May 26, 2017 | News
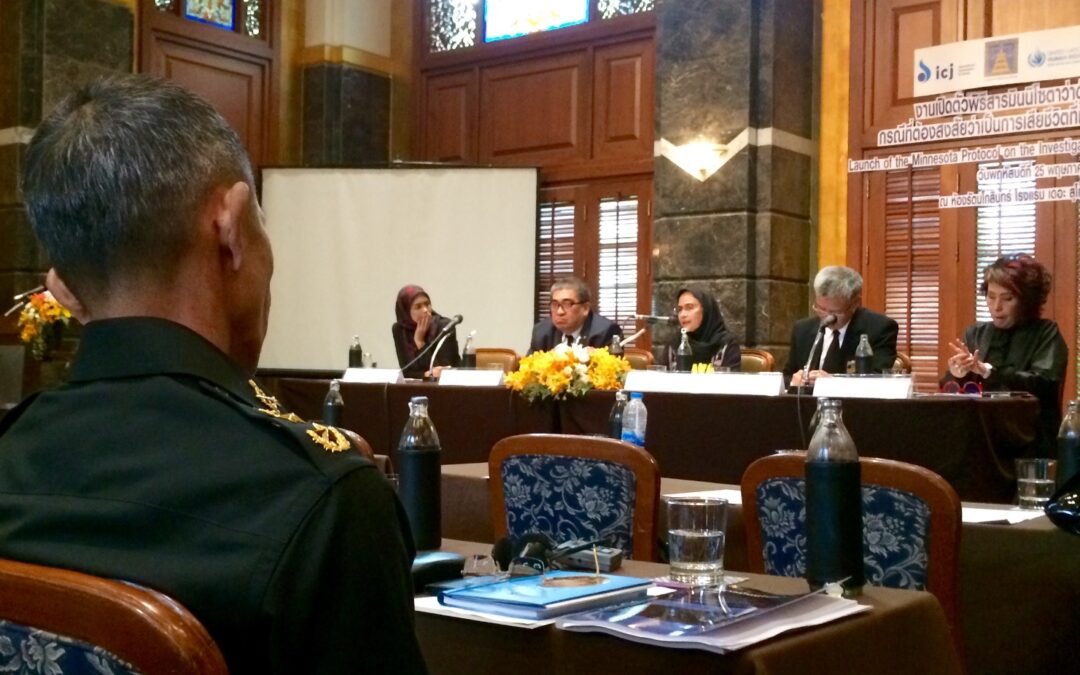
The ICJ has launched the revised Minnesota Protocol on the Investigation of Potentially Unlawful Death (2016) in Thailand, together with the Thai Ministry of Justice, the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights and the German Embassy in Bangkok.
The launch on Thursday coincided with a parallel launch of the revised Minnesota Protocol by the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights in Geneva.
The Minnesota Protocol is a companion document to the UN Principles on the Effective Prevention and Investigation of Extra-legal, Arbitrary and Summary Executions (1989), and sets a common standard of performance in investigating potentially unlawful death and a shared set of principles and guidelines for States, as well as for institutions and individuals who play a role in death investigations.
The launch was attended by representatives of the Ministry of Justice, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Royal Thai Police, the Office of the Attorney General, the Ministry of Defence, and the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand.
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia and member of the Forensics and Legal Working Groups which assisted with the revision the Minnesota Protocol, opened the event for the ICJ by commending Thailand for hosting the first national launch of the revised Minnesota Protocol.
“Investigations play a key role in accountability by upholding the right to life which is guaranteed by Article 6 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which Thailand is a State Party,” said Abbott. “All over the world we witness impunity in cases of unlawful death because either investigations do not take place or are inadequate and non-compliant with international law and standards.”
“The Minnesota Protocol makes it clear that investigations must be prompt, effective and thorough, as well as independent, impartial and transparent, and we expect that the revised Minnesota Protocol will help Thailand and other States to meet that obligation,” added Abbott. “The ICJ wishes to take this opportunity to reaffirm our long-standing commitment to the Thai authorities to assist them in efforts to implement Thailand’s international human rights obligations.”
The other speakers at the launch were:
- Ms Pitikarn Sitthidech, Director General, Rights and Liberties Protection Department, Ministry of Justice
- Ms Katia Chirizzi, Deputy Head, Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), Regional Office for Southeast Asia
- Prof. Stuart Casey-Maslen, Project Manager of the revision of the Minnesota Protocol, University of Pretoria
- Dr Pornthip Rojanasunan, Adviser, Central Institute for Forensic Science (CIFC) and member of the Expert Advisory Panel of the revision of the Minnesota Protocol
- Ms Angkhana Neelapaijit, Commissioner, National Human Rights Commission of Thailand and Victim Representative
- Mr Kittinan Thatpramuk, Deputy Director General, Department of Investigation, Office of the Attorney General
- Pol.Lt.Col. Payao Thongsen, Commander, the Special Criminal Cases Office 1, Department of Special Investigation (DSI)
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, t: +66 94 470 1345; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Universal-Minnesota Protocol-Advocacy-2017-ENG (PDF, English)
Universal-Minnesota-Protocol-Advocacy-2017-THA (PDF, Thai)
Universal-Minnesota Protocol-Advocacy-2017-BUR (PDF, Burmese)

May 4, 2017 | News
Thailand should immediately end the practice of arbitrarily detaining persons in unofficial places of detention said the ICJ today.
The statement came after it was revealed that human rights lawyer, Prawet Prapanukul, who had been arbitrarily detained for five days at a detention facility inside a military base in Bangkok, finally appeared and was charged at the Bangkok Criminal Court on 3 May 2017.
During the morning of 29 April 2017, military officers invoked Head of National Council for Peace and Order (NCPO) Order 3/2015 to arrest Prawet Prapanukul and search his residence in Bangkok, seizing a number of items located at the property including computers, phones and hard-drives.
The whereabouts of Prawet Prapanukul were unknown until the afternoon of 3 May 2017, when Prawet Prapanukul contacted several lawyers including Thai Lawyers for Human Rights (TLHR) and said he had been held at the Nakhon Chaisri temporary remand facility inside the 11th Army Circle military base in Bangkok.
“Prawet Prapanukul’s five-day incommunicado detention without being brought before the courts or access to legal counsel amounts to an arbitrary detention in violation of his rights under international law and consequently he should be provided with appropriate reparation,” said Kingsley Abbott, the ICJ’s Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia.
“To ensure the protection of all persons while in detention, Thailand has a duty to detain people in officially recognized places of detention, to have their names and places of detention made available to interested persons and to bring them before a court without delay within 48-hours,” he added.
According to TLHR, on 3 May 2017, Prawet Prapanukul was charged with ten counts of the highly restrictive crime of lese majeste (article 112 of the Criminal Code), three counts of a sedition-like offence (article 116 of the Criminal Code), and violation of article 14(3) of the Computer Crime Act.
The ICJ has previously raised concerns about abusive recourse to these laws.
Pursuant to article 91(3) of the Thai Criminal Code, it is possible that, if convicted of these charges, Prawet Prapanukul could receive a maximum sentence of 50-years imprisonment.
“Freedom of expression, as protected under international law, must never be criminalized. In any event, imprisonment is never a proportionate penalty for the exercise of free expression, let alone the unthinkable possibility of 50-years, which would set a new recorded record for a sentence for lese majeste,” Abbott said.
On 25 April 2017, after reviewing Thailand’s compliance with its obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which Thailand is a State Party, the Human Rights Committee, the international expert body charged with supervising the implementation of the ICCPR, issued its Concluding Observations in which it noted that in Thailand “individuals were reportedly often detained without charge and held incommunicado at undisclosed places of detention for periods of up to seven days, with no judicial oversight or safeguards against ill-treatment and without access to a lawyer.” The Human Rights Committee observed that Thailand should immediately release all victims of arbitrary detention and provide them with full reparation.
“The fact that Thailand arbitrarily detained Prawet Prapanukul at a military facility just five days after the Human Rights Committee issued its Concluding Observations criticizing Thailand’s practice of detaining people incommunicado in undisclosed placed of detention demonstrates a worrying contempt for its international human rights obligations as pointed out by the Committee,” Abbott added.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, t: +66 94 470 1345 ; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Thailand-Prapanukul-detention-News-2017-ENG (full text with background, in PDF)
Thailand-Prapanukul-detention-News-2017-THA (Thai version, in PDF)

Feb 13, 2017 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights (TLHR) have made a submission to the UN Human Rights Committee in view of its forthcoming review of the implementation of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights by Thailand.
In their submission, the ICJ and TLHR have brought to the Committee’s attention their concerns in relation to the following issues:
- Constitutional and legal framework within which the Covenant is implemented;
- States of emergency;
- Right to life and prohibition of torture and cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment;
- Right to liberty and security of the person, treatment of persons deprived of their liberty, right to a fair trial and independence of judiciary; and
- Freedoms of expression and association and right to peaceful assembly.
Thailand-ICCPR Submission ICJ-TLHR-Advocacy-Non legal submissions-2017-ENG (Full text in PDF)
Thailand-ICCPR Submission ICJ-TLHR-Advocacy-Non legal submissions-2017-THA (Thai version, in PDF)

Sep 23, 2016 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ, speaking at the UN Human Rights Council, highlighted concerns with criminalization of political gatherings, arbitrary detention, use of military for law enforcement, and trials of civilians before military courts, in Thailand.
The statement was made during discussion of the outcome of the Second Universal Periodic Review (UPR) of Thailand.
While congratulating Thailand on completion of the UPR, the ICJ oral statement continued as follows:
However, the ICJ is disappointed that several key recommendations concerning restrictions of civil and political rights in the country did not enjoy the support of Thailand.
The interim Constitution, put in place by the military government after the May 2014 coup, remains in force. Article 44 gives the government sweeping, unchecked powers inconsistent with the fundamental pillars of the rule of law and human rights.
The military government has issued numerous orders and announcements under the interim Constitution, including some that criminalize political gatherings, allow arbitrary detention for up to seven days without charge, and provide military officers broad powers of law enforcement.
At least 1,811 civilians have faced proceedings in military courts contrary to international law and standards, many merely for exercising their rights to free expression and peaceful assembly.
Thailand did not accept any of the recommendations to remove these restrictions on the rule of law and human rights.
While the ICJ welcomes the Order of 12 September 2016 ending the practice of prosecuting civilians in military courts for crimes committed after that date, approximately 500 civilian cases remain in military courts.
The ICJ is also concerned that in July the government charged three human rights defenders with criminal defamation for raising allegations of torture in the deep South.
The ICJ urges Thailand to accept and implement recommendations relevant to:
- revoking the interim Constitution and all NCPO orders and announcements that are contrary to the rule of law and respect for human rights;
- transferring all pending civilian cases to civilian courts and set aside the convictions of all civilians prosecuted in military courts since the 2014 coup; and
- ending all harassment of human rights defenders in Thailand.
The statement may be downloaded in English and in Thai in PDF here:
thailand-hrc33-upr-advocacy-non-legal submission-2016-eng
thailand-hrc33-upr-advocacy-non-legal-submission-2016-tha
Sep 20, 2016 | News
The ICJ expresses its disappointment with today’s verdict criminalizing the work of human rights defender, Andy Hall, and calls upon Thailand to decriminalize defamation and amend the Computer Crime Act in line with international standards protecting freedom of expression.
This morning, Thailand’s Southern Bangkok Criminal Court found Andy Hall guilty of defaming a Thai fruit processing company under Article 328 of the Thai Criminal Code and violation of Article 14(1) of the Computer Crime Act, and sentenced him to a fine of THB 200,000 (USD$ 5,700) reduced to THB 150,000 (USD $4,300); and four years imprisonment, reduced to three years and suspended for two years.
Andy Hall has said he will appeal the verdict.
“Human rights defenders such as Andy Hall have the right to exercise freedom of expression in advocating for the protection and realization of human rights – a right that Thailand has a duty to protect,” said Kingsley Abbott, Senior International Legal Adviser at the ICJ.
“Unfortunately, there are numerous examples of criminal defamation and the Computer Crime Act being used against human rights defenders in Thailand, a practice that must end, including through a substantial reform of these laws,” he added.
The ICJ and Lawyers Rights Watch Canada submitted a joint amicus curiae brief in the proceedings, arguing that the imposition of harsh penalties such as imprisonment or large fines on a human rights defender risk having a ‘chilling effect’ on the exercise of freedom of expression, which Thailand is bound to protect pursuant to its international legal obligations.
The ICJ anticipates the arguments contained in the joint amicus will be considered on appeal.
“It is also disappointing that the Court did not appear to take into account the recent decision of the Phuket Provincial Court in the Phuketwan case, which found that the Computer Crime Act was not intended to be used in cases of alleged defamation,” said Abbott.
On 1 September 2015, the Phuket Provincial Court acquitted two journalists of criminal defamation and violations of the Computer Crime Act after the Royal Thai Navy complained the journalists defamed it when, on 17 July 2013, the journalists reproduced a paragraph from a Pulitzer prize-winning Reuters article that alleged “Thai naval forces” were complicit in human trafficking.
The criminal defamation proceedings brought against Andy Hall are among several that have been brought against human rights defenders in Thailand in recent years.
Others examples include the charges laid against activists Pornpen Khongkachonkiet, Somchai Homloar and Anchana Heemina in July 2016 for raising allegations of torture in the deep South; and those brought against activists protesting various development projects in Thailand which are allegedly having an adverse impact on communities.
Background
Today’s case is one of four criminal and civil proceedings (two criminal and two civil) a Thai fruit processing company, Natural Fruit Company Ltd., has brought against Andy Hall in relation to the report of a Finnish NGO, Finnwatch, published in January 2013, called Cheap Has a High Price.
Andy Hall’s research was included in the report which alleged that labour rights violations were taking place at Natural Fruit Company Ltd., whose employees included migrant workers from Myanmar.
In September 2015, a Thai Appeal Court upheld the dismissal of the other criminal defamation proceeding Natural Fruit Company Ltd. brought against Andy Hall. That proceeding is currently before the Supreme Court. Two civil proceedings are also before the Thai courts but have been suspended pending resolution of the two criminal proceedings.
The use of criminal defamation laws, carrying penalties of imprisonment, against human rights defenders reporting on alleged human violations, constitutes a violation of Thailand’s obligations under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), to which it is a state party.
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-eng (full text in PDF)
thailand-verdict-andy-hall-case-news-press-release-2016-tha (full text in Thai, PDF)
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; e: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, t: +66 9 4470 1345, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org