Apr 1, 2021 | Agendas, Events, News
Migrants and asylum seekers must be provided adequate procedural guarantees in asylum procedures and in immigration detention, a group of experts and judges asserted during a seminar for Greek and Italian judges held by the ICJ, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), and Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) on 29-31 March.
Asylum applicants should have access to adequate information about the procedure and their entitlements in a language they understand, access to a reliable communication system with the authorities, the availability of interpreters, access to legal aid, and reasoned decisions, experts said during the seminar, held in the framework of the FAIR plus project. Speakers further emphasized that immigration detention must be subject to automatic review by an independent body with a power to release detainees, especially when removal is no more an option.
More than 30 judges from Italy and Greece came together for this event to discuss procedural guarantees for migrants and asylum seekers, related to the safe third country concept, the access to legal assistance and interpretation, safeguards related to immigration detention, and procedural guarantees in the asylum procedure, especially in the accelerated procedures.
A summary of the discussions
On the first day, the judges exchanged overviews of national systems and presented some specific questions regarding the Italian and the Greek systems. Following the discussion on the safe third country concept and its implementation in Greece, an Italian judge presented recent developments in the Italian case-law, and the role of the judge, country of origin information, accelerated procedures, the length of procedures and the question of credibility assessment.
On the second day, the discussion related to the impact of Covid-19 pandemic on the rights of migrants and asylum seekers took place. The situation in Greece and in Italy was described by judges, in particular in relation to the access to the asylum procedure, the lawfulness of detention, the right to health and the question of access to a personal hearing when some of the hearings take place electronically.
An overview of the situation of immigration detention in Italy and Greece was presented by an Italian lawyer and an expert from UNHCR Greece. Speakers highlighted that in cases when people cannot be returned, they should not be kept in detention without a legal basis.
Accelerated procedures in law and in practice in both countries have been introduced by UNHCR Greece and Italy were addressed through a case-study and discussion, covering mainly the specific needs in accelerated procedures, automatic suspensive effect of appeals, and time limits in the accelerated procedures.
Finally on the last day, two lectures were delivered by Ledi Bianku, a former judge of the European Court for Human Rights, and an Associate Professor at the University of Strasbourg. First, looking into the guarantees in asylum and migration proceedings, Ledi Bianku stressed the need to always provide asylum applicants adequate information about the procedure and their entitlements in a language they understand, access to a reliable communication system with the authorities, the availability of interpreters, access to legal aid, and reasoned decisions in order to provide access to an effective remedy. In the second part of his intervention, Mr. Bianku discussed the detention of migrants, where he stressed the need for automatic review of detention, especially when removal is no more an option, by an independent body with a power to release.
The FAIR plus project is a judicial training and cooperation project supported by the European Union’s Justice programme, focusing on four countries Ireland, Greece, Italy and the Czech Republic. The aim of the project is to contribute to better judicial protection of the fundamental rights of migrants across the EU. Within the project the ICJ and partners are drafting of training materials and relevant legal briefings, implement training of the existing judicial trainers in the target countries, conduct four national trainings, two transnational seminars, and an international roundtable. The project is implemented in collaboration with national partners: Immigrant Council of Ireland (ICI), Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna (SSSA), Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) and Forum for Human Rights (Czech Republic).
Please find the agenda here.

Aug 27, 2019 | News
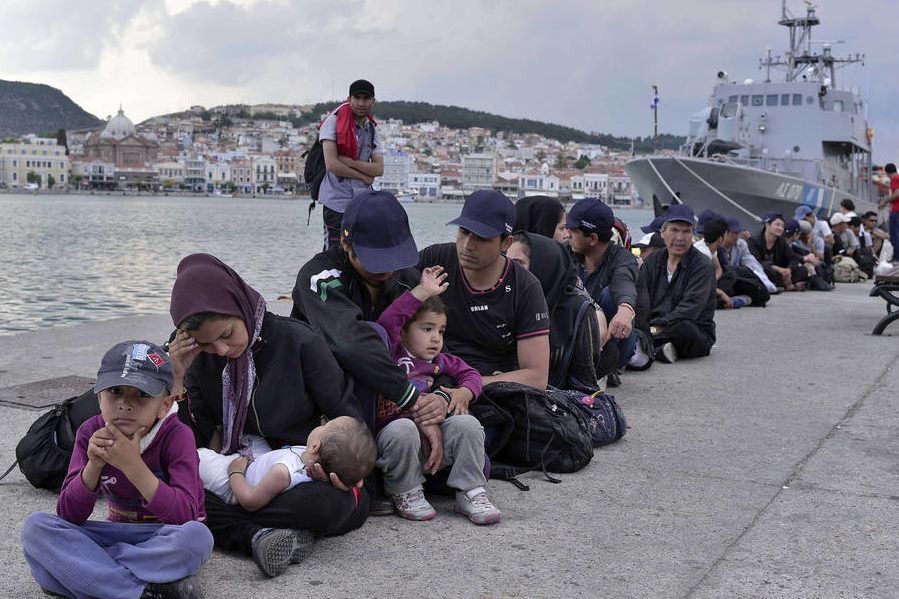
Following the killing of an Afghan boy in the Moria reception center in Greece, the ICJ calls on the Greek authorities to effectively implement measures of protection prescribed to Greece this May by the European Committee on Social Rights.
According to information by the UN High Commissioner for refugees, the 15-year-old Afghan boy was killed and two other boys injured after a fight broke out at the Moria reception centre on the Greek island of Lesvos.
The safe area at the Moria Reception and Identification Centre, RIC, hosts nearly 70 unaccompanied children, but more than 500 other boys and girls are staying in various parts of the overcrowded facility without a guardian and exposed to exploitation and abuse.
“This is not a situation unique to Moria. In other parts of Greek islands and also on mainland Greece human rights of migrant children are being violated,” said Karolína Babická, ICJ Legal Adviser.
Security of children as well as access to basic needs, such as appropriate shelter, food water or medical care, were the focus of a recent case the ICJ brought together with ECRE and Greek Council for Refugees (GCR) to the European Committee on Social Rights (ECSR).
The ECSR acknowledged the urgency of the situation and decided on immediate measures in the case already on 23 May 2019.
“It is unacceptable that the decision on interim measures has not yet been implemented by the Greek government and now we have to witness such tragic events like a death of a child in the camp,” said Karolína Babická.
“It is a sad wake-up call to the Greek administration that the situation cannot remain like this,” she added.
In its decision, the Committee members required the Greek government to immediately provide migrant children with appropriate shelter, food, water, education and medical care; to remove unaccompanied migrant children from detention and from Reception and Identification Centers (RICs) at the borders, place them in suitable accommodation for their age and appoint effective guardians.
“Greece must urgently bring those children to safety and make sure their basic needs are met and human rights are protected, in order to comply with its international legal obligations,” said Róisín Pillay, ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme Director.
Contact:
Karolína Babická, Legal Adviser, ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme, m +32 475 46 2067 ; e: Karolina.Babicka(a)icj.org

Jan 31, 2019 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
For the past two years the ICJ and its partners Refugee Rights Turkey (RRT), the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE) and Mülteci-Der (MD) have provided trainings and training materials for Turkish lawyers on international human rights law relating to migration and asylum as part of the project Fostering Access to Rights for Migrants, Refugees and Asylum-Seekers in Turkey.
The project has worked to enhance access to justice for migrants, refugees and asylum-seekers, through establishing, equipping and supporting a well-informed group of lawyers and civil society organizations in Turkey and link them with their counterparts in EU Member States to defend the rights of migrants, refugees and asylum-seekers.
In a public event on the 17 December 2019 hosted in Ankara to mark the conclusion of the project, the ICJ and its partners presented a promotional video describing the work conducted throughout the project.
Watch video here:
(Rough Turkish subtitles available but will be revised at a later stage | Turn the Turkish subtitle by clicking on CC.)
The project “Fostering Access to Rights for Migrants, Refugees and Asylum-Seekers in Turkey” is funded by the European Instrument for Democracy and Human Rights (EIDHR) of the European Union.

Jan 18, 2019 | News
A legal challenge to the violations of migrant children’s social rights on mainland Greece and its North Eastern Aegean islands has been lodged by the ICJ and the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE) before a European body specialized in the protection of social rights at the European level.
The legal action, taken in the form of a collective complaint to the European Committee on Social Rights, catalogues the numerous instances of Greece failing its child care and protection obligations towards migrant children by leaving them in conditions of squalor, insecurity and violence.
The complaint to the Committee, an impartial body which oversees the protection of certain economic and social rights by assessing the conformity of domestic law and practice with the European Social Charter, has been supported by the Greek Council for Refugees and includes reports from Médecins Sans Frontières on health and living conditions of migrant children in Lesvos.
Amongst the most blatant infringements of migrant children’s rights described in the complaint has been the systematic and ongoing absence of sufficient accommodation facilities and the lack of an effective guardianship system for unaccompanied children in Greece, exposing them to significant protection risks, including homelessness and placement in detention.
Such severe deficiencies in basic care facilities has led to dire living conditions which deprive children of their most fundamental rights.
Overcrowded, insalubrious and dangerous conditions prevail most obviously on the North Eastern Aegean islands where the standards of human dignity and special protection accorded to children by virtue of their particular status under international human rights law are repeatedly violated.
The complaint notes that the dearth in basic care facilities for migrants in Greece extends to medical services, particularly on the islands, which has a serious knock-on effect on hygiene, sanitation and substantive physical and mental health care and treatment for children.
In addition, mixed living arrangements, limited, if not non-existent security patrols and deficient guardianship systems have led to numerous reports of sexual abuse, violent assaults, harassment and humiliation of migrant children in camps on the Greek islands.
The consequences of the conditions listed in the complaint have been, in certain locations, children self-harming and even attempting suicide.
“Greece’s deference to the violations being committed against migrant children on its territory has gone on for far too long without any foreseeable improvement on the horizon.
Transfers of migrant children and vulnerable persons from the islands to the mainland are paralysed by a shortage of places on the mainland and administrative encumbrances.
All the while, children are left to languish in a forgotten environment of impoverishment and destitution.
This legal challenge to Greece’s indifference will hopefully pave the way for institutional condemnation and for substantive change in the protection of society’s most vulnerable” says Amanda Taylor, Senior EDAL Coordinator at the European Council on Refugees and Exiles.
“As signatory of the European Social Charter, Greece is under an international obligation to ensure that migrant children in its jurisdiction have access to basic economic and social rights. Particularly in the case of migrant children, who find themselves in a vulnerable situation, remaining even for a short period of time in such terrible conditions as currently exist in Greece, is likely to result in irreparable harm and injury and have a detrimental and non-reversible impact on their development,” said Karolína Babická, Legal Adviser for Europe and Central Asia with the ICJ.
“This complaint refers to two of the most pressing protection issues in Greece; the protection of unaccompanied minors and the conditions prevailing on the Greek islands after the launch of the EU-Turkey Statement, where migrant children are stranded. In December 2018, almost two out of three unaccompanied children in Greece were deprived of a place in long-term accommodation facility for minors. At the same time, 30% of the 14,600 persons remaining on the Greek islands were children. Thus, the procedure initiated before the European Committee of Social Rights can significantly contribute to guaranteeing the respect of migrant children’s rights in Greece,” said Alexandros Konstantinou, member of the Legal Unit of the Greek Council for Refugees.
The complaint awaits examination and determination by the European Committee on Social Rights.
As part of the complaint and in order to immediately alleviate the situation which migrant children face in Greece, ECRE and ICJ have urgently requested Greece to remove migrant children from unsuitable and overcrowded camps on the islands; to provide them with adequate and age-appropriate facilities, sufficient food, water and medical care, and with effective and competent guardians; and to remove unaccompanied migrant children from detention and place them in tailored accommodation suitable for their age.
Read the full complaint here.

Apr 25, 2018 | Events, News, Video clips
Today, the ICJ-European Institutions held the final event of its EU and OSI funded FAIR project (Fostering Access to justice for Immigrant children’s Rights) in the European Parliament in Brussels. Two videos have also been produced.
This is the closing event of a two-year long project, which aimed at strengthening access to justice for migrant children in the EU.
Migrant children in the EU face violations of their human rights every day.
Lack of access to their families, to information, guardians and legal assistance, lack of access to housing or education, unlawful detention – are few examples of what the children suffer.
The event in the European Parliament was hosted by four political groups and three Members of the EP took part in the panel discussions, on challenges migrant children face in their access to justice and on ways forward and what the EU could do to further advance the rights of some of the most vulnerable people at EU territory.
The panel discussions also included specific cases that national lawyers are dealing with in Italy, Greece, Germany and Ireland on behalf of migrant children.
Julien Makalu, a young engineering student shared his own experience when he arrived to Greece as unaccompanied minor some years ago.
During the FAIR project, the ICJ-European Institutions:
The FAIR project co-funded by the Rights, Equality and Citizenship Programme of the European Union and OSIFE.
Download the flyer and agenda of the event here:
Universal – A2J Migrant Children Flyer – 2018 – ENG (Flyer)
Universal – A2J Migrant Children Agenda – 2018 – ENG (Agenda)
Watch the videos of the FAIR Project and the FAIR Project’s retreat
From 4 to 8 October 2017, 19 lawyers from Bulgaria, Germany, Greece, Italy, Ireland, Malta and Spain met together and with experts to strategize about their cases of access to justice for migrant children and on accessing international human rights mechanisms. The workshop took place on the French border near Geneva, allowing UN treaty bodies experts and members to participate.









