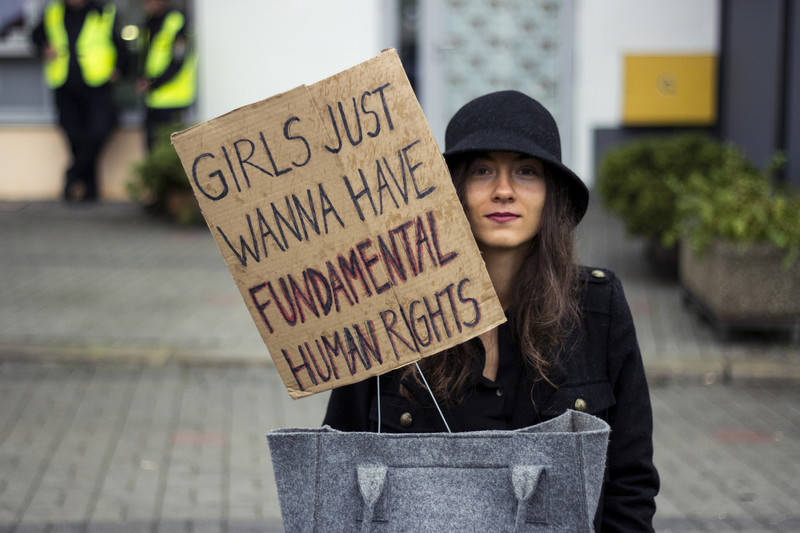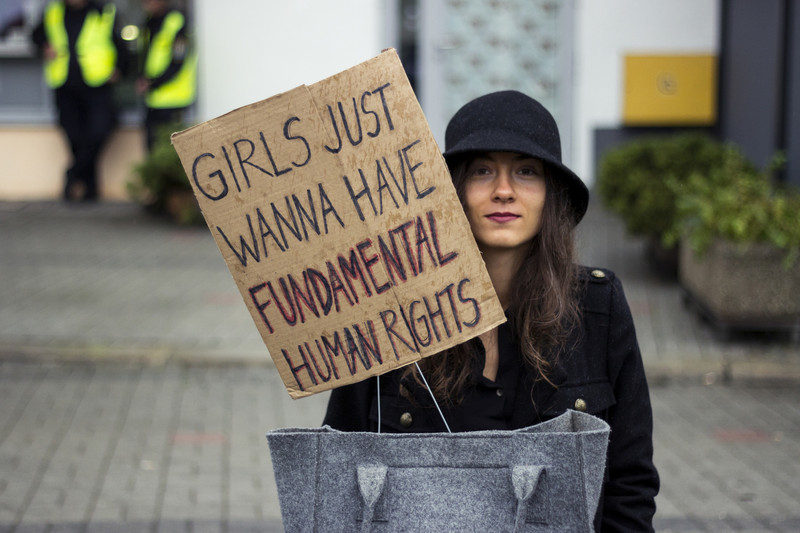Apr 28, 2020 | Advocacy, News, Open letters
The ICJ today called on the South African government to take measures to ensure access to justice and the full fulfillment of the economic, social and cultural rights of all in the country.
The South African authorities must also remove legal hurdles in accessing just compensation for rights violations occurring during nationwide lockdown, the ICJ said.
The call comes as South Africa enters its final week of a lockdown period, which initially began on 26 March 2020. Since the beginning of the lockdown period the ICJ has been working closely with a broad coalition of local civil society organizations and movements called the C19 People’s Coalition.
“The ICJ applauds South Africa on its announcement that it will commit 10% of its GDP to a social relief and economic support package addressing poverty and in inequality which has been exacerbated by COVID-19,” said Arnold Tsunga, ICJ Africa Director.
“However we note with concern the high levels of repression and human rights abuses committed by enforcement officers enforcing Lockdown Regulations and the inadequacy of social assistance measures to ensure an effective elimination of poverty in accordance with South Africa’s international and domestic human right obligations.”
- Repression and human rights abuses by enforcement officers during Lockdown
Both the Disaster Management Act and Lockdown Regulations enacted in terms of it create doubt about whether victims of violations of human rights in the enforcement of lockdown will be able to claim compensation for such violations.
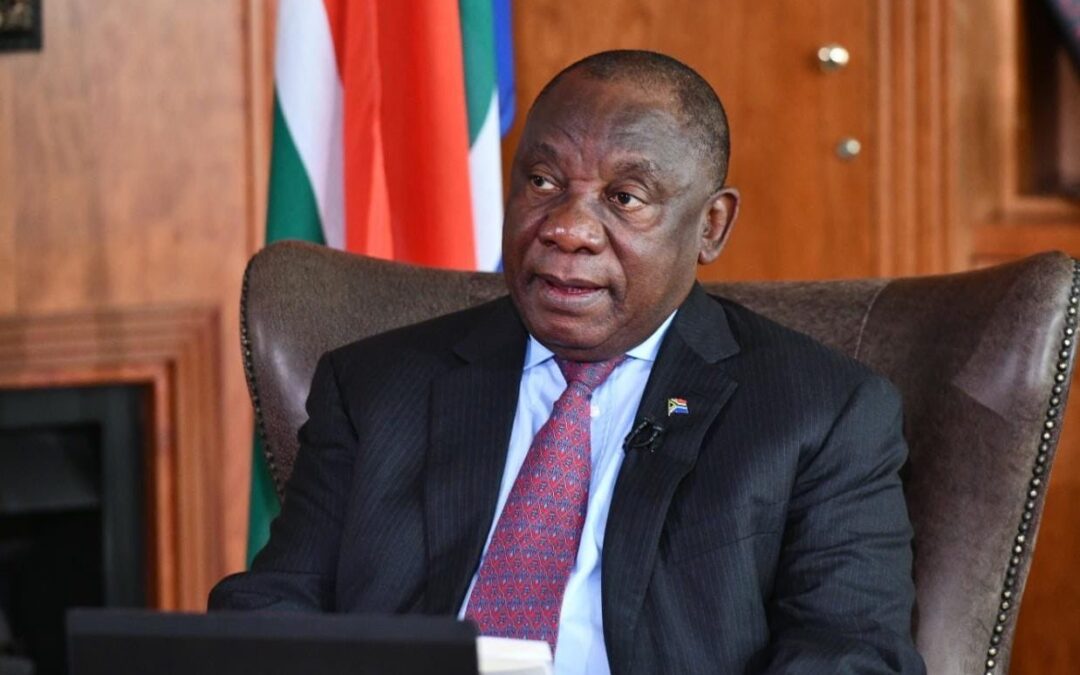
The ICJ has therefore written to President Cyril Ramaphosa (photo) and Speaker of the National Assembly Thandi Modise calling on the authorities to make the necessary legal amendments required to ensure the full protection of the right to access to justice, which includes the right to effective remedies and reparation.
The ICJ calls on authorities to ensure the amendment of the National Disaster Act and Lockdown Regulations to ensure that victims of human rights abuses have full and effective access to the right to remedy and reparation including compensation.
- Inadequate Social Assistance provided
Despite the large stimulus package announced by President Ramaphosa on 21 April, the C19 People’s Coalition has correctly argued that the new COVID-19 social grant of R350 ($18.44 USD) per month for unemployed persons is less than a third of the R1227 ($64.65) that government itself estimates individuals require to be lifted out of poverty.
In addition, the increase of the Child Support Grant of R500 ($26.35) per month appears, contrary to what the President’s announcement suggested, to be allocated per caregiver not per child thus drastically reducing its potential impact.
The ICJ calls on authorities to ensure the full provision of a social safety net to all in South Africa by: 1) raising the levels of all non-contributory social assistance benefits to a level that ensures an adequate standard of living for recipients and their families; and 2) ensuring that those between the ages of 18 and 59 with little or no income have access to social assistance.
These two measures were among those specified in the Concluding Observations of the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights to South Africa.
South Africa declared a moratorium on all evictions during the lockdown period on 26 March after local organizations and the ICJ had called for such a move.
Later amendments to Lockdown Regulations made it a criminal offence for any person to evict any other person. Despite this, evictions continue in some places unabated as is illustrated by statements of Abahlali BaseMjondolo and Abahlali BaseMjondolo Women’s League late last week.
These evictions have sometimes been violent and accompanied by serious allegations of attempted murder of community members and human rights defenders.
The ICJ calls on authorities to ensure the immediate cessation of all evictions. The President of South Africa and the Parliament of South Africa must make sure that police officers, security and other companies and government officials participating in evictions are clearly, decisively and publicly held to account.
Those carrying out evictions should be prosecuted in accordance with Lockdown Regulations. The police and prosecuting authorities should also investigate and where sufficient evidence exists pursue prosecution of those found to have committed crimes of violence or similar offences against those who are subjected to or defend against such evictions.
“The continued violent attacks experienced by human rights defenders and those simply trying to retain their homes is unacceptable. The time has come for the President of South Africa and Parliament of South Africa to intervene directly to prevent any further such attacks generally, but in particular with regard to Abahlali BaseMjondolo settlements in KwaZulu-Natal,” added Arnold Tsunga, ICJ Africa Director.
Contact:
Tim Fish Hodgson, ICJ Legal Adviser, t: +2782871990 ; e: tim.hodgson(a)icj.org
Shaazia Ebrahim, ICJ Media Officer, t: +27716706719 ; e: shaazia.ebrahim(a)icj.org
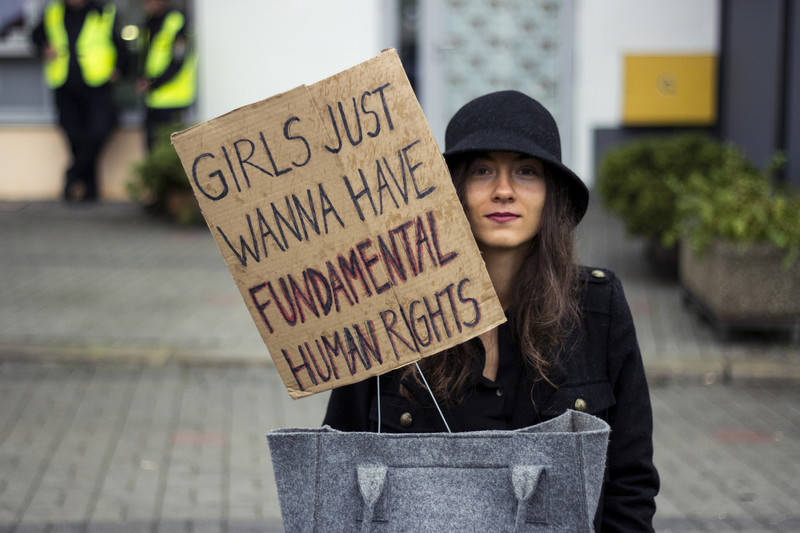
Apr 14, 2020 | Advocacy, News
The ICJ and 108 other organizations are deeply concerned by relentless attempts to roll back sexual and reproductive rights in Poland.
On 15 and 16 April Poland’s Parliament will again debate two draft bills that would severely limit access to safe abortion care and would criminalize the provision of sexuality education.
If enacted into law these bills would place women’s and adolescents’ health and well-being at risk and violate Poland’s international human rights obligations.
Full statement, in PDF: Poland-COVID-19 Abortion bill-Advocacy-2020-ENG)

Apr 10, 2020 | News
The ICJ today called upon the Myanmar government to ensure that everyone in the country, particularly those from communities affected by conflict, has access to critical information about COVID-19. This call includes putting an immediate end to restrictions on internet access in Rakhine and Chin States.
The ICJ said that there must not be undue restrictions on the right of people to seek and impart such information, in line with international law and standards protecting the right to freedom of expression and information.
“Access to information is absolutely essential for the protection of communities, especially their right to health during the COVID-19 outbreak,” said Frederick Rawski, ICJ Director for Asia and the Pacific. “This is especially true in areas of Myanmar affected by conflict. The wholesale blocking of internet access in Rakhine and Chin States, including access to websites of popular ethnic media outlets, has no justifiable basis in international law and will only serve to undermine efforts to mitigate the spread of the virus.”
On 26 March 2020, the Minister of Transport and Communications stated in a media interview that despite the COVID-19 pandemic, the internet shutdown in Rakhine and Chin States would not be lifted until hate speech, misinformation and the conflict with the Arakan Army are addressed. The Minister’s statement appears to defy the UN Secretary-General’s appeal for a global ceasefire as well as the respective statements of members of Myanmar’s diplomatic community and of several ethnic armed organizations, including the Arakan Army, to cease hostilities in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. On 9 April 2020, the UN Special Rapporteur on Myanmar called for the same.
Instead, on 30 March 2020, pursuant to section 77 of the Telecommunications Law, the Ministry of Transport and Communications (MoTC) ordered major telecommunications networks to take down hundreds of websites on the dubious ground of containing misinformation. The MoTC did not disclose the full list of websites ordered to be blocked as well as the factual and legal basis that justified issuing the order. Under Section 77, the MoTC can direct a telecommunications provider to suspend services in the event of an “emergency situation.” It is not clear whether the misinformation relates to COVID-19 or if the pandemic is the pretext for the order.
As of 1 April 2020, media outlets of the Rakhine and Karen ethnic communities were among the websites to which access was blocked from major telecommunications providers. Access to Voice of Myanmar’s website, whose editor-in-chief had faced charges under Myanmar’s Counter-Terrorism Law until 9 April 2020 for publishing an interview with the Arakan Army, was also blocked.
The ICJ has previously expressed concern at the Myanmar Government’s use of the Telecommunications Act to justify an internet shutdown in the context of the conflict in Rakhine State. This practice does not comply with human rights law and standards. The Act itself is fundamentally flawed and must be amended. Among other defects, the Act does not define the scope of an “emergency situation.”
“Keeping these overbroad restrictions in place in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic puts the government in violation of international law. It is also counterproductive to the goal of stopping the spread of the virus and minimizing its impact on the country’s most vulnerable populations,” said Rawski.
Download the statement in Burmese here.
Contact:
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Regional Director, e: Frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Related work:
Event: ICJ hosts workshop on fair trial rights for Myanmar’s ethnic media
Report: Curtailing the Right to Freedom of Expression and Information in Myanmar
Statement: States must respect and protect rights in fighting COVID-19 misinformation

Apr 9, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
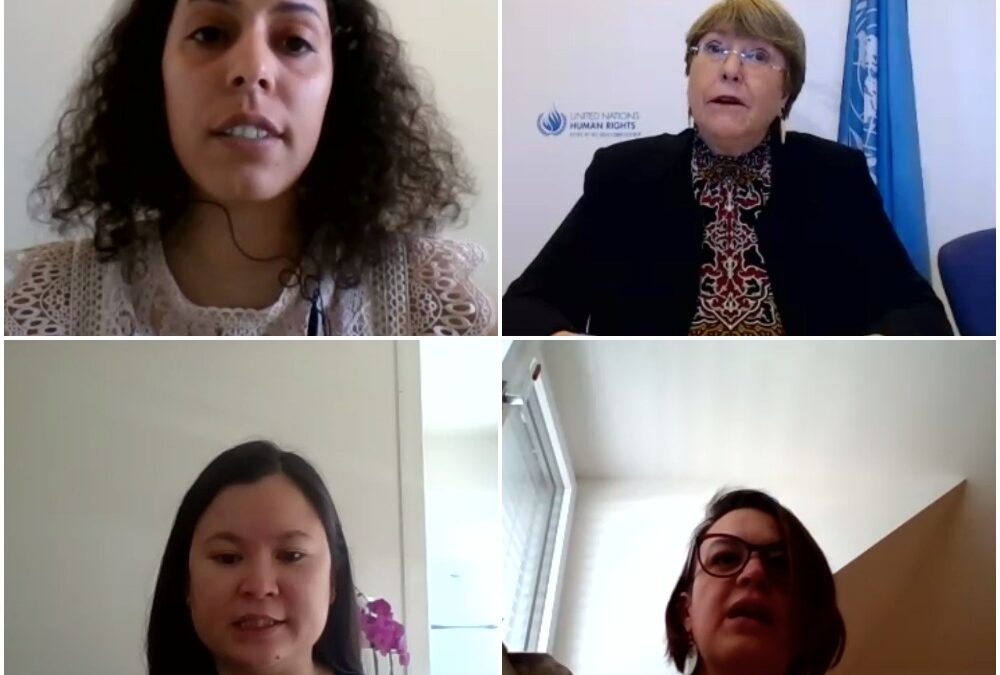
The ICJ has joined other NGOs highlighting key human rights issues in the COVID-19 pandemic, at a virtual meeting of the UN Human Rights Council.
In the informal conversation, exceptionally organised by video-conference, the High Commissioner for Human Rights presented a statement, as did the President of the Council and a number of States, followed by several statements by NGOs.
The ICJ joined statements delivered by CIVICUS (on civil and political rights), ISHR (on the UN system response), and FORUM-Asia (on economic, social and cultural rights), on behalf of a large number of NGOs from around the world.
The statements focussed on, among other things:
- the obligations of States individually and collectively to mobilize the maximum available resources to respond to the pandemic and protect those at risk, including by respecting, protecting and fulfilling economic, social and cultural rights;
- the need to guard against abuse of emergency powers and undue restrictions on fundamental rights, including non-discrimination, freedom of expression and right to access information, the right to privacy, rights of persons deprived of liberty, and taking into account the situation of particularly-at-risk groups;
- the role of the Human Rights Council, Special Procedures and Secretary General to monitor, report on, and respond to human rights aspects of the pandemic and States’ responses, and ensuring that civil society continues to be able to participate in all relevant UN and other processes.
The full statements may be downloaded in PDF format here:
Civil and Political Rights: UN-JointStatement-COVID19CPR-2020-final
Economic, Social and Cultural Rights: UN-JointStatement-COVID19ESCR-2020-final
United Nations Mechanisms: UN-JointStatement-COVID19UN-2020-final
Abbreviated versions were delivered in the dialogue, due to the limited time available.
In extensive and detailed closing remarks, the High Commissioner responded to many of the questions and observations made during the discussion, concluding, on the topic of access to justice in times of crisis, as follows (unofficial transcription):
“Courts become more important than ever to safeguard rights in times when major decisions with broad impact are being taken and implemented at great speed. In these circumstances, we have already seen the real risk for abuse of power, legal over-generalization and mistake. The courts must remain available to address these issues, if necessary of course by modifying their working methods. We have seen courts in many countries taking measures to ensure they remain accessible while protecting their staff and clients.”
A video recording of the event can be viewed here.
The High Commissioner’s specific remarks on access to justice can be accessed directly here.
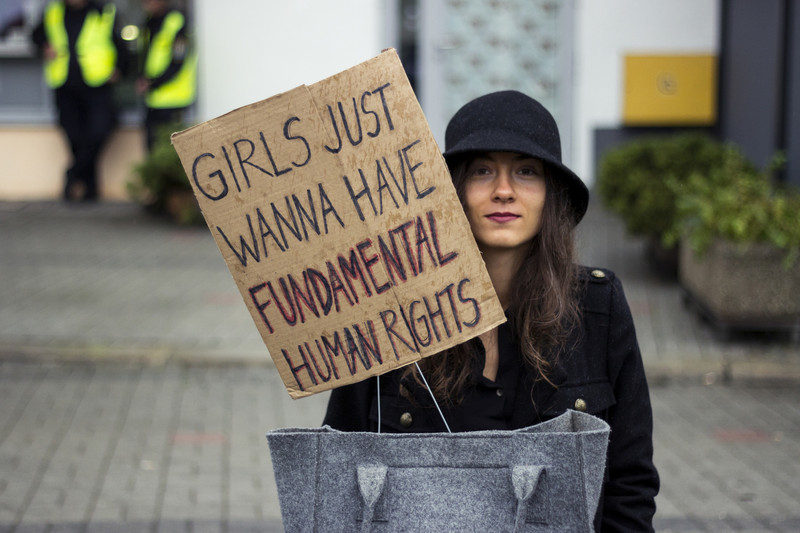
Apr 9, 2020 | Advocacy, News
A joint statement signed by the ICJ and 102 other organizations.
The COVID-19 pandemic and public health crisis is presenting grave challenges for health care systems across Europe.
As European countries work to address the pandemic, protect their populations, and meet the increased demand on health care workers and health care facilities it is vital that they adopt measures to safeguard the health, human dignity, physical and mental integrity, and reproductive autonomy of women and girls in the region.
In many countries the lack of government measures to guarantee individuals’ safe and timely access to essential sexual and reproductive health services, goods, and information during the pandemic is of particular concern.
Women and girls – this statement refers to women and girls, as the majority of individuals who are needing abortion care identify as such but it equally applies to all individuals who may become pregnant and need abortion care or other sexual and reproductive health care – are facing significant restrictions in safely accessing essential sexual and reproductive health services, particularly timely abortion care, post abortion care, and emergency contraception.
Such restrictions disproportionately impact individuals belonging to marginalized groups, including women living in poverty, women with disabilities, Roma women, undocumented migrant women, adolescents, and women at risk or who are survivors of domestic and sexual violence.
These restrictions also create unnecessary risks of exposure to COVID-19 for women and girls and their families as well as for health care providers.
Particularly grave barriers are arising for women and girls living in European countries where abortion care is illegal or severely restricted, and where as a result they must travel to other countries to access legal care or must obtain abortion medication from outside their own jurisdiction.
These issues can also arise in those European countries where individuals are forced to go through burdensome or harmful administrative processes to access abortion care or where they may have difficulty finding doctors in their country willing to provide care.
We applaud those governments that have moved swiftly to safeguard access to essential time- sensitive sexual and reproductive health care during this time, in particular through ensuring access to telehealth and early medical abortion from home.
We call on all other European governments to follow suit and to follow the guidance of medical and public health experts.
We call on the six European countries (Andorra, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, Poland and San Marino) where abortion is illegal or severely restricted to urgently reform these laws, which place women’s health and lives at risk.
Limitations on travel and transport now compound the impact of these highly restrictive laws. Individuals in these countries may no longer be able to travel abroad or to obtain medication for abortion sent by post from medical providers in other countries. As a result, they face heightened risks to their health and wellbeing.
We call on those countries where abortion is legal but where clinical services are unavailable or difficult to access due to a range of barriers, including medically unnecessary requirements that oblige individuals to take multiple or unneeded trips to health care facilities or undergo mandatory hospitalization, to urgently eradicate those barriers and ensure access to services.
Urgent steps should also be taken to ensure that refusals of care because of private beliefs by doctors do not jeopardize timely access to legal abortion care.
In accordance with human rights obligations3 and the recommendations of medical experts4 the following measures should be adopted, and at a minimum remain in place for the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic:
- Ensure that abortion is treated as essential and time-sensitive health care and guarantee access to care in a timely manner.
- Authorize and make available in a timely manner telehealth consultations for anyone who is seeking abortion care or information. Specific measures should be adopted to ensure that telehealth consultations are free or low cost and easily accessible for marginalized groups.
- Guarantee timely access to early medical abortion throughout each jurisdiction and allow doctors to prescribe the necessary medication via telehealth consultation.
- Allow individuals to take all abortion medication at home. Requirements in some European countries that one pill must be taken in the physical presence of a doctor or in a health care facility should be removed.
- Remove mandatory waiting periods prior to abortion as well as mandatory counselling requirements or ensure counselling can be conducted through telehealth consultation.
- Authorize primary care doctors and midwives to provide early medical abortion.
- Adopt health system safeguards to guarantee access to care in cases where early medical abortion is not possible or is contraindicated, for individuals who need abortion care later in pregnancy or post-abortion care, or who may need to visit a health care facility for other reasons. Travel in such cases should be deemed essential and permitted even where governments have otherwise restricted free movement.
- Where a doctor’s authorization is required, this should be limited to one doctor. Requirements for multiple doctors’ approval of an abortion should be removed.
- Guarantee timely access to prenatal testing and psychosocial support where requested.
- Guarantee an adequate number of providers willing and able to provide abortion care throughout the country and widely publicize information on how women can identify health care professionals willing and available to provide abortion care. Urgently ensure that refusals of care by doctors do not jeopardize access to abortion care in a time of crisis.
- Widely disseminate information on those changes to SRHR policies and health care services that are being made in the context of COVID-19 responses.
- Ensure access to contraception including emergency contraception, including through authorizing telehealth consultations and provision of emergency contraception over the counter in pharmacies without a prescription.
Finally, we call on all policy makers across the European region to reject proposals that purport to restrict access to safe abortion care during the COVID-19 pandemic. These disingenuous proposals simply serve to exacerbate the current public health crisis and have negative effects on the health, lives, and wellbeing of women and girls.
Download the full statement with additional information and the list of signatories