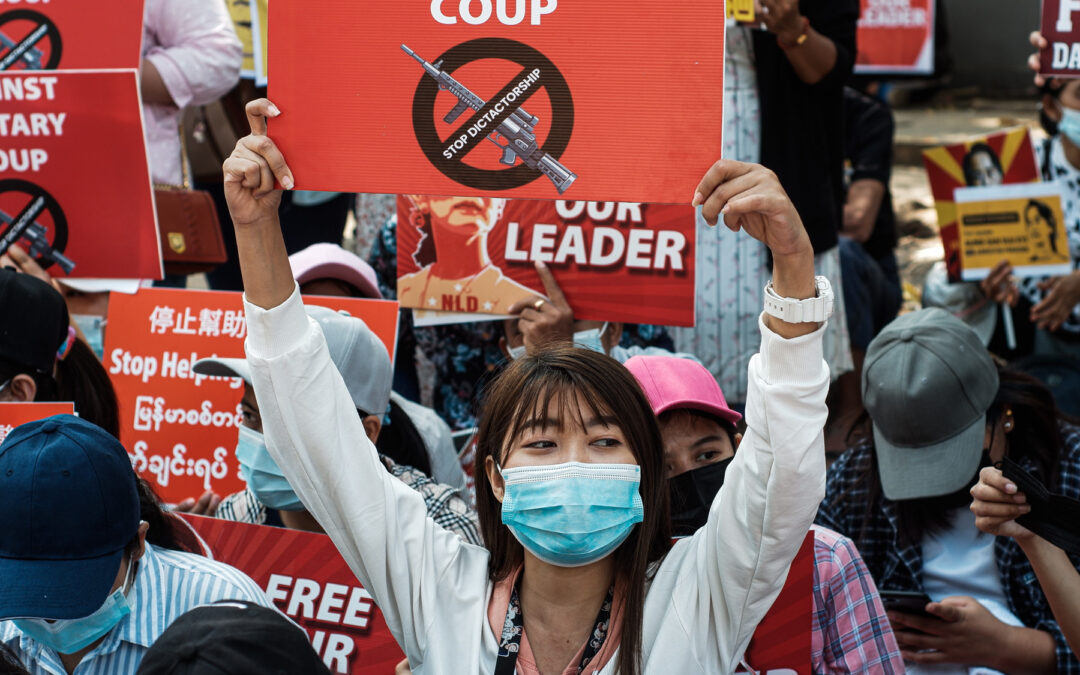
Mar 2, 2021 | News
Myanmar’s military government should reverse its post-coup d’etat revisions of legal protections for human rights in the country, the ICJ and Human Rights Watch said today.
Myanmar’s State Administration Council (SAC), appointed by the country’s military after it overthrew the elected civilian government on February 1, 2021, has dictated key revisions to the country’s legal system that criminalize even peaceful protests, and enable violations of the right to privacy and arbitrary arrests and detention. The changes were made through orders signed by the commander-in-chief, Sr. Gen. Min Aung Hlaing, on behalf of the SAC, and outside the parliamentary process.
“As Myanmar’s military increasingly relies on excessive force and intimidation to quell peaceful protests against its coup, it is trying to give a veneer of legality to its actions by subverting existing protections in the legal system.”
“These revisions, which violate the principle of legality and Myanmar’s international obligations, in no way excuse or legitimate the widespread violations of human rights now taking place in Myanmar.”
– Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Director of Law and Policy.
Since the coup on February 1, the military junta has:
- arbitrarily suspended sections of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017), removing basic protections, including the right to be free from arbitrary detention and the right to be free of warrantless surveillance and search and seizure;
- amended the Penal Code to create new offenses and expand existing offenses to target those speaking critically of the coup and the military, and those encouraging others to support the “Civil Disobedience Movement”;
- amended the Ward and Tract Administration Law to reinstate the requirement to report overnight guests;
- amended the Code of Criminal Procedure to make the new and revised offenses non-bailable and subject to warrantless arrest; and
- amended the Electronic Transactions Law to prevent the free flow of information and criminalize the dissemination of information through cyberspace, including expression critical of the coup or the acts of the junta.
Under international legal standards, any restrictions on human rights must be strictly necessary to protect a legitimate interest and proportionate to the interest being protected, even in times of public emergency or for legitimate national security purposes (conditions that do not apply in Myanmar currently). The orders issued by the SAC fail to meet that standard, as they will arbitrarily interfere with the exercise of rights protected under international law, including freedom of expression, freedom of peaceful assembly, the right to liberty, and the right to privacy. Certain rights, such as the rights to bodily integrity and nondiscrimination, are not subject to restriction.
“By stripping the people of Myanmar of their basic rights, the military is once again demonstrating its disdain for international human rights protections,” said Linda Lakhdhir, Asia legal advisor at Human Rights Watch. “The junta cannot justify the oppression of Myanmar’s inhabitants through the unilateral creation of arbitrary new laws.”
Contact
Osama Motiwala, ICJ Asia-Pacific Communications Officer, e: osama.motiwala(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org
Analysis of Legal Code Changes
Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017)
On February 13, the State Administration Council arbitrarily suspended sections 5, 7 and 8 of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens, eroding basic protections for individuals.
Section 5 required the presence of two witnesses whenever the police enter a residence for the purposes of search or seizure “to ensure that there is no damage to the privacy or security of the citizen.” The suspension of that protection significantly raises the risk of abuses during searches and arrests.
Section 7 required a court order for any detention of more than 24 hours. Suspension of the provision will facilitate violations of international law, which provides that any person detained on a criminal charge be promptly taken before a judge.
Section 8 provided protections of an individual’s right to privacy by prohibiting search and seizure, surveillance, spying, or any investigation affecting the privacy, security, and dignity of the individual without a court order – protections that the junta has removed. Under international law no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with their privacy, family, home or correspondence.
Penal Code Amendments
On February 14, the SAC announced amendments to the Penal Code that could lead to criminal liability for thousands of demonstrators exercising their rights to free expression of their views, and anyone publicly criticizing the military coup d’etat through any means.
The SAC inserted a new provision, section 505A, that could be used to punish comments regarding the illegitimacy of the coup or the military government, among others. The new section would criminalize comments that “cause fear,” spread “false news, [or] agitates directly or indirectly a criminal offense against a Government employee.” Violation of the section is punishable by up to three years in prison.
Section 505(a) previously made it a crime to publish or circulate any “statement, rumor or report” “with intent to cause, or which is likely to cause, any officer, soldier, sailor or airman, in the Army, Navy or Air Force to mutiny or otherwise disregard or fail in his duty.” It has been replaced with much broader language clearly designed to penalize those encouraging members of the civil service of the security services to join the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Under the revised provision, any attempt to “hinder, disturb, damage the motivation, discipline, health and conduct” of the military personnel and government employees and cause their hatred, disobedience or disloyalty toward the military and the government is punishable by up to three years in prison.
The SAC also significantly broadened the “treason” provisions in section 124 of the Penal Code. Section124A, which already criminalized comment that “bring into hatred or contempt” or “excite disaffection against” the government, was expanded to include comments relating to the defense services and defense services personnel, effectively criminalizing any criticism of the military or military personnel. Violation of the section is punishable by up to 20 years in prison.
The newly added section 124C imposes a prison term of up to 20 years on anyone who intends to “sabotage or hinder the performance of the Defense Services and law enforcement organizations who are engaged in preserving the stability of the state.” This provision would criminalize efforts to encourage security forces to join the Civil Disobedience Movement or permit unauthorized protests.
Finally, under section 124D, a person can be sentenced up to seven years in prison if they hinder a government employee from carrying out their duties. This provision is so broad that any actions of protesters could be interpreted as preventing security personnel or defense service officers from performing their duty.
Code of Criminal Procedure
On February 14 the junta amended the Code of Criminal Procedure Amendment Law to make offenses under sections 505A, 124C and 124D non-bailable and subject to arrest without a warrant.
Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21)
The amendments to the Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21) further increase the military’s ability to conduct surveillance on people’s movements, in particular on human rights defenders seeking shelter away from their own homes. Amendments to section 17 of the Act require all overnight guests from other wards or villages to be reported to the ward or village tract administrator, who are authorized by section 13 to “take action” against any who “failed to inform the guest list.” Section 27 reintroduces criminal sanctions for failing to report overnight guests. Such provisions existed under previous military governments and were deeply resented.
Electronic Transactions Law (Law No 7/ 2021)
On February 15, the junta also amended the Electronic Transactions Law to include, among others, provisions that had been proposed in the draft Cybersecurity Law.
As was true under that much-criticized draft law, the amended Electronics Transactions Law permits government agencies, investigators, or law enforcement to access personal data in relation to “cyber-crimes,” “cyber misuse” or any criminal investigation.
The amendments also include several provisions (articles 38(d) and (e)) that provide criminal penalties for “unauthorized” access to online material and that could be used to prosecute whistle blowers, investigative journalists, or activists who use leaked material for their work.
Section 38B criminalizes “obtaining, disclosing, using, destroying, modifying, disseminating, or sending someone’s personal data to anyone else without approval,” with one to three years in prison. While the protection of the right to privacy online is important, this provision goes well beyond legitimate protections on privacy and imposes arbitrary restrictions on freedom of expression.
In particular, “personal data” is defined in a manner so broad as to include virtually any information associated with a person. The law is therefore impermissibly vague and overbroad, as it would likely prevent even the disclosure of information about anyone involved in alleged human rights violations, including by human rights defenders and journalists.
Section 38C criminalizes the creation of “misinformation or disinformation with the intent of causing public panic, loss of trust or social division on cyberspace,” and provides for imprisonment of one to three years in addition to fines. These provisions are similarly vague and overbroad and unnecessarily and disproportionately limit the exercise of expression online, including criticism of the coup and the military junta.
***
Download the full statement here.

Jul 5, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today joined 91 other NGOs in calling on the UN Human Rights Council to act in response to the downward spiral for human rights in Venezuela.
The joint statement was delivered on behalf of the group by Human Rights Watch during a general debate (check against delivery).
“Spiralling downwards with no end in sight”: That’s how a group of UN Special Procedures, including the Special Rapporteurs on health, adequate housing, extreme poverty and food categorized Venezuela in January of this year. This is also the title of a report released by the OHCHR on June 22, which paints a devastating picture of arbitrary detentions and extrajudicial killings coupled with a severe shortage of food and basic medicines.
One Venezuelan mother interviewed by OHCHR said: “I have a little baby that cries and cries because I can´t feed her. The baby’s milk formula costs 3 million Bolivars and my husband only makes 1.2 million a month. (…) My neighbours told me that if I don’t vote for the Government they will take the food, the cash bonus and my house from me. They control the electoral authority, so they know for which party you vote.”
The UN Human Rights Council can no longer look away. Venezuela has spiralled into a human rights and humanitarian crisis that demands urgent action. The crackdown on dissent continues. The population has lost an average of 11 kilos in 2017. Most Venezuelans go to bed hungry, and according to the UNHCR, more than 1.5 million Venezuelans have fled the country, for reasons including political persecution, violence, and the ongoing humanitarian crisis. As a result, a 2,000 percent increase in asylum applications has been recorded across Latin America since 2014, and hundreds of thousands remain in an irregular situation, which increases their vulnerability.
Today’s joint statement delivered by Peru on behalf of 53 States adds to the chorus of international concern. The Human Rights Council also needs to step up and address the human rights violations suffered by the Venezuelan people at the hands of a member of this Council. We encourage continued reporting by the High Commissioner, and hope that today’s joint statement paves the way for the international investigation that the High Commissioner has called for and which is so desperately needed.
Acceso a la Justicia
Acción Solidaria
ACCSI Acción Ciudadana Contra el SIDA
Action for Solidarity
African Centre for Democracy and Human Rights Studies
ALAPLAF
Ana Belloso
ASOADNA
Asociación Civil Fuerza, Unión, Justicia, Solidaridad y Paz (FUNPAZ)
Aula Abierta
Canada Venezuela Democracy Forum
Cátedra de Derechos Humanos de la Universidad Centrooccidental Lisandro Alvarado
Center for Justice and International Law
Centro de Acción y Defensa por los Derechos Humanos – Cadef
centro de Derechos Humanos de la Universidad Metropolitana (CDH-UNIMET)
Centro de Derechos Humanos, Universidad Católica Andrés Bello
Centro de Documentación en Derechos Humanos “Segundo Montes Mozo S.J.” (CSMM)
Centro de Formación para la Democracia (CFD Venezuela)
Centro de Justicia y Paz – CEPAZ
Centro de Promoción y Defensa de los Derechos Sexuales y Reproductivos – PROMSEX
Centro para la Paz y los DDHH de la Universidad Central de Venezuela
Centro para la Paz y los DDHH Universidad Central de Venezuela
Centro Regional de derechos Humanos y Justicia de Genero: Corporación Humanas
Cisfem
CIVICUS
Civilis Derechos Humanos
Clínica Jurídica de Migrantes y Refugiados de la Universidad Diego Portales
Codevida
Comisión de Derechos Humanos de la Facultad de Ciencias Jurídicas y Políticas de la Universidad del Zulia
Comisión de Derechos Humanos de la Federación de Colegios de Abogados de Venezuela del Estado Tachira
Comisión para los Derechos Humanos del estado Zulia, Codhez
Comisión para los Derechos Humanos y la Ciudadanía (CODEHCIU)
COMITE POR UNA RADIOTELEVISIÓN DE SERVICIO PÚBLICO
Conectas Direitos Humanos
Convite AC
Coordinadora Nacional de Derechos Humanos
Defensa y Justicia Carabobo
Defiende venezuela
Dejusticia
Epikeia, Observatorio Universitario de Derechos Humanos
Espacio Público
EXCUBITUS derechos humanos en educacion
FADNNA
Federación interamericana de Abogados capitulo Venezuela seccional Anzoategui
Foro Penal
Franciscans International
Fundacion Aguaclara
Fundación Espacio Abierto
FUNDACION ETNICA INTEGRAL
Fundación Niños, Niñas y Adolescentes
Fundación para el Debido Proceso (DPLF)
Fundamujer
Humano Derecho Radio Estacion
Human Rights Watch
Iniciativa Por Venezuela
Institute on Race, Equality and Human Rights
International Commission of Jurists
International Movement Against All Forms of Discrimination and Racism (IMADR)
International Service for Human Rights
Ipys Venezuela
Juventud Unida en Acción
Laboratorio de Paz
Madres de Soacha (Colombia)
María Estrella de la Mañana
Maria Eugenia
Misión Scalabriniana Ecuador
Monitor Social A.C. (Venezuela-Edo. Nva Esparta)
Movimiento Vinotinto
Mulier
Observatorio de Derechos Humanos de la Universidad de Los Andes
Observatorio Venezolano de Conflictividad Social (OVCS)
Observatorio Venezolano de la Salud
Organización StopVIH
PADF Honduras
Padres organizados de Venezuela
Paz y Esperanza
Pedro Luis Echeverria
PEDRO NIKKEN
Prepara Familia
Promoción Educación y Defensa en DDHH (PROMEDEHUM)
Revista SIC del Centro Gumilla
Robert F Kennedy Human Rights
Seguridad en Democracia (SEDEM)
Sin Fronteras IAP
Sinergia, Red Venezolana de Organizaciones de la Sociedad Civil
Thais Parra
Transparencia Venezuela
UCV
Una Ventana a la Libertad
Unión Afirmativa de Venezuela
Union Vecinal para la Participación Ciudadana A.C
West African Human Rights Defenders Network
World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT)

May 18, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Speaking today at a special session of the UN Human Rights Council, the ICJ joined calls for an independent international inquiry into the use lethal and other force by Israeli security forces in Eastern Gaza.
The statement read as follows:
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) deplores apparent violations of international law by Israeli security forces during the past six weeks in Eastern Gaza near the border with Israel, in relation to demonstrations by Palestinians.
The ICJ is concerned at the many killings and serious injuries associated with the excessive, unjustified or otherwise unlawful use of force, including the killing of a number of children.
The ICJ recalls that international human rights law permits use of lethal force only when strictly necessary to protect life. The ICJ understands that Israel has taken the position that only the international law of armed conflict, and not international human rights law, was applicable, and that all lethal force used against protestors was justified. The ICJ insists that human rights law – and specifically, standards on the use of force in law enforcement contexts – was indeed applicable, and that the use of lethal force was in the circumstances wholly unjustified.
Excessive force, including lethal force, has apparently been used against unarmed persons who do not pose a threat to life. Irrespective of legal regime, such use of force is manifestly inconsistent with the principles of necessity and proportionality.
The ICJ joins the call for this Council to establish an independent Commission of Inquiry or similar investigation, to ensure accountability for serious violations of international law.
Update: The session concluded with the adoption (29 yes, 2 no, 14 abstained) by the Council of a resolution establishing a Commission of Inquiry.

Mar 27, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
On 27 March 2018, the ICJ, Thai Lawyers for Human Rights (TLHR) and Cross Cultural Foundation (CrCF) made a joint follow-up submission to the UN Human Rights Committee on Thailand’s implementation of the Committee’s prioritized recommendations.
On 23 March 2017, during its 119th Session, the Human Rights Committee adopted its concluding observations on the second periodic report of Thailand under article 40 of the International Covenant of Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR).
Pursuant to its rules of procedure, the Committee requested Thailand to provide a follow up report on its implementation of the Committee’s recommendations made in paragraphs 8 (constitution and legal framework) 22 (extrajudicial killings, enforced disappearances and torture) and 34 (conditions of detention) of its concluding observations by 23 March 2018. To date, the Thai authorities are yet to file their follow-up report with the Committee.
In their joint submission to the Human Rights Committee, the ICJ, TLHR and CrCF detailed their concerns in relation to Thailand’s failure to implement the Committee’s recommendations in paragraphs 8 and 22 of its concluding observations. The three organizations’ submission focuses on their concerns arising from the following:
Constitution and legal framework
- Orders by the Head of the National Council for Peace and Order (‘HNCPO’); and
- Escalation in use of HNCPO Order No. 3/2558 to restrict fundamental freedoms.
Extrajudicial killings, enforced disappearances and torture
- Allegations of widespread use of torture and other ill-treatment;
- Incommunicado detention;
- Southern Border Provinces; and
- Threats and reprisals against persons working to bring to light cases of alleged torture, ill–treatment and enforced disappearance.
Read also
ICJ and Thai Lawyers for Human Rights, Joint submission to the UN Human Rights Committee, 13 February 2017
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser for Southeast Asia, e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Thailand_Joint-Follow-up-Human-Rights-Committee-Submission-march-2018 (Full submission in ENG, PDF)
Thailand-Follow up HRC-Advocacy-Non legal submission-2018-THA (Thai version, in PDF)

Dec 13, 2016 | News
The ICJ and Human Rights Commission of Pakistan (HRCP) urge the Pakistani authorities to fully engage with the UN human rights body by answering its questions comprehensively.
The call follows the recent adoption by the United Nations Human Rights Committee of a document raising a multiplicity of concerns about Pakistan’s human rights record.
“It is encouraging to see Pakistan’s increased engagement with United Nations human rights mechanisms in recent years”, said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Asia Director.
“But it is important that the Government does not stop here and now takes the additional constructive step of answering all the Committee’s questions truthfully and honestly,” he added.
In November 2016, during its 118th session, the Human Rights Committee adopted a document known as a List of issues in relation to Pakistan’s compliance with the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), in which the Committee asked multiple questions about the country’s human rights record, including:
- Fair trial concerns as a result of the expanded jurisdiction of military courts following the introduction/adoption of the 21st Amendment to the Constitution, including the criteria for and the process of selecting cases to be tried by military courts, the qualifications of judges presiding over those courts and their proceedings;
- Reintroduction of the death penalty and the wide scope of its application, including the mandatory death sentence for “blasphemy”;
- Broad and vaguely defined “blasphemy offences”, their disproportionate use against individuals belonging to religious minorities; the large number of “blasphemy” cases instituted on the basis of false accusations; and the lack of mechanisms to protect judges who hear “blasphemy” cases and those accused of blasphemy from intimidation and threats;
- Rights of Ahmadis, including their “right to profess, practice and propagate” their religion without interference;
- Repatriation of Afghan refugees, including information on the adoption of a draft national refugee law and a comprehensive policy on the voluntary repatriation and management of Afghan nationals;
- Rights of women, including steps taken by the Government to prevent and punish persistent violence (sexual and otherwise) against women, including so-called honour killings;
- Torture and other ill-treatment, extrajudicial killings, and enforced disappearances, including steps taken by the Government to implement the Supreme Court’s judgment in the Muhabbat Shah case, which held military authorities responsible for the enforced disappearance of at least 28 people from a Malakand internment centre.
This is the first time Pakistan’s human rights record is being reviewed by the Human Rights Committee, the treaty body that monitors implementation of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights by its State parties, since Pakistan ratified the Covenant in 2010.
The next step in the review process is for Pakistan to respond to the questions framed in the List of Issues.
The Human Rights Committee will undertake a comprehensive review Pakistan’s compliance with and implementation of the ICCPR and adopt concluding observations in July 2017.
“It is of the utmost importance to Pakistan to derive greater benefit from its engagement with the UN human rights mechanisms by making a sincere effort to answer the concerns of the Committee,” said I A Rehman, Secretary General of HRCP.
Background
Pakistan ratified the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) in June 2010. Following ratification/accession, every state party to the ICCPR is required to submit an initial “state report” containing information on the implementation of each provision of the treaty.
Pakistan submitted its initial state report to the Human Rights Committee in October 2015.
In light of the information provided in the State report, as well as information received from civil society, the Human Rights Committee then prepares a List of Issues containing particular issues of concern to the Committee, and asking whatever questions it sees fit in light of those concerns.
The answers provided by the State party to those questions, as well as other information submitted by civil society and others form the basis of the “review” of the State’s compliance with the treaty.
The State is not obligated to reply to the List of Issues in advance of the review session, but in practice most do.
The State replies are presented to the Committee at the beginning of the review and are the starting point for the interactive dialogue between the Committee and the State under review.
During the review, the Committee meets with State representatives who present answers to the List of Issues and respond to the Committee’s questions.
At the end of the session, the Committee adopts Concluding Observations, which highlight the Committee’s concerns and make recommendations to the State on improving the implementation of the ICCPR.
Pakistan’s ICCPR review is scheduled to take place in July 2017.
Contact
Sam Zarifi, ICJ Asia Pacific Regional Director (Bangkok), t: +66 807819002; email: sam.zarifi(a)icj.org
Pakistan-list-of-issues-advocacy-2016-eng (in PDF)