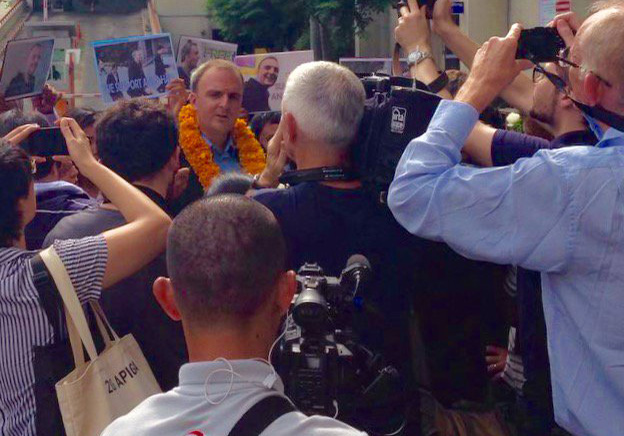Jul 9, 2018 | News
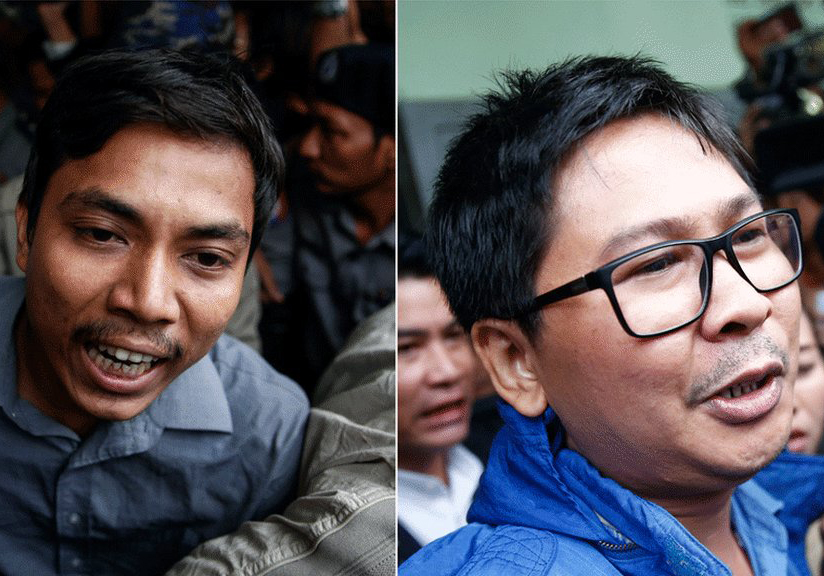
Today the ICJ called on Myanmar’s prosecutorial authorities to immediately end the prosecution of Reuters journalists Wa Lone and Kyaw Soe Oo.
The two have been subject to prosecution solely for doing their job as journalists and for exposing human rights violations in Rakhine State, including unlawful killings in Inn Dinn Village admitted to by the military.
In Yangon this morning a Northern District Court Judge accepted charges filed under the 1923 Official Secrets Act.
This decision permits ongoing prosecution of the journalists and extends their detention.
“The prosecution has failed to provide credible evidence of any wrongdoing throughout six months of hearings. It is therefore hard to imagine a valid legal rationale for allowing ongoing prosecution of the journalists,” said Mr Sean Bain, legal adviser for the ICJ in Yangon.
Section 253(1) of Myanmar’s Code of Criminal Procedure requires a judge to dismiss charges against accused persons if the evidence presented fails to warrant a conviction.
A motion for charges to be dismissed on this basis, submitted by defense lawyers, was effectively rejected by the decision today.
“Today’s decision raises real concerns about the independence and impartiality of the judiciary and prosecution when confronted with politically sensitive cases,” Bain said.
“The case significantly undermines the government’s stated commitments to reforming and building public confidence in judicial process,” he added.
ICJ legal advisers have monitored the case and were present in Court today. The journalists were first detained on 12 December 2017 and had no access to legal representation for almost two weeks.
“The case is also emblematic of the lack of adherence to fair trial rights in Myanmar,” Bain said.
“Their confinement remains unlawful given an initial period of incommunicado detention without access to lawyers, and other flagrant violations of the fair trial rights guaranteed in the Constitution, statues and international law.”
“Authorities should immediately end criminal proceedings against these men who appear to have been lawfully doing their job as investigative journalists,” he added.
The detention and prosecution of anyone, including journalists, based solely on the collection and publication of evidence relevant to serious human rights violations, is inconsistent with international law and standards on freedom of expression and on human rights defenders.
Article 14 of the 1990 UN Guidelines on the Role of Prosecutors states that prosecutors are obliged to discontinue prosecution when the investigation shows the charges to be unfounded.
Myanmar’s new Code of Ethics for Law Officers, launched in 2017, requires prosecutors to protect rights enshrined in the Constitution and to “provide a proper and fair administration of justice.”
The right to legal counsel is a bedrock rule of law principle that is set out in a range of international human rights laws and standards, including in article 11 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Sections 19 and 375 of the Myanmar Constitution guarantee the right of legal defense, as does Myanmar’s Code of Criminal Procedure (section 340), Courts Manual (section 455(1)), the Police Manual (section 1198c) and the Prisons Act (section 40).
Fair trial rights, freedom of expression, and the right to liberty are also recognised by the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Also relevant are the UN Declaration on Human Rights Defenders, and the Global Principles on National Security and the Right to Information (The Tshwane Principles).
Contact:
Sean Bain, ICJ legal adviser, e: sean.bain(a)icj.org
Read also:
ICJ (May 2016), Handbook on Habeas Corpus in Myanmar – English and Burmese
ICJ (December 2017), Reuters Journalists in Myanmar: respect their rights, end their incommunicado detention – English and Burmese
Full text in Burmese (PDF): Myanmar-drop-charges-against-Reuters-journalists-News-Press-releases-2018-BUR

Dec 18, 2017 | News
The ICJ today called on Myanmar authorities to immediately disclose the whereabouts of two journalists who have been detained incommunicado for nearly one week, and to grant prompt access to lawyers and families.
Reuters reporters Wa Lone and Kyaw Soe Oo have not been heard from since they were arrested by police in Yangon on Tuesday 12 December.
“Fair trial rights violations seriously undermine the rule of law in Myanmar. All detainees must be allowed prompt access to a lawyer and to family members,” said Frederick Rawski, the ICJ’s Asia-Pacific Regional Director.
“Authorities are bound to respect these rights in line with Myanmar law and the State’s international law obligations,” he added.
The right to legal counsel is a bedrock rule of law principle that is set out in a range of international human rights laws and standards, including in article 11 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Sean Bain, Legal Adviser for the ICJ, said that jurists should assess if the journalists’ detention conforms to applicable laws.
“Their situation appears to constitute arbitrary detention,” he said. “The judiciary should immediately review the lawfulness of detention and demand their release if it is indeed unlawful.”
“Judges and lawyers in Myanmar have an opportunity to assert their independence by challenging the unlawful actions of officials. Such blatant violations of fair trial rights should not go unanswered,” he added.
State media reports the journalists were charged under the 1923 Official Secrets Act in connection with their work investigating actions of security forces in Rakhine State.
More than 650,000 people, mostly Rohingya Muslims, fled to Bangladesh as a result of military operations following attacks on police posts in August by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army.
Reuters has reported from both sides of the Myanmar-Bangladesh Border.
“The treatment of these reporters threatens freedom of expression. The harsh penalties they face sends a clear message to other journalists that they could face the same consequences for doing their job,” said Rawski.
In Myanmar, colonial-era laws were invoked to bring criminal charges against journalists in at least three jurisdictions in 2017.
Offences in these laws are often broadly defined, carry harsh penalties, and are open to abuse by authorities.
Journalists who received ten-year jail terms in 2014 under the Official Secrets Act were later released in a Presidential amnesty.
Amendments proposed at the time in parliament were rejected.
“The abuse of archaic laws like the Official Secrets Act must end. It is within the power of the National League for Democracy-dominated legislature to review these laws with a view to aligning them with the rights reflected in Myanmar’s constitution and in international law,” Rawski added.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director, t: +66 6 4478 1121 ; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Sean Bain, ICJ International Legal Adviser, e: sean.bain(a)icj.org
Background
The UN Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers emphasize that, “Governments shall further ensure that all persons arrested or detained, with or without criminal charge, shall have prompt access to a lawyer, and in any case not later than 48 hours from the time of arrest or detention.”
Sections 19 and 375 of the Myanmar Constitution also guarantee the right of legal defense, as does Myanmar’s Code of Criminal Procedure (section 340), Courts Manual (section 455(1)), the Police Manual (section 1198c) and the Prisons Act (section 40).
Sections 21(c) and 376 of the Constitution and section 61 of the Code of Criminal Procedure state that persons cannot be detained for more than 24 hours without a judge’s order.
The right to legal defense implies the right to access legal counsel during this 24-hour period.
Under section 403 of the Courts Manual, a detainee can be remanded only once he or she has appeared before a judge. It is unknown if the two Reuters journalists have appeared in court.
Competent judges are empowered to compel a search for a detainee if they have reason to believe the person is confined unlawfully, as per section 100 of the Criminal Procedure Code.
Lawyers and family members may also request the courts to review the lawfulness of detention, by submitting a habeas corpus petition to the High Court and or to the Supreme Court.
The Tshwane Principles on National Security and the Right to Information, which address the right to access and to share information, as an aspect of freedom of expression in the context of national security, affirm that journalists “should not be prosecuted for receiving, possessing or disclosing classified information to the public, or for conspiracy or other crimes based on their seeking or accessing classified information.”
Read also
Handbook on Habeas Corpus in Myanmar
Right to Counsel: The Independence of Lawyers in Myanmar
Myanmar-Reuters Journos-News-Press releases-2017-BUR (Story in Burmese, PDF)
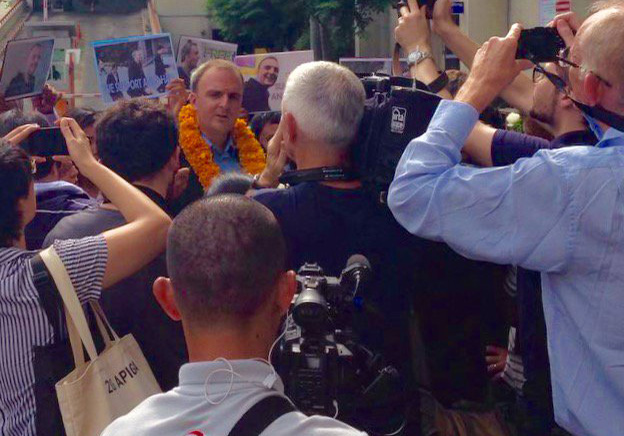
Sep 20, 2016 | News
The ICJ expresses its disappointment with today’s verdict criminalizing the work of human rights defender, Andy Hall, and calls upon Thailand to decriminalize defamation and amend the Computer Crime Act in line with international standards protecting freedom of expression.
This morning, Thailand’s Southern Bangkok Criminal Court found Andy Hall guilty of defaming a Thai fruit processing company under Article 328 of the Thai Criminal Code and violation of Article 14(1) of the Computer Crime Act, and sentenced him to a fine of THB 200,000 (USD$ 5,700) reduced to THB 150,000 (USD $4,300); and four years imprisonment, reduced to three years and suspended for two years.
Andy Hall has said he will appeal the verdict.
“Human rights defenders such as Andy Hall have the right to exercise freedom of expression in advocating for the protection and realization of human rights – a right that Thailand has a duty to protect,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser at the ICJ.
“Unfortunately, there are numerous examples of criminal defamation and the Computer Crime Act being used against human rights defenders in Thailand, a practice that must end, including through a substantial reform of these laws,” he added.
The ICJ and Lawyers Rights Watch Canada submitted a joint amicus curiae brief in the proceedings, arguing that the imposition of harsh penalties such as imprisonment or large fines on a human rights defender risk having a ‘chilling effect’ on the exercise of freedom of expression, which Thailand is bound to protect pursuant to its international legal obligations.
The ICJ anticipates the arguments contained in the joint amicus will be considered on appeal.
“It is also disappointing that the Court did not appear to take into account the recent decision of the Phuket Provincial Court in the Phuketwan case, which found that the Computer Crime Act was not intended to be used in cases of alleged defamation,” said Abbott.
On 1 September 2015, the Phuket Provincial Court acquitted two journalists of criminal defamation and violations of the Computer Crime Act after the Royal Thai Navy complained the journalists defamed it when, on 17 July 2013, the journalists reproduced a paragraph from a Pulitzer prize-winning Reuters article that alleged “Thai naval forces” were complicit in human trafficking.
The criminal defamation proceedings brought against Andy Hall are among several that have been brought against human rights defenders in Thailand in recent years.
Others examples include the charges laid against activists Pornpen Khongkachonkiet, Somchai Homloar and Anchana Heemina in July 2016 for raising allegations of torture in the deep South; and those brought against activists protesting various development projects in Thailand which are allegedly having an adverse impact on communities.
Background
Today’s case is one of four criminal and civil proceedings (two criminal and two civil) a Thai fruit processing company, Natural Fruit Company Ltd., has brought against Andy Hall in relation to the report of a Finnish NGO, Finnwatch, published in January 2013, called Cheap Has a High Price.
Andy Hall’s research was included in the report which alleged that labour rights violations were taking place at Natural Fruit Company Ltd., whose employees included migrant workers from Myanmar.
In September 2015, a Thai Appeal Court upheld the dismissal of the other criminal defamation proceeding Natural Fruit Company Ltd. brought against Andy Hall. That proceeding is currently before the Supreme Court. Two civil proceedings are also before the Thai courts but have been suspended pending resolution of the two criminal proceedings.
The use of criminal defamation laws, carrying penalties of imprisonment, against human rights defenders reporting on alleged human violations, constitutes a violation of Thailand’s obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which it is a state party.
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-eng (full text in PDF)
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-tha (full text in Thai, PDF)
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 9 4470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org

Jun 2, 2016 | News
The ICJ is alarmed by the intimidation and harassment experienced by bloggers in Singapore recently, perpetrated by police authorities.
In the last few days, the homes of four bloggers were raided and their phones and laptops confiscated, without the legal process or justification required by international standards.
The ICJ strongly urges the Government of Singapore to stop this harassment and ensure that bloggers are protected against such unjustified interference with or reprisals for the exercise of their right to freedom of expression.
“By resorting to this kind of harassment and intimidation of bloggers, Singapore is showing complete disregard for human rights and the rule of law,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific.
“The Government of Singapore must stop intimidating citizens who express their political opinions openly. The actions taken by the Singaporean police against the four bloggers do not only constitute an attack on freedom of opinion and expression in the country, but also clearly violates their right to privacy,” he added.
On 27 May 2016, the Election Department of Singapore filed police reports alleging that bloggers Roy Ngerng and Teo Soh Lung, and The Independent Singapore, an independent news website, violated the rules against election advertising ahead of polling day.
Under Singapore’s election rules, campaigning is prohibited 24-hours prior to polling day, which is called the “Cooling-Off Day”.
Roy Ngerng and Teo Soh Lung were alleged to have written posts on their social media accounts expressing support for the opposition candidate, Mr. Chee Soon Juan.
The Independent Singapore, on the other hand, was alleged to have published articles that amount to election advertising.
The ICJ considers that provisions or interpretations of Singapore’s election laws that would impose a sweeping ban on all political expression in relation to particular candidates in a 24-hour period prior to polling day, including the expression of opinions by private individuals without remuneration, cannot constitute a demonstrably justified and proportionate restriction on freedom of opinion and expression under international standards.
Early this year, the delegation representing the Government of Singapore said as it went through the 2nd cycle of the Universal Periodic Review that “no one in Singapore is prosecuted for criticizing the government or its policies.”
The delegation emphasized that Singapore’s Constitution guarantees the right to freedom of expression.
The Government of Singapore also accepted recommendations made by other States at the Universal Periodic Review to “ensure the full enjoyment of the right to freedom of expression”.
It also accepted the recommendation to protect bloggers from persecution and harassment for the exercise of their human rights.
The ICJ urges the Government of Singapore to remain true to the commitments it made during the recent Universal Periodic Review and respect the right to freedom of expression of bloggers.
Contact:
Emerlynne Gil, ICJ’s Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, t: +668 4092 3575 ; e: emerlynne.gil(a)icj.org
Additional information
On 6 May 2016, The Independent Singapore published two articles: 5 Highlights of DPM Speech and Workers’ Party and the Bukit Batok by-election – what WP members said.
The first article reported about the speech of the Deputy Prime Minister of Singapore at the rally of the ruling party, the People’s Action Party (PAP), wherein he expressed support for the PAP candidate.
The second article reported statements made by the Workers’ Party (WP) members on key issues relating to the elections.
On 7 May 2016, it published the article Tan Cheng Bock Denies involvement in posting by irrational group of PAP fans, where it reported on how the former Member of Parliament, Dr. Tan, disavowed statements he allegedly made and that were posted on the Facebook group which favor the ruling party.
On 31 May 2016, Roy Ngerng and Teo Soh Lung were interrogated for three hours by police. The two were interrogated separately. Teo Soh Lung was accompanied by her lawyer, while Roy Ngerng was not.
After the interrogation, the police accompanied the bloggers back to their respective homes. The police searched their homes without warrants or their consent, and confiscated their mobile phones, laptops, and hard disks. After the search, Roy Ngerng was taken back to the police station and interrogated for another few hours.
At the police station, law enforcement authorities intimidated Roy Ngerng into logging in and out of his social media accounts and his blog, The Heart Truths, in their full view and presence.
The publisher and editor of The Independent Singapore were likewise interrogated separately by the police, on 31 May 2016 and 1 June 2016. Their mobile phones and laptops were also confiscated by the police after their interrogation.
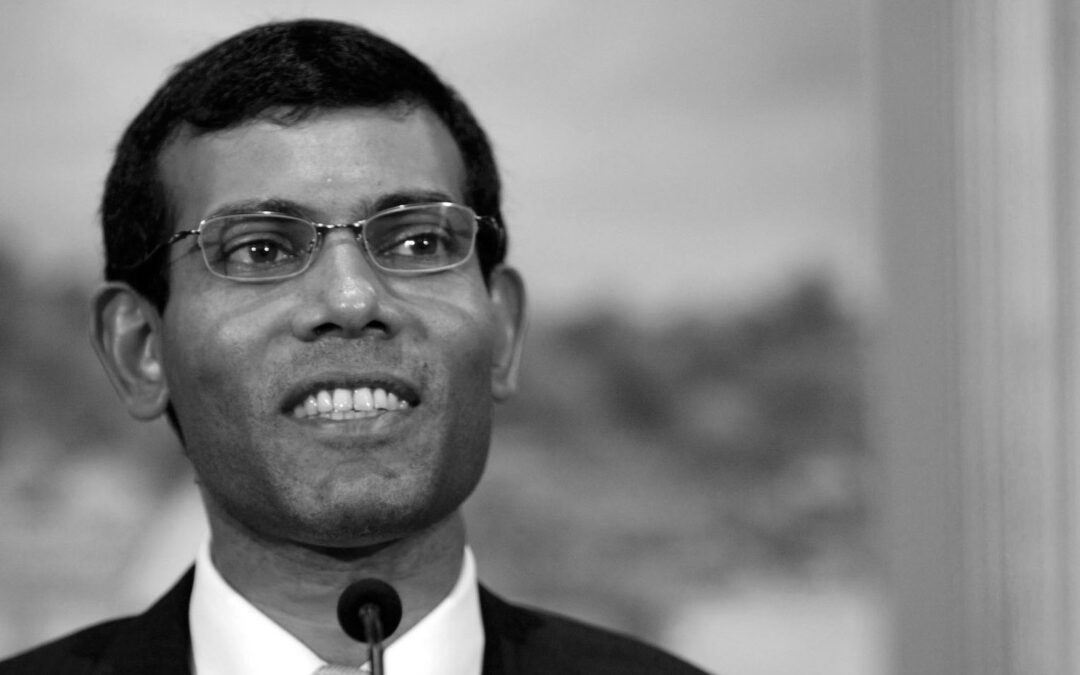

Sep 14, 2015 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
In advance of the UN Human Rights Council’s adoption of the outcome of its review of the Maldives’ human rights record as part of the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) process, the ICJ has submitted a written statement.
It highlights the Maldives’ failure to accept and implement a number of member states’ UPR recommendations.
In particular, the ICJ pointed out the urgent need for Maldives to accept and implement recommendations regarding the following issues, among others:
- Strengthening the independence and impartiality of the judiciary;
- Strengthening the independence and impartiality of the Judicial Service Commission;
- Strengthening the National Human Rights Commission, in accordance with the Paris Principles;
- Strengthening women’s representation in the judicial profession;
- Immediately releasing former president Mohamed Nasheed and other political prisoners, and ensuring the fairness of any further legal proceedings in such cases; and
- Safeguarding freedom of expression and media, association and peaceful assembly by investigating cases of human rights abuse and violations against journalists, civil society and human rights defenders, and taking effective measures to prevent further abuses
The Council will consider member states’ UPR recommendations for the Maldives during its 30th session on 24 September 2015, ahead of which the Maldives government will be expected to formally respond and indicate which of the recommendations it will commit to implement.