlarının uygulanmasını denetleyen Avrupa Konseyi Bakanlar Komitesi’ne detaylı bir bildirim sundu. Gruplar, Türkiye’nin 11 Mayıs’ta kesinleşen ve Kavala’nın derhal tahliye edilmesini gerektiren bu önemli kararı göz ardı ederek, Kavala’nın haklarını ihlal etmeye devam ettiğini belirtti.
İnsan Hakları İzleme Örgütü Türkiye Direktörü Emma Sinclair-Webb, “Avrupa Mahkemesi, Kavala’nın alıkonmasının hukuka aykırı olduğuna ve bağlayıcı kararının gereği olarak Türkiye’nin Kavala’yı derhal tahliye etmesi gerektiğine karar verdi” dedi. Emma Sinclair-Webb, “Bakanlar Komitesi, 4 Haziran toplantısında, hiçbir Avrupa Konseyi üyesi devletin insan hakları savunucularını susturmaması gerektiğine dair net bir mesaj vererek buna uyması için Türkiye’ye baskı yapmalıdır” dedi.
Bu karar, Türkiye’nin kötü niyetle ve siyasi amaçlarla bir bireyin haklarına müdahale ettiğini ve Avrupa İnsan Hakları Sözleşmesi’nin 18. maddesini ihlal ettiğini tespit eden Türkiye aleyhindeki ilk nihai karar olduğundan özel bir önem taşımakta. AİHM, Osman Kavala’yı Kasım 2017’den bu yana alıkoyup yargılayan Türk makamlarının “başvuranın bir insan hakları savunucusu olarak susturulmasını sağlamak için örtülü bir amaç taşıdığını” tespit etmişti.
Avrupa Mahkemesi, Kavala/Türkiye kararında (Başvuru no. 28749/18), madde 5/1 (özgürlük ve güvenlik hakkı), madde 5/4 (alıkonmanın yasaya uygunluğuna ilişkin ivedi karar alma hakkı) ve nadiren kullanılan madde 18 (haklara getirilecek kısıtlamaların sınırlanması) ile birlikte madde 5/1’in ihlal edildiğine karar vermiştir. Karar, Türkiye’nin Kavala’yı tahliye etmesini zorunlu kılmış, tutukluluğunun devam etmesinin ihlalleri devam ettireceğini ve Sözleşmenin 46(1) maddesi uyarınca AİHM kararlarına uyma yükümlülüğünü ihlal edeceğini belirtmiştir.
Bir hakimlik 2013 İstanbul Gezi Parkı protestolarını darbe girişimine bahane olarak kullandığı ve 15 Temmuz 2016 askeri darbe girişimine müdahil olduğu iddiasıyla, Kavala’nın 1 Kasım 2017’de tutuklanmasına karar vermiştir. 18 Şubat 2020’de Kavala ve diğer sekiz sanık, Gezi Parkı davasında “cebir ve şiddet kullanarak hükümeti ortadan kaldırmaya teşebbüs” suçlamasından beraat etmiştir.
Ancak Kavala cezaevinden tahliye edilmemiş ve bir hâkim kararıyla 2016 darbesiyle ilgili devam eden bir soruşturmayla ilişkili olarak “anayasal düzeni cebir, şiddet kullanarak ortadan kaldırmaya teşebbüs” suçlamasıyla tekrar tutuklanmıştır. Tekrar tutuklanmasından kısa bir süre önce Cumhurbaşkanı Recep Tayyip Erdoğan halka açık şekilde Kavala’nın beraatini eleştirmiştir. Kavala haftalar sonra, aynı delillere ve soruşturma dosyasına dayanan bir başka suçlama ile (casusluk) bir kez daha tutuklanmıştır.
Uluslararası Hukukçular Komisyonu Avrupa ve Orta Asya Programı Direktörü, Róisín Pillay, “Tutukluluğun devamına ilişkin yargı kararlarının silsilesi ve tutuklamanın yasallığı konusunda nesnel bir değerlendirmenin olmaması, kararların siyasi beklentiler tarafından yönlendirildiğini ve Kavala’nın tahliyesini önlemek için düzenlenmiş bir siyasi çaba olduğunu göstermektedir.” dedi. Pillay, “Avrupa Mahkemesi’nin kararından bu yana Türkiye, Kavala’nın insan haklarını ihlal etmeye devam etti” tespitinde bulundu.
Türkiye’de insan hakları savunucularına yönelik taciz daha genel olarak gazetecilere, seçilmiş siyasetçilere, hukukçulara, hükümeti eleştirdiği düşünülenlere yönelik keyfi alıkoymalar ve yargısal tacizin bir parçası. Bu eğilim Avrupa Konseyi, Avrupa Birliği ve insan hakları örgütlerine ait birçok raporla belgelendirilmiştir.
Türkiye İnsan Hakları Davalarına Destek Projesi Ortak Direktörü Ayşe Bingöl Demir “Kavala’ya karşı yürütülen yıldırma kampanyası, onun tahliye edilmemesi ve hakkındaki suçlamaların düşürülmemesi, Türkiye’deki tüm insan hakları savunucuları için oluşan baskı ortamının sürmesine sebep olmuştur” dedi.
Üç örgüt, detaylı tavsiyelerde bulunarak Bakanlar Komitesi’ni:
- Avrupa Mahkemesinin kararı gereği Osman Kavala’nın derhal tahliyesinin sağlanması için Türkiye Hükümetine çağrıda bulunmaya, kararın açık şekilde devam eden tutukluluğa ve baskıları da kapsaması gerektiğini vurgulamaya,
- Kavala/Türkiye kararını nitelikli denetim prosedürü altında izlenmek üzere sınıflandırmaya ve Sözleşmenin 18. maddesi altında öncü dava olarak kabul etmeye,
- Kavala’nın devam eden tutukluluğunun kesinleşen AİHM kararlarının bağlayıcılığına ilişkin Sözleşmenin 46. maddesini ihlal ettiği tespit etmeye ve Kavala’nın tahliye edilmemesinin Madde 46/4 prosedürünü (ihlal işlemleri) başlatacağını tespit etmeye,
- Türkiye Hükümetine, Kavala’nın serbest bırakılmasının Covid-19 salgını bağlamında ek bir aciliyete sahip olduğunu ve salgının alıkonma esnasında sağlığına yönelik mevcut tehlikeyi artırdığını vurgulamaya
- Mahkemenin, Kavala’nın haklarının ihlal edildiğine, toplantı, örgütlenme ve ifade özgürlüğünü kullanmasının hatalı şekilde kendisini suçlamak için delil olarak kullanıldığına ilişkin tespitleri doğrultusunda, Türkiye Hükümeti’nden Kavala’nın susturulmak amacıyla soruşturulduğu ve alıkonduğu tüm dosyalarda tüm suçlamaların düşürülmesini talep etmeye davet etmiştir.
Örgütler ayrıca, Türkiye’nin insan hakları savunucularının ve diğer hükümeti eleştirdiği düşünülenlerin siyasi amaçlarla alıkonmalarına ve yargılanmalarına son verilmesine yönelik kararın uygulanması için alınması gereken genel tedbirleri belirlediler. Genel tedbirler, Türkiye’nin hukukun üstünlüğüne ilişkin yapısal sorunlarına odaklanmaktadır. Bu yapısal sorunlar arasında yürütmenin Türkiye’de yürütmenin yargısı ve savcılıkları üzerindeki kontrolü; Cumhurbaşkanı ve ona bağlı diğer yetkililer tarafından, sıklıkla yapılan halka açık konuşmalar aracılığıyla mahkeme kararlarına doğrudan siyasi müdahalede bulunmaya yönelik yaygın eğilime ilişkin açık deliller yer almaktadır. Sözleşme ile korunan hakların kullanılmasının suç haline getirilmesi, insan hakları savunucularına ve hükümeti eleştirdiği düşünülenlere karşı açılan birçok davanın ortak yönünü oluşturmaktadır.
Kavala_v_Turkey-Execution-JointSubmissionR9_2-ICJHRWTLP-LegalSubmission-2020-tur (download the submission in Turkish)
Kavala_v_Turkey-Execution-JointSubmissionR9_2-ICJHRWTLP-LegalSubmission-2020-eng (downaload the submission)
For more information, please contact:
Massimo Frigo (English) massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, +41229793800