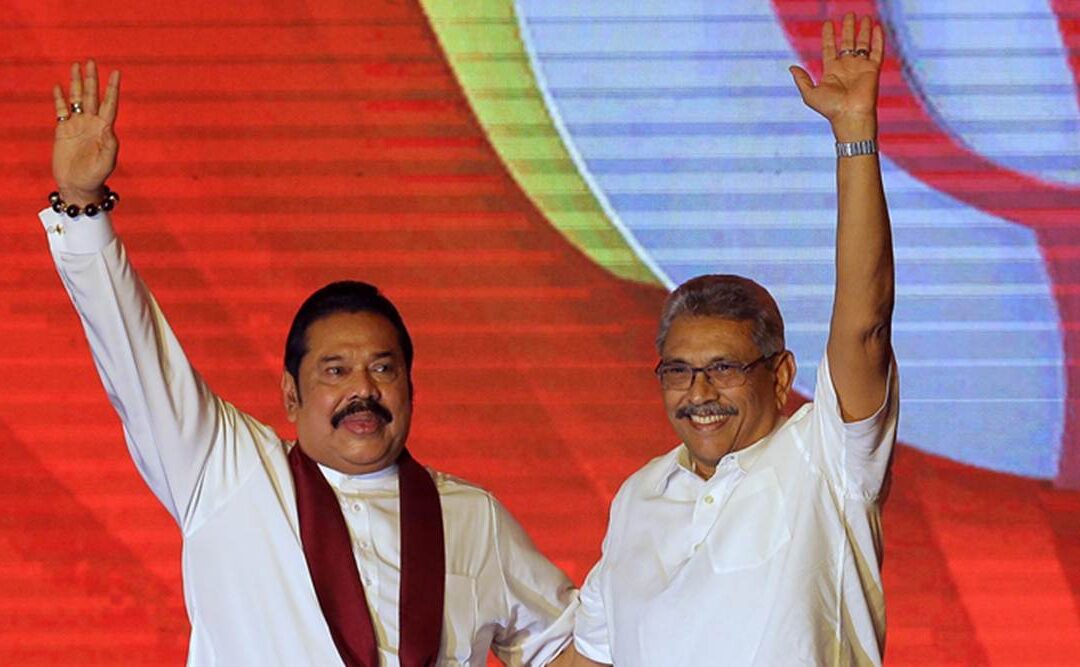
Sep 14, 2020 | News
The Sri Lankan parliament should reject the Sri Lankan Government’s efforts to amend the country’s constitution to provide unfettered powers to the President while encroaching on the powers of the legislature and infringing upon the independence of the judiciary, said the ICJ today.
“The proposed 20th Amendment, which bestows an already powerful executive president with additional powers with no effective checks on him, essentially placing him above the law,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General. “These amendments would tilt the balance of State power heavily on the side of the executive and in particular on a single person.”
The proposed 20th Amendment to the Constitution bill rolls back most of the reforms brought about by the 19th Amendment to the Constitution, the passage of which the UN Human Rights Council welcomed as “promoting democratic governance and oversight of key institutions”.
The 19th amendment, adopted in 2015, had imposed certain limits to the Executive President’s authority and powers, including in respect of terms of the office of President, the capacity to dissolve Parliament and to fast-track legislation. It also removed the blanket immunity the President enjoyed from legal proceedings. Critically, it had established a Constitutional Council which restrained the President’s discretion in appointing key governmental actors including in the judiciary, the Attorney General and the Inspector General of Police.
The ICJ notes that the 20th amendment appears to reproduce much of the regressive features of the old 18th amendment, which the 19th amendment had been brought about to correct.
“Sri Lanka’s Executive branch has a poor record of respecting human rights and the rule of law, and the 19th Amendment was an effort to impose the checks and balances necessary for the rule of law,” said Sam Zarifi. “The constitutional changes being proposed would take the country back to the dark days of Executive impunity.”
“We are particularly concerned that these changes would undermine the independence of the judiciary, as the President would have unfettered discretion to appoint the superior judiciary, including the Chief Justice, the President and Judges of the Court of the Appeal, and to control the Judicial Service Commission,” said Sam Zarifi.
The JSC is the body entrusted with the power to appoint, promote, transfer exercise disciplinary control and dismiss judicial officers of the subordinate courts. The changes would also grant the President the power to nominate members of the Judicial Service Commission (JSC) other than its Chairman which is ex officio, the Chief Justice.
The UN Basic Principles on the Independence of the Judiciary states that “Any method of judicial selection shall safeguard against judicial appointments for improper motives.”
Under international standards and recommendations of the UN Special Rapporteur on the Independence of the Judiciary, appointments to the judiciary should not be vested solely with the executive.
A judicial appointment process which gives the President full discretion would inevitably result in the significant erosion of the independence and impartiality of the Sri Lankan judiciary.
Moreover, several checks placed on the President’s powers by the 19th Amendment have also been removed while giving him greater legal immunity. The President would also be granted sole power to appoint the cabinet, assign to himself any cabinet portfolio and been given unfettered discretion in relation to the appointment and dismissal of the Prime Minister. The President would also retain the power to dissolve the Parliament within one year.
Contact
For questions and clarifications: Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala(a)icj.org
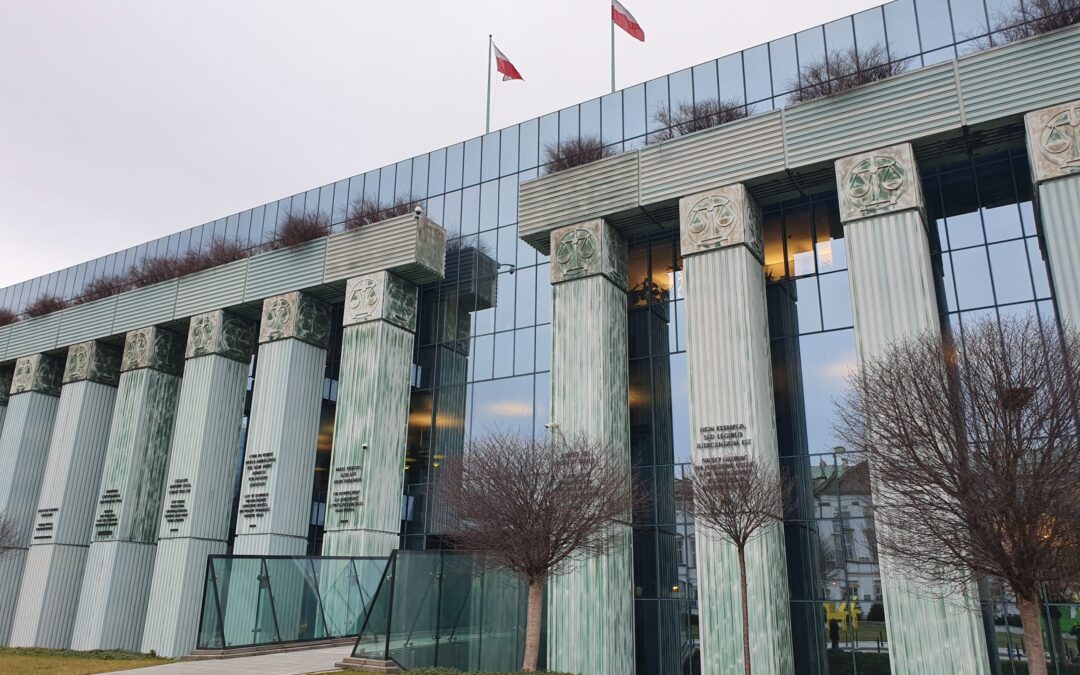

Jun 4, 2020 | News
The ICJ today raised concern at the threat of criminal proceedings against Judge Igor Tuleya on charges arising from the judge’s independent exercise of his judicial functions. The ICJ called on the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court not to lift his immunity at its 9th June hearing.
Judge Tuleya faces prosecution for having allowed the presence of media in a sensitive case concerning the investigations on the 2017 budget vote in the Polish House of Representatives (Sejm) that took place without the presence of the opposition.
He has been charged with ‘failing to comply with his official duties and overstepping his powers’ for having allegedly disclosed a secret of the investigation to ‘unauthorized parties’.
The accusations stem from the initiative of the judge to allow media and the public in the courtroom while issuing his ruling. Usually rulings on investigations are issued behind closed doors in Poland but the criminal procedure code allows judges to make the hearing public “in the interest of justice”.
“Judge Tuleya should not face any criminal proceedings to begin with for his actions in delivering his ruling in public, which is in accordance with national law”, said Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser for the ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme. “His immunity must be maintained and the ‘Muzzle Act’ that allowed for these abusive prosecutions should be immediately scrapped.”
These proceedings are the first case of implementation the draconian Act amending the Law on the Common Courts, the Law on the Supreme Court and Some Other Laws, signed into law on 4 February and widely known as the ‘Muzzle Act’, which gave competence to waive judicial immunity to the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court.
“As highlighted by the recent ruling of the EU Court of Justice, the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court is not independent and is open to undue influence or interference by political authorities. It should therefore not rule on issues pertaining to the disciplinary or criminal responsibility of judges, including a waiver of their immunity,” Massimo Frigo added.
Background
On 19 November, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) delivered a ruling in the case A.K. and others (C-585/18, C-624/18, C-625/18), on a preliminary question by the Supreme Court of Poland. The preliminary question asked whether the recently established Disciplinary and Extraordinary Chambers of the Supreme Court could be considered to be independent.
The CJEU ruled that a court cannot be considered independent “where the objective circumstances in which that court was formed, its characteristics and the means by which its members have been appointed are capable of giving rise to legitimate doubts, in the minds of subjects of the law, as to the imperviousness of that court to external factors, in particular, as to the direct or indirect influence of the legislature and the executive and its neutrality with respect to the interests before it and, thus, may lead to that court not being seen to be independent or impartial with the consequence of prejudicing the trust which justice in a democratic society must inspire in subjects of the law.”
Based on this ruling, the Labour, Criminal and Civil Chambers of the Supreme Court declared that the Disciplinary and Extraordinary Chambers of the Supreme Court were not properly constituted and independent.
According to the UN Basic Principles on the Independence of the Judiciary, judges are entitled to a fair hearing in all disciplinary proceedings (principle 17). In order for such a hearing to be fair, the decision-maker must be independent and impartial.
International and European standards on the independence of the judiciary provide that judges should have immunity from criminal prosecution for decisions taken in connection with their judicial functions in the absence of proof of malice, and any procedure for removing immunity must itself be independent (see for instance, UN Special Rapporteur on the Independence of Judges and Lawyers, paras 65-67 and 98; Council of Europe Committee of Ministers, para 68; Consultative Council of European Judges, para 20; ICJ Practitioners Guide no 13, pp. 27-30).
On 26 February 2020, the Polish Prosecutor’s Office requested a waiver of Judge Tuleya’s immunity in order to press criminal charges which might lead to imprisonment. The waiver will be examined on the 9 June 2020 by the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court appointed by the government.
In an open letter of 5 February 2020, 44 ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members denounced the recent legislative changes adopted by the Polish government threatening the role and the rights of judges and denouncing the risks faced by legal practitioners when fighting for the rule of law. Two weeks later, the risks highlighted by the letter have become reality for an increasing number of Polish judges, including Judge Tuleya.
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser, Europe and Central Asia Programme, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org, t: +41 22 979 38 00

Mar 15, 2018 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today spoke at the United Nations on impunity and the situation for human rights in Peru.
The oral statement was made during the discussion at the Human Rights Council of the Universal Periodic Review outcome for Peru. It read as follows (translation from the original Spanish):
“Mr President,
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ) recognizes the progress made by the Peruvian State in the field of human rights and its openness in relation to the recommendations made in the current cycle of the Universal Periodic Review.
The ICJ regrets, however, that the investigation and punishment of those responsible for the serious human rights violations that occurred during the internal armed conflict have not received the attention they deserve. On the contrary, the fight against impunity has receded with the granting of pardon and presidential grace to former president Alberto Fujimori who was serving a prison sentence for a series of crimes against humanity committed during his term. The presidential grace grants immunity from investigations and prosecutions in course or to be opened in the future.
One of the recommendations (111.97) that Peru accepts with qualifications refers to investigations and reparations to the thousands of women who suffered forced sterilization during the Fujimori administration. The measures of pardon and grace granted would exonerate Fujimori from investigation and punishment for this and other serious crimes. The ICJ urges the Peruvian State to implement the recommendations of the international community with full respect for international standards that prohibit impunity for serious violations of human rights.
Thank you Mr President.”
The ICJ oral statement complements a related written statement by the ICJ at the session.

Nov 1, 2012 | News, Publications, Reports
 The Sri Lankan government must immediately cease its assault on the independence of the judiciary, the ICJ said in a new report.
The Sri Lankan government must immediately cease its assault on the independence of the judiciary, the ICJ said in a new report.
May 31, 2012 | News
The ICJ called upon the Moroccan authorities to comply with international law and remove the blanket immunity contained in the draft law 01-12 on the “Fundamental Guarantees for the Members of the Royal Armed Forces”.
The draft law, in particular Article 7, attempts to guarantee members of the Moroccan armed forces absolute immunity from criminal prosecution for operations carried out under the orders of a superior within the national territory.
It also requires the State to protect members of the armed forces from prosecution as well as from public criticism or condemnation.
The ICJ is deeply concerned that the law attempts to grant immunity for all serious crimes prohibited by international law that might be committed by the Members of the Royal Armed Forces under the orders of their superiors, including war crimes, crimes against humanity, acts of genocide, torture and enforced disappearances.
The law also does not provide for any legal measures against superiors when their orders violate the law.
“The draft law violates Morocco’s obligations under international law, which prohibits any immunity from legal proceedings in respect of crimes under international criminal law, including gross human rights violations”, whether the perpetrators act under orders from a superior officer or independently”, said Alice Goodenough, Legal Adviser for ICJ’s Middle East and North Africa Programme. “The draft law 01-12 should be amended to ensure that those who carry out or participate directly in committing crimes under international law, as well as those who have command responsibility, are held criminally responsible for such conduct.”
The ICJ is concerned that over the past fifty years, Moroccan armed forces and other security services have acted with impunity, unaccountable to either the courts or Parliament.
They have enjoyed effective immunity from any legal proceedings over their role in the human rights violations documented in the 2005 report of the Moroccan Truth Commission (the IER), including unlawful killings, summary executions, enforced disappearances, arbitrary detentions, and torture and other ill-treatment, the ICJ notes.
“This draft law, if adopted, will institutionalize the impunity that has prevailed over past and present human rights abuses in Morocco,” Goodenough added. “Moroccan authorities must refrain from adopting this law or any other measures that foster or contribute to impunity.”
Contact:
Alice Goodenough, Middle East & North Africa Legal Adviser, t +41 22 979 3811; e-mail: alice.goodenough(at)icj.org