
Aug 27, 2019 | News
The ICJ welcomes yesterday’s ratification by Uzbekistan of the CIS Convention on Legal Assistance and Legal Relations in Civil, Family and Criminal Matters 2002, also called the Chisinau Convention. The law on ratification was signed by President Shavkat Mirziyoyev.
The ICJ calls on the Uzbek authorities to take measures to make the Convention’s protective guarantees effective.
“This is a major step forward by Uzbekistan to get its extradition system up to standard with the rest of the world”, said Massimo Frigo, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser. “. “Its ratification of this treaty considerably steps up human rights guarantees in extradition.”
The Chisinau Convention enshrines several human rights guarantees to protect against extraditions that may breach the human rights of the transferred person, including the prohibition to transfer persons where they risk the death penalty or torture or cruel, inhuman and degrading treatment.
“The ratification of the Convention is a very important first step. An effective implementation of these guarantees in the legal and law enforcement systems is necessary now.” said Dmitry Nurumov, ICJ Central Asia Legal Consultant.
Background
Last May, the ICJ held, together with the General Prosecutor’s Office of Uzbekistan, UNODC Regional Office for Central Asia and the Regional Office for Central Asia of OHCHR, a regional and a national seminar on comparative practices in extradition in the CIS and European legal systems, including with regard to human rights guarantees in these procedures.
In 2017, the ICJ issued a report documenting the shortcomings in the Russian Federation, Central Asia and European countries in their extradition systems and other transfer procedures.
The ratification by Uzbekistan of the Chisinau Convention meets part of the recommendations formulated by the ICJ in these occasions.
Contact:
Massimo Frigo, Senior Legal Adviser, e: massimo.frigo(a)icj.org , t: +41229793805

May 6, 2019 | Agendas, Events
Today, the ICJ, together with the General Prosecutor’s Office of Uzbekistan, UNODC and OHCHR are holding the first regional meeting of prosecutors from Central Asia and the Russian Federation to discuss international law and standards in the field of extradition, mutual legal assistance, the rule of law and human rights.
The workshop aims to facilitate exchange of experiences regarding the law and practice of extradition in European and Central Asian countries. Presentations at the workshop will analyse international law and standards on effective criminal justice co-operation and the protection of human rights in extradition, and their application in practice..
The workshop will present cases of mutual cooperation in the field of criminal law from national courts as well as from international mechanisms such as the European Court of Human Rights, the UN Committee against Torture and the UN Human Rights Committee.
The workshop is taking place in Tashkent (Uzbekistan) and is hosted by the Prosecutor General’s Office of Uzbekistan.
More than twenty prosecutors from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan the Russian Federation Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan are participating in the event that includes international experts from UNODC, ICJ, including ICJ Commissioner and Emeritus Spanish Supreme Court Justice, José Antonio Martin Pallin, and Italian Prosecutor Lorenzo Salazar.
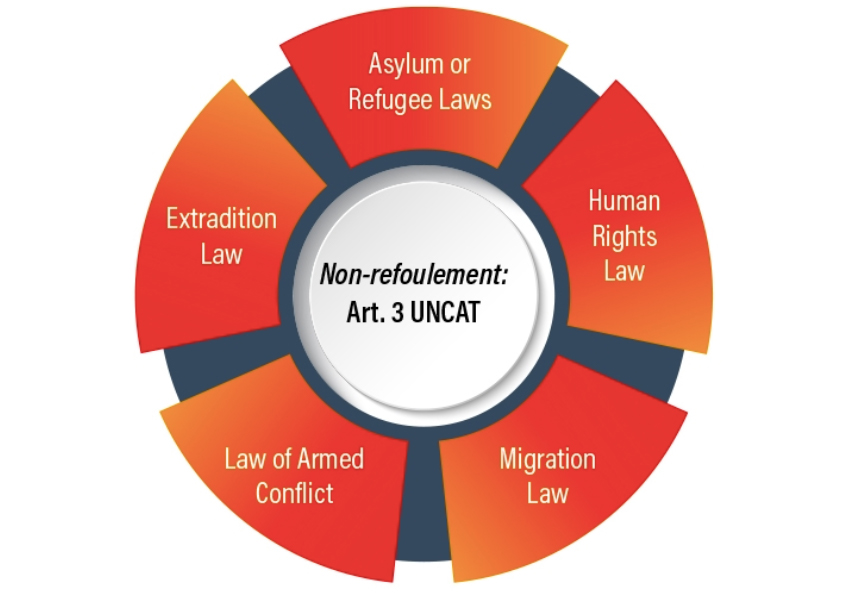
Mar 14, 2018 | News
The new CTI tool on non-refoulement covers:
- constitutional and legislative provisions;
- national procedures;
- procedural rights to be guaranteed to those facing deportation or expulsion;
- training; and
- visa and stay arrangements for when return is prohibited.
There is also a section on non- refoulement in the extradition context.
The purpose of this and other CTI Implementation Tools is to inspire other States to take action through exchanges of good practices.
The tool also provides timely and practical information and advice for States in light of the recently released UN Committee against Torture’s General comment on the implementation of Article 3 of the Convention in the context of Article 22.
Some of the laws mentioned in this tool detail the powers that can be exercised by State authorities to remove a person and the constraints on those powers, as well as the relevant administrative and judicial procedures to be followed. National legislation has also detailed the rights of persons within those procedures (photo).
The tool was developed for the CTI by the ICJ with the support of the University of Bristol’s Human Rights Implementation Centre.
CTI’s series of UNCAT Implementation Tools are available here.

Jan 8, 2018 | Advocacy, Cases, Legal submissions, News
The ICJ and other organizations have intervened today before the European Court of Human Rights challenging expulsions of asylum seekers from Hungary to Serbia.
The International Commission of Jurists (ICJ), the European Council on Refugees and Exiles (ECRE) and the Dutch Council for Refugees have submitted today a third party intervention before the Grand Chamber of the European Court of Human Rights in the case of Ilias and Ahmed v. Hungary.
The case challenges the systematic practice by the Hungarian authorities to send back to Serbia foreign nationals asking for asylum under the pretention that Serbia is a safe third country in which to ask for international protection.
The intervening organizations have argued before the Court that:
- a removal that exposes an applicant to the risk of refoulement and deprives them of protections under international and EU law, is prohibited regardless of whether the decision was taken on the basis of the safe third country concept or the country was included in a “safe third country” list.
- International law requires, inter alia, a rigorous scrutiny of the applicant’s arguable claim of potential prohibited treatment, access to an effective remedy following a negative decision, and access to the rights under the 1951 Refugee Convention.
- Application of the safe third country concept for EU Member States is contingent on the applicant being admitted to the territory and having effective access to a fair asylum procedure in the safe third country
- An assessment of whether restrictions on the freedom of movement of migrants, imposed in a border or international zone, amount to deprivation of liberty under Article 5 ECHR must be based on the impact of these measures on the individuals concerned.
Hungary-ECtHR-amicusbrief-cases-Ilias&Ahmed-ICJ&others-2018-ENG (download the third party intervention)
Background
Ilias Ilias and Ali Ahmed, both Bangladeshi nationals, fled their home country in arrived at the Hungarian-Serbian border on 15 September 2015 after having briefly crossed through Serbia during their trip.
Having asked immediately for asylum in Hungary, they were confined for days in a transit zone, a ” a confined area of some 110 square metres, part of the transit zone, surrounded by fence and guarded by officers”.
Their applications were rejected on the very same day of their application on the grounds that they could have asked for asylum in Serbia, considered by Hungary a safe third country, and appeals were rejected.
They were removed to Serbia on 8 October 2015.

Dec 5, 2017 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ today addressed an emergency Special Session of the UN Human Rights Council on Myanmar, outlining key requirements for the protection of the Rohingya minority, including safe and voluntary return of refugees.The Special Session is expected to adopt a resolution to address “The human rights situation of the minority Rohingya Muslim population and other minorities in the Rakhine State of Myanmar.”
The ICJ statement read as follows:
“It is encouraging that the Governments of Bangladesh and Myanmar have recognized the right of displaced Rohingya to return to their places of residence.
However, any provisions for return must comply with international law, including as regards non-refoulement. Effective guarantees that all displaced persons will be able to return to their place of prior residence in a safe, dignified, voluntary and sustainable manner, without discrimination, are essential.
Rohingya refugees must also be provided with alternatives to return, including the option of seeking international protection. Anything short of this would amount to their forcible return and thus violate the non-refoulement principle.
It is of the utmost urgency that the gross and systematic violations that have given rise to the forced displacement are immediately brought to an end and that measures are taken to prevent their recurrence, including by holding perpetrators responsible.
No-one may be forcibly returned to the current circumstances that prevail in Rakhine State, and voluntary returns will only ultimately take place if and when refugees are satisfied they are not returning to further violations in Myanmar.
Any provisions for restrictions on freedom of movement upon return are also of concern, particularly given past experience, with internment camps housing tens of thousands of Muslims displaced in 2012 still in place. Such restrictions elsewhere in Rakhine State contribute to violations of, among other things, the human rights to life, to health, to food, to education and to livelihoods.
To ensure that the rights of refugees are respected and protected, Bangladesh and Myanmar should immediately seek to ensure that UNHCR is involved, and its guidance followed, in any discussion of repatriation processes.
The Government of Myanmar must cooperate with the UN-mandated Fact Finding Mission to independently establish facts and provide a proper foundation for effective responses to human rights violations and humanitarian crises in Rakhine State, as well as in Shan and Kachin States, whose populations also face related patterns of human rights violations by military and security forces.”
The Council adopted a resolution at the end of the session, which reflects many of the concerns raised by the ICJ and others: A_HRC_S_27_L1









