Mar 4, 2021 | News
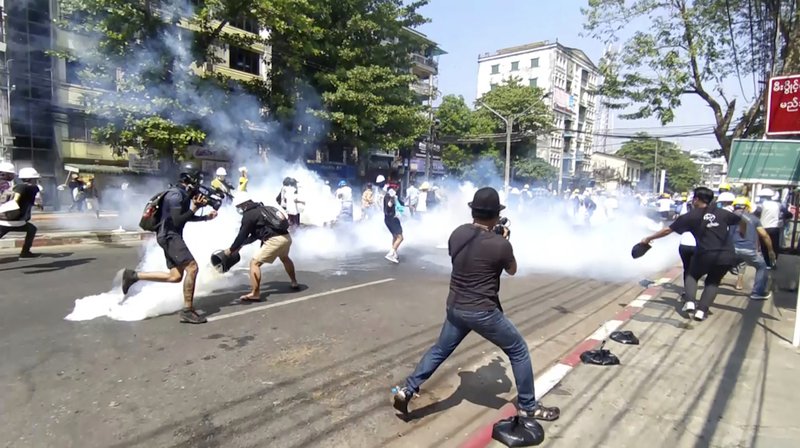
The escalating killing of peaceful protestors by Myanmar’s security forces should be independently investigated as possible crimes against humanity, said the ICJ today on the eve of a closed-door UN Security Council session on the situation.
According to reliable information provided to the ICJ, security forces have unlawfully killed approximately 50 unarmed people – including at least five children – in more than 10 cities on different days since the military overthrew the civilian government on 1 February 2021. On 3 March, at least 38 people were reported killed by security forces.
In addition, numerous protestors have been injured and a total of 1,498 people have been arrested, charged or sentenced in relation to the military coup, according to The Assistance Association for Political Prisoners (AAPP).
“As the scale of the violence continues to increase, seemingly as part of a systematic, centralized policy to use lethal force against peaceful protestors, it is hard to escape the conclusion that Myanmar’s security forces are perpetrating crimes against humanity,” said Kingsley Abbott, Director of Global Accountability and International Justice at the ICJ. “This underscores the urgent need for all states, including the permanent members of the UN Security Council, to stop shielding the Myanmar military and work together towards opening avenues to justice for the Myanmar people.”
The UN Security Council will meet this Friday for a closed-door session at the request of the United States which is President of the Council in March 2021.
“The UN Security Council should immediately refer Myanmar to the International Criminal Court for a full independent and effective investigation,” added Abbott.
In addition to acts that may constitute murder as a crime against humanity, security forces have also reportedly committed acts which, when committed in a widespread and systematic manner, would amount to other crimes against humanity, including imprisonment, torture, and enforced disappearance – all of which also go towards supporting the existence of an attack.
“These killings and other crimes under international law are a direct result of the culture of impunity that has been allowed to persist in Myanmar for decades,” added Abbott. “All states should support the different accountability initiatives underway, including the Independent Investigative Mechanism for Myanmar which is collecting evidence for use in future legal proceedings.”
“It is long past time for perpetrators of serious human rights violations in the country to be brought to justice before the International Criminal Court or in any national jurisdictions willing and able to exercise universal jurisdiction.”
Background
On 12 September 2018, following an independent investigation, the United Nations Independent International Fact-Finding Mission on Myanmar called for Myanmar’s military to be “…investigated and prosecuted in an international criminal tribunal for genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes” concerning alleged violations in Shan, Kachin and Rakhine States and elsewhere throughout the country.
Under general international law, including customary international law and treaties and statutes of international criminal courts, crimes against humanity must be prosecuted. The authoritative definition of crimes against humanity is contained in the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Under Article 7 of the Rome Statute, for killings to amount to crimes against humanity, they must be committed as part of a widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, with knowledge of the attack. According to the elements of crimes of the Rome Statute, “’Attack directed against a civilian population’ in these context elements is understood to mean a course of conduct involving the multiple commission of acts referred to in Article 7, paragraph 1, of the Statute against any civilian population, pursuant to or in furtherance of a State or organizational policy to commit such attack. The acts need not constitute a military attack. It is understood that ‘policy to commit such attack’ requires that the State or organization actively promote or encourage such an attack against a civilian population.”
Generally speaking, “widespread” refers to the geographical scope of the attack and the number of victims, but not exclusively. “Systematic” refers to the organized nature of the acts of violence and the improbability of their random occurrence.
Myanmar is not a State Party to the Rome Statute of the ICC. However, the ICC is investigating crimes committed against the Rohingya minority as part of waves of violence in Rakhine State in 2016 and 2017 where one element or part of the crime was committed inside Bangladesh, which is a party to the Rome Statute. The ICC would be able to conduct a full investigation of the situation in Myanmar if the UN Security Council used its Chapter VII powers to refer the matter to the ICC pursuant to Article 13(b) of the Rome Statute.
Universal jurisdiction refers to the legal concept that States have the authority, and in some cases the obligation, to bring proceedings in relation to certain crimes, including crimes against humanity, because they are so serious it does not matter where the crimes were committed or the nationality of the perpetrators or the victims. States are generally entitled to exercise jurisdiction for serious under crimes under international law.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, ICJ Director of Global Accountability and International Justice; e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Secretary General, sam.zarifi(a)icj.org

Mar 2, 2021 | News
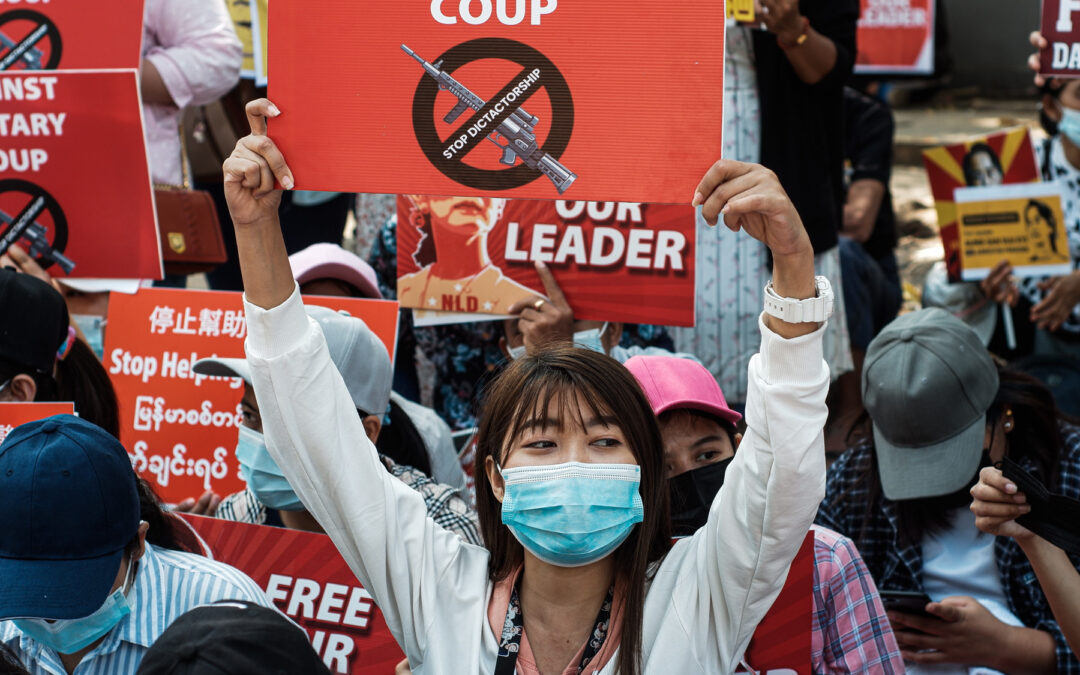
Myanmar’s military government should reverse its post-coup d’etat revisions of legal protections for human rights in the country, the ICJ and Human Rights Watch said today.
Myanmar’s State Administration Council (SAC), appointed by the country’s military after it overthrew the elected civilian government on February 1, 2021, has dictated key revisions to the country’s legal system that criminalize even peaceful protests, and enable violations of the right to privacy and arbitrary arrests and detention. The changes were made through orders signed by the commander-in-chief, Sr. Gen. Min Aung Hlaing, on behalf of the SAC, and outside the parliamentary process.
“As Myanmar’s military increasingly relies on excessive force and intimidation to quell peaceful protests against its coup, it is trying to give a veneer of legality to its actions by subverting existing protections in the legal system.”
“These revisions, which violate the principle of legality and Myanmar’s international obligations, in no way excuse or legitimate the widespread violations of human rights now taking place in Myanmar.”
– Ian Seiderman, ICJ’s Director of Law and Policy.
Since the coup on February 1, the military junta has:
- arbitrarily suspended sections of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017), removing basic protections, including the right to be free from arbitrary detention and the right to be free of warrantless surveillance and search and seizure;
- amended the Penal Code to create new offenses and expand existing offenses to target those speaking critically of the coup and the military, and those encouraging others to support the “Civil Disobedience Movement”;
- amended the Ward and Tract Administration Law to reinstate the requirement to report overnight guests;
- amended the Code of Criminal Procedure to make the new and revised offenses non-bailable and subject to warrantless arrest; and
- amended the Electronic Transactions Law to prevent the free flow of information and criminalize the dissemination of information through cyberspace, including expression critical of the coup or the acts of the junta.
Under international legal standards, any restrictions on human rights must be strictly necessary to protect a legitimate interest and proportionate to the interest being protected, even in times of public emergency or for legitimate national security purposes (conditions that do not apply in Myanmar currently). The orders issued by the SAC fail to meet that standard, as they will arbitrarily interfere with the exercise of rights protected under international law, including freedom of expression, freedom of peaceful assembly, the right to liberty, and the right to privacy. Certain rights, such as the rights to bodily integrity and nondiscrimination, are not subject to restriction.
“By stripping the people of Myanmar of their basic rights, the military is once again demonstrating its disdain for international human rights protections,” said Linda Lakhdhir, Asia legal advisor at Human Rights Watch. “The junta cannot justify the oppression of Myanmar’s inhabitants through the unilateral creation of arbitrary new laws.”
Contact
Osama Motiwala, ICJ Asia-Pacific Communications Officer, e: osama.motiwala(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org
Analysis of Legal Code Changes
Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens (2017)
On February 13, the State Administration Council arbitrarily suspended sections 5, 7 and 8 of the Law Protecting the Privacy and Security of Citizens, eroding basic protections for individuals.
Section 5 required the presence of two witnesses whenever the police enter a residence for the purposes of search or seizure “to ensure that there is no damage to the privacy or security of the citizen.” The suspension of that protection significantly raises the risk of abuses during searches and arrests.
Section 7 required a court order for any detention of more than 24 hours. Suspension of the provision will facilitate violations of international law, which provides that any person detained on a criminal charge be promptly taken before a judge.
Section 8 provided protections of an individual’s right to privacy by prohibiting search and seizure, surveillance, spying, or any investigation affecting the privacy, security, and dignity of the individual without a court order – protections that the junta has removed. Under international law no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with their privacy, family, home or correspondence.
Penal Code Amendments
On February 14, the SAC announced amendments to the Penal Code that could lead to criminal liability for thousands of demonstrators exercising their rights to free expression of their views, and anyone publicly criticizing the military coup d’etat through any means.
The SAC inserted a new provision, section 505A, that could be used to punish comments regarding the illegitimacy of the coup or the military government, among others. The new section would criminalize comments that “cause fear,” spread “false news, [or] agitates directly or indirectly a criminal offense against a Government employee.” Violation of the section is punishable by up to three years in prison.
Section 505(a) previously made it a crime to publish or circulate any “statement, rumor or report” “with intent to cause, or which is likely to cause, any officer, soldier, sailor or airman, in the Army, Navy or Air Force to mutiny or otherwise disregard or fail in his duty.” It has been replaced with much broader language clearly designed to penalize those encouraging members of the civil service of the security services to join the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Under the revised provision, any attempt to “hinder, disturb, damage the motivation, discipline, health and conduct” of the military personnel and government employees and cause their hatred, disobedience or disloyalty toward the military and the government is punishable by up to three years in prison.
The SAC also significantly broadened the “treason” provisions in section 124 of the Penal Code. Section124A, which already criminalized comment that “bring into hatred or contempt” or “excite disaffection against” the government, was expanded to include comments relating to the defense services and defense services personnel, effectively criminalizing any criticism of the military or military personnel. Violation of the section is punishable by up to 20 years in prison.
The newly added section 124C imposes a prison term of up to 20 years on anyone who intends to “sabotage or hinder the performance of the Defense Services and law enforcement organizations who are engaged in preserving the stability of the state.” This provision would criminalize efforts to encourage security forces to join the Civil Disobedience Movement or permit unauthorized protests.
Finally, under section 124D, a person can be sentenced up to seven years in prison if they hinder a government employee from carrying out their duties. This provision is so broad that any actions of protesters could be interpreted as preventing security personnel or defense service officers from performing their duty.
Code of Criminal Procedure
On February 14 the junta amended the Code of Criminal Procedure Amendment Law to make offenses under sections 505A, 124C and 124D non-bailable and subject to arrest without a warrant.
Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21)
The amendments to the Ward or Village Tract Administration Law (13/2/21) further increase the military’s ability to conduct surveillance on people’s movements, in particular on human rights defenders seeking shelter away from their own homes. Amendments to section 17 of the Act require all overnight guests from other wards or villages to be reported to the ward or village tract administrator, who are authorized by section 13 to “take action” against any who “failed to inform the guest list.” Section 27 reintroduces criminal sanctions for failing to report overnight guests. Such provisions existed under previous military governments and were deeply resented.
Electronic Transactions Law (Law No 7/ 2021)
On February 15, the junta also amended the Electronic Transactions Law to include, among others, provisions that had been proposed in the draft Cybersecurity Law.
As was true under that much-criticized draft law, the amended Electronics Transactions Law permits government agencies, investigators, or law enforcement to access personal data in relation to “cyber-crimes,” “cyber misuse” or any criminal investigation.
The amendments also include several provisions (articles 38(d) and (e)) that provide criminal penalties for “unauthorized” access to online material and that could be used to prosecute whistle blowers, investigative journalists, or activists who use leaked material for their work.
Section 38B criminalizes “obtaining, disclosing, using, destroying, modifying, disseminating, or sending someone’s personal data to anyone else without approval,” with one to three years in prison. While the protection of the right to privacy online is important, this provision goes well beyond legitimate protections on privacy and imposes arbitrary restrictions on freedom of expression.
In particular, “personal data” is defined in a manner so broad as to include virtually any information associated with a person. The law is therefore impermissibly vague and overbroad, as it would likely prevent even the disclosure of information about anyone involved in alleged human rights violations, including by human rights defenders and journalists.
Section 38C criminalizes the creation of “misinformation or disinformation with the intent of causing public panic, loss of trust or social division on cyberspace,” and provides for imprisonment of one to three years in addition to fines. These provisions are similarly vague and overbroad and unnecessarily and disproportionately limit the exercise of expression online, including criticism of the coup and the military junta.
***
Download the full statement here.
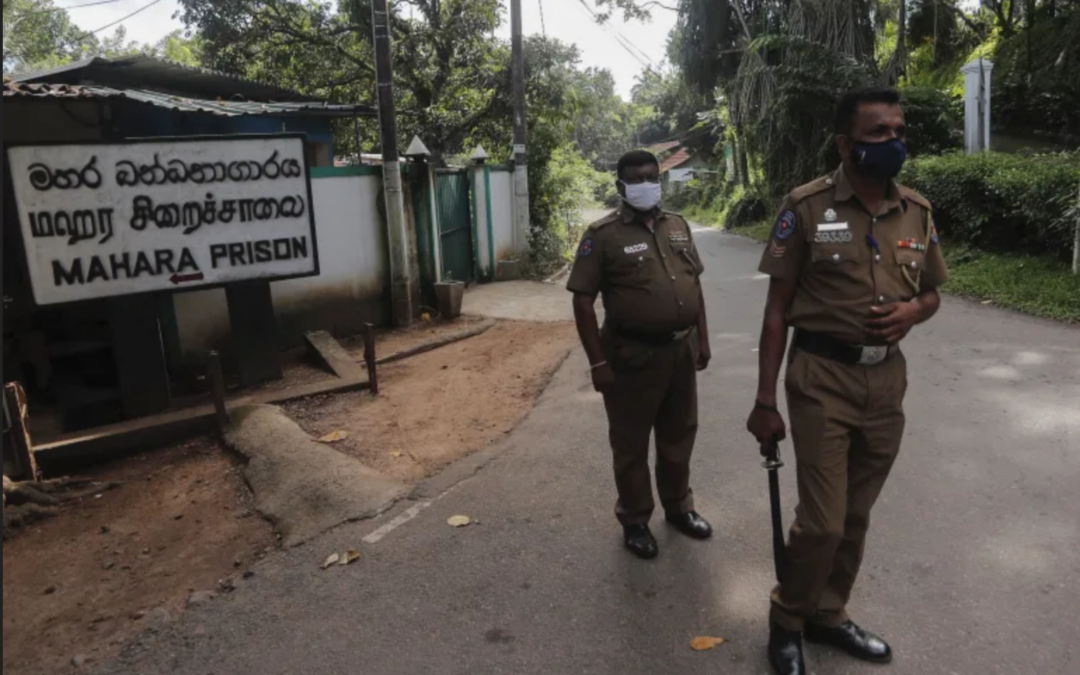

Dec 2, 2020 | News
The ICJ today called upon the Sri Lankan authorities to conduct a prompt, thorough and impartial investigation into the events involving the use of lethal force by prison guards at Mahara prison on 29 and 30 November, which left at least nine inmates killed and over hundred others injured.
The action by the guards was taken in response to unrest resulting from protests by inmates over unsafe and overcrowded conditions in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The ICJ also called for urgent measure to address the unsafe conditions in Sri Lankan prisons to protect the right to health and life, including where necessary by releasing detainees.
“The tragic events of Mahara prison are a consequence of the failure of the Sri Lankan authorities to effectively address the situation of prison conditions, which has turned into a full blown human rights and public health crisis in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic”, said Ian Seiderman, ICJ Legal and Policy Director
The unrest was the culmination of a series of protests staged by the prisoners demanding an increase in coronavirus testing and new isolation facilities for infected prisoners. According to Senaka Perera, President of the Committee for Protecting the Rights of the Prisoners, around 200 inmates of the Mahara prison have been infected with COVID-19.
While the Minister of Rehabilitation and Prison Reforms and the Inspector General of Police have instructed the Criminal Investigation Department to probe the unrest caused at the Mahara Prison, the Minister of Justice has formed a separate five-member committee, chaired by former High Court Judge Kusala Saorini Weerawardena, to conduct its own investigation.
The ICJ recalls that under international law, the use of lethal force by State authorities is only permissible where strictly necessary to protect life. This standard should govern any investigation, and those responsible for unlawful conduct resulting in death or injuries to prisoners must be held to account.
“In addition to ensuring accountability and redress for any violations at the Mahara Prison, the authorities must act swiftly to meet the legitimate grievances of detainees throughout the country”, added Ian Seiderman.
“An effective response is not optional, but is necessary to fulfill the State’s legal obligation to provide for equal access to healthcare and health services to prisoners, who are among the most vulnerable to the ravages of COVID-19 in highly unsafe, enclosed and overcrowded environments.” Seiderman added.
The incident follows a wave of similar protests in several other prisons in the country. On 18 November, five inmates who were under quarantine at the Old Bogambara Prison attempted to break out and an inmate was shot dead when the prisoner officers opened fire at the fleeing inmates.
The ICJ called for the release of detainees who are particularly at risk of losing their life or suffering severe health effects from COVID-19. This would also apply to other convicts who could be released without compromising public safety, such as those sentenced for minor, non-violent offences.
Background
Speaking in Parliament on Monday, Minister of Rehabilitation and Prison Reforms Dr. Sudharshini Fernandopulle stated that the Government has taken steps to reduce overcrowding by directing COVID-19 positive prisoners out of the prisons to the Welikanda Hospital and moving all women inmates to the Kandakadu Rehabilitation Centre. She also stated that a mechanism has been put in place to obtain bail for those arrested for minor drug offences. Moreover, a presidential pardon has been granted to over 600 convicts of minor offences who were in remand due to their inability to pay the required fine.
Several UN bodies, including the WHO and OHCHR, came together in recommending that States consider limiting the deprivation of liberty including pretrial detention, to a measure of last resort and enhance efforts to resort to non-custodial measures.
Contact
Osama Motiwala, Communications Officer – osama.motiwala(a)icj.org

Sep 25, 2020 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ has joined other NGOs in urging the UN Human Rights Council to respond effectively to the crisis for human rights in the Philippines.
The joint oral statement was delivered by the World Organization against Torture (OMCT) on behalf of the group of international and Philippino NGOs, during a general debate on country situations. It read as follows:
“Madam President,
I speak on behalf of 35 organisations, deeply concerned by the situation in the Philippines. We urge this Council to respond credibly to the grave findings and recommendations of the recent OHCHR report.
Developments since that report indicate further deterioration, with ongoing incitement to kill by the President, the promotion of an architect of the anti-drug strategy to police chief, the passing of an overbroad anti-terror law ripe for abuse, the conviction of journalist Maria Ressa and shutdown of media network ABS-CBN, the murder of activists and a journalist and a new spike in police killings.
In terms of cooperation, the Philippines refused access to OHCHR in the preparation of the report and continues to bar entry to Special Procedures. The Secretary-General and High Commissioner have raised significant concerns over reprisals. The Government does not acknowledge widespread and systematic killings as a problem, in fact it encourages them and rejects the OHCHR’s findings. Serious violations continue.
The Government’s announced Inter-Agency Panel lacks any transparency and directly involves branches of Government implicated in these abuses. As such, it clearly cannot satisfy international standards of independence,[1] nor can it be seen as credible or safe for victims to engage with.
Madam President,
Our organisations have urged and continue to urge this Council to launch an independent international investigation.
The High Commissioner has clearly asked the Council to renew her mandate to monitor and report on the wider situation, as well as to provide technical cooperation to “implement the report’s recommendations,” and “continue to pursue accountability”. We urge this Council – at absolute minimum – to ensure continued monitoring and reporting on all aspects of the situation as clearly recommended by the High Commissioner. Anything less would not only be an insult to victims and their families, but send a green light to perpetrators that they can continue with impunity, with disastrous consequences on the ground.
Thank you.”
Co-signatories:
- Action Network Human Rights Philippines (AMP)
- Amnesty International
- Article 19
- Child Alert Mindanao
- Children’s Legal Rights and Development Center (CLRDC)
- CIVICUS Alliance
- Coalition Against Summary Executions
- Families of Victims of Involuntary Disappearance (FIND)
- Franciscans International
- Franciscan Sisters of the Immaculate Conception
- Free Legal Assistance Group (FLAG)
- Freedom House
- Harm Reduction International
- Human Rights Watch
- In Defense of Human Rights and Dignity Movement (iDEFEND)
- International Coalition for Human Rights in the Philippines (ICHRP)
- International Commission of Jurists
- International Drug Policy Consortium
- International Federation for Human Rights (FIDH)
- International Service for Human Rights
- Karapatan Alliance Philippines
- Medical Action Group
- National Union of Journalists of the Philippines
- Network Against Killings in the Philippines (NakPhil)
- Partnership Mission for People’s Initiatives (PMPI)
- Philippine Alliance of Human Rights Advocates (PAHRA)
- Philippine Misereor Partnership Inc. (PMPI)
- Philippine Human Rights Information Center
- Salinlahi Alliance for Children’s Concerns
- Swiss Catholic Lenten Fund (SCLF)
- Tambayan
- The Asian Forum for Human Rights and Development (FORUM-ASIA)
- Task Force Detainees of the Philippines
- World Council of Churches
- World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT)
[1] See for instance the UN Principles on the Effective Prevention and Investigation of Extra-legal, Arbitrary and Summary Executions, adopted by the Economic and Social Council in its resolution 1989/65 of 24 May 1989; and Human Rights Committee, General Comment no. 36 on the right to life (article 6).