
Jun 29, 2021 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today addressed the UN Human Rights Council in the Interactive Dialogue on the Report of the Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences.

Jun 18, 2021 | Agendas, Events, News
On 22 June, the ICJ, Human Rights Watch, the Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies, the Center for Reproductive Rights and the International Planned Parenthood Federation, with the co-sponsorship of the Kingdom of Spain, organize an online event on the 10th anniversary of the Council of Europe’s Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence (Istanbul Convention).
This side event at the margin of the 47th regular session of the UN Human Rights Council has convened expert speakers to illustrate the situation of human rights protection to combat and prevent violence against women in Europe, how the Istanbul Convention has crucially contributed to this goal and the obstacles to its effective implementation.
Preventing and combating violence against women, as well as its causes and consequences, are a priority of the UN Human Rights Council. While UN standards are central to achieving this goal, regional standards have to date provided a key contribution in this field. The Council of Europe’s Istanbul Convention is the most far-reaching international treaty specifically designed to counter violence against women.
On 11 May 2021, the Istanbul Convention turned 10 years old. It is now time to take stock of the achievements that this Convention has contributed to as well as the challenges ahead, including countering the spread of misinformation about the Convention and ensuring states continue to champion its principles and standards.
Women and girls are still suffering the aftermaths of the COVID-19 crisis. The pandemic effects have shown a worrying increase on violence against women. The universalization of the Istanbul Convention is more important than ever because the pandemic has unveiled the “permanent shadow pandemic” that women and girls are suffering around the world.
When: Tuesday June 22nd, 13:00 – 14:00 CEST
Where: Zoom
Language: English
Panelists
- María Isabel Sanchís, Senior Advisor, Office of the Commissioner on Violence against Women of the Government of Spain
- Dubravka Šimonović, UN Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences
- Dame Silvia Cartwright, former Governor General of New Zealand, former CEDAW member, Commissioner of the International Commission of Jurists
- Professor Feride Acar, former chairwoman of CEDAW and GREVIO
- Hillary Margolis, Senior Researcher, Women’s Rights Division, Human Rights Watch
Moderator Massimo Frigo, UN Representative, ICJ
To confirm your participation and receive connection details, please RSVP to Massimo Frigo, email: Massimo.Frigo@icj.org .
Event-Invitation-Side Event-IstanbulConvention-UN-HRC47-final-2021-eng (download the event leaflet)

Dec 10, 2020 | News
ICJ’s 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence underscores the need for justice systems to be more responsive.
The campaign commenced on 25 November, International Day for the Elimination of Violence against Women, and ended today on Human Rights Day. The campaign presented “an impact story” poster series, Facebook live interviews and opinion pieces on gender-based violence in Africa, Asia, Latin America, Middle East and North Africa.
The campaign underscored that harmful traditional norms and gender stereotypes provide the backdrop for the systematic and widespread abuse of women and girls’ human rights across the globe; it also emphasized the need to maintain essential services for survivors of gender-based violence (GBV) during COVID-19 lockdowns, including ensuring a continuum of adequate criminal justice response.
“Violence against women and girls around the world has increased in this global pandemic. Governments have a duty to ensure that their response to Covid-19 includes preventing such violence. For instance, all hotline services for reporting domestic violence must remain open during lockdowns and be considered part of essential services. The police must likewise be ready to act speedily if required. They must be made aware that women and girls are especially vulnerable at this time,” said ICJ Commissioner Ambiga Sreenevasan from Malaysia.
Throughout the campaign, the ICJ also underscored the ongoing need to support civil society organizations’ and women human rights defenders’ response to GBV, as well as the need to strengthen the judiciary’s capability to respond to GBV by enhancing its reliance on international human rights law and standards.
“The authorities have turned a blind eye to gender-based violence for far too long and it is time to prioritize combatting the phenomenon effectively, including through legislative reform and awareness raising,” said ICJ Commissioner Marwan Tashani from Libya.
Poster Series
Imrana Jalal (ICJ Commissioner, Fiji)
Mikiko Otani (ICJ Commissioner, Japan)
Ambiga Sreenevasan (ICJ Commissioner, Malaysia)
Marwan Tashani (ICJ Commissioner, Libya)
Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh (ICJ Africa Regional Programme Director)
Saïd Benarbia (ICJ MENA Programme Director)
Carolina Villadiego Burbano (ICJ Legal and Policy Adviser, Latin America)
Sexual Violence & Criminal Law in Zimbabwe
Amy Alabado Avellano (Family Court Judge, Philippines)
Savithri Wijesekera (Executive Director of Women In Need, Sri Lanka)
Nahla Haidar (ICJ Commissioner, Lebanon)
Saman Zia-Zarifi (ICJ Secretary General)
Tshabalala v S (South African Constitutional Court judgment on the doctrine of common purpose applied to rape)
Infographic
The Case for Reform: Criminal Law and Sexual Violence in Zimbabwe
Facebook Live Interviews
The Case for Reform: Criminal Law and Sexual Violence in Zimbabwe with Elizabeth Mangenje (ICJ Legal Adviser, Africa Regional Programme)
The State of GBV in the Middle East and North Africa Region with Nahla Haidar El Addal (ICJ Commissioner, Lebanon)
Women’s Access to Justice – What does justice mean for women in the context of COVID-19? (Joint initiative of ICJ, UN Women, and OHCHR)
Women’s Access to Justice – What does justice mean for women prisoners? (Joint initiative of ICJ, UN Women, and OHCHR)
Op-eds
Mujeres, justicia y pandemia, by Carolina Villadiego Burbano
Yet another treaty aims to protect African women. But how will it be enforced? by Nokukhanya Farisè and Tanveer Rashid Jeewa
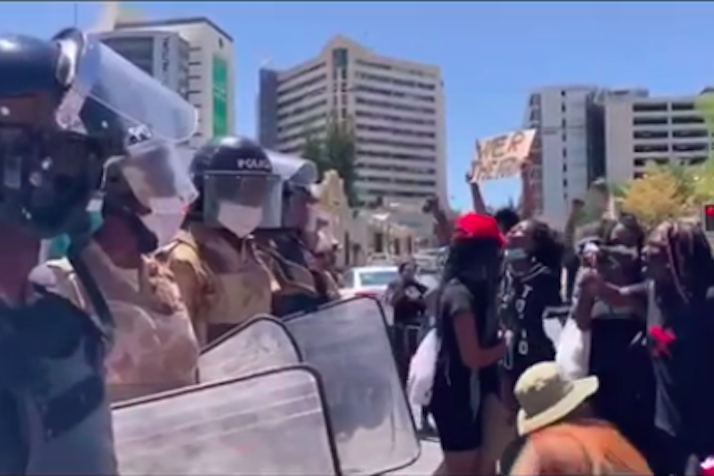

Oct 13, 2020 | News
Today the ICJ condemned the apparent widespread ill-treatment and arbitrary arrest of peaceful demonstrators protesting gender based violence on Saturday 10 October in Windhoek.
The demonstrators were allegedly met with tear gas, and a number of them were subject to serious beatings by police forces.
Some 25 persons, including journalists, were arrested during the demonstrations. They were initially charged with breaching a law forbidding the public gathering of more than 50 people, though the charges were dropped on Monday.
The ICJ is calling for a prompt, thorough, impartial and effective investigation into the alleged police abuse, in line with Namibian law and the countries international legal obligations.
Officials responsible should be held accountable.
“Instead of taking seriously the demands made by the protestors and to take steps to ensure that gender based violence is addressed in a meaningful and constructive way, the police themselves appeared to have engaged in violent action against those exercising their rights to peacefully assembly and express their view,” said Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, ICJ Africa Regional Programme Director.
The ICJ also called on the authorities to protect the right of individuals in the country to peacefully and protest, rights which are protected under Namibia’s Constitution and international law.
The ICJ said that the Public Gatherings Proclamation Act, requiring prior permission for assemblies of more than 50 people in public spaces, should be repealed or revised, as incompatible with its international legal obligations.
The ICJ has also called on Namibia to address the underlying concerns raised by the protests, notably that during the COVID-19 pandemic, gender-based violence has been exacerbated during lockdown restrictions.
In Namibia, reports of femicide and gender based violence steadily increasing and on average “three rape cases were reported to the Namibian police every day for 18 months.”
Background
The recent #ShutItAllDown and #ShutitAllDownNamibia movements, spontaneously started on social media after the killing of a young woman, Shannon Wasserfall, have led to a series of protests against government’s failure to adequately address the scourge of gender based violence in Namibia.
The protestors, predominantly young women, last week handed over a petition to government which includes a list of 24 demands. raising concerns about the poor State response to gender-based violence in Namibia.
The protestors allege that Namibian police are “negligent and nonchalant” with investigating violent crime committed against women. They are demanding that government do more to protect women against such violence, including by ensuring that survivors of gender-based violence have access to justice.
The rights to freedom of assembly and expression, freedom from ill-treatment, and prohibitions on arbitrary arrest are guaranteed under the international human rights treaties to which Namibia is a party, including the African Charter on Human and Peoples Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, and the Convention against Torture, as well as the Namibian Constitution.
Contact
Kaajal Ramjathan-Keogh, Director of ICJ’s Africa Regional Programme, c: +27845148039, e: kaajal.keogh(a)icj.org
Nokukhanya Farisè, Legal Adviser, nokukhanya.farise(a)icj.org

Sep 21, 2020 | News, Op-eds
An opinion piece by Ruth Panjaitan, ICJ National Legal Adviser in Indonesia.
Amid the COVID-19 outbreak in Indonesia, the House Representatives and the Law and Human Rights Ministry have continued their deliberation of the controversial Criminal Code revision as a priority bill.
The International Commission of Jurists has previously expressed concern that a number of provisions in the bill are inconsistent with Indonesia’s obligations under international human rights law. These provisions relate to the right to privacy, freedom of speech and freedom of association.
There are provisions in the draft that would have dire consequences for women’s rights in Indonesia. For instance, if implemented in its current form, the bill would explicitly criminalize cohabitation or the act of two consenting adults living together as heterosexual sexual partners outside of a legal marriage. Persons found guilty of cohabitation would risk up to six months of imprisonment or a fine of approximately Rp 10 million (US$633).
The act of cohabitation is currently not a criminal offence under the existing Criminal Code. However, Indonesian women who live with their partners outside of marriage are often stigmatized as women “of low honor”. In addition, there are some regions in Indonesia that have adopted local ordinances prohibiting cohabitation, such as in Batam and Aceh, as this practice is disfavored by the authorities because of harmful gender stereotypes and their interpretations of religious and cultural norms.
These local ordinances are being used by the local Public Order Agency (Satpol PP) and self-appointed “moral police” to publicly shame cohabiting couples, especially the women.
There have been numerous instances where the neighbors of a cohabiting couple have barged into private homes and publicly chastised the couple. In 2017, a couple’s house in Jakarta’s neighboring city of Tangerang was raided by men from the neighborhood who punched the couple, stripped them naked, paraded them around the community, and forced them to confess that they were living together “illegally”. The perpetrators recorded the incident on video, which unfortunately later went viral on social media.
Local vigilantes account for the biggest percentage of those who invade the privacy of those accused of cohabitation.
The National Commission on Violence Against Women (Komnas Perempuan) noted that gender-based violence of this nature often led women to experience excessive stress, depression, mental health disorder, sometimes even resulting in suicide attempts.
Under the bill, the prosecution of this offense can be initiated by a complaint filed by the spouse, parents and children. With written approval from family members, village heads may also file a complaint.
Consequently, this may serve to legitimize more arbitrary police and vigilante raids based on “mere suspicion” of any family member. This may also potentially empower abusive family members to accuse survivors of domestic violence, of a crime.
Since same-sex marriage is not legal in Indonesia, lesbian, bisexual and transgender women are at risk if they decide to cohabit as couples. Furthermore, this provision will also threaten women in remote areas who could only afford to have religious and/or adat (customary) marriage.
First, the criminalization of cohabitation constitutes an arbitrary and unlawful interference with people’s privacy. The right to privacy is protected under international human rights law, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) by which Indonesia is bound.
The right to privacy is central to the protection of human dignity and forms the basis of any democratic society. It supports and reinforces other rights, including the right of women to freely choose when or if she will marry.
The UN Human Rights Committee, the supervisory body for the ICCPR, has made clear that states have an obligation to adopt legislative measures to give effect to the prohibition against interferences with and attacks against the right to privacy – and to take measures to ensure the protection of this right.
Second, the criminalization of cohabitation violates other human rights guaranteed by the ICCPR, including the right to family life, a right that, as international human rights law acknowledges, may be exercised and enjoyed by two cohabiting partners without the need for them to be married to one another.
Third, the criminalization of cohabitation would constitute prohibited discrimination and a violation of the right to “equality before the law” and “equal protection of the law without discrimination for all” under international human rights law binding on Indonesia.
The House must therefore reject this bill because of its gender discriminatory nature and arbitrary interference with the right to privacy.
To download in Bahasa Indonesia , click here.
This article was first published in The Jakarta Post, available at: https://www.thejakartapost.com/academia/2020/09/05/consenting-adults-living-together-is-not-a-crime.html










