
Jul 14, 2015 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
Today, the ICJ delivered an oral statement before the Human Rights Committee during a half a day of general discussion in view of the Committee’s ongoing elaboration of a new General Comment on Article 6 (Right to Life) of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
The ICJ’s oral statement focussed on the following:
- the principles of equality before the law, equal protection of the law and non-discrimination, as well as non-refoulment;
- State Parties’ duty to protect the right to life in respect of conduct of private actors;
- State Parties’ duty to take measures to protect and ensure the right to life in connection with acts of gender-based violence against women and violence against individuals based on their real or imputed sexual orientation and/or gender identity or expression;
- the relationship between the right to life and certain economic, social and cultural rights;
- the extraterritorial reach of the Covenant; and
- the application of Article 6 during situations of armed conflict.
Universal-ICJ oral statement HALF DAY GENERAL DISCUSSION ON GC-Advocacy-2015-ENG (full text in PDF)

Mar 3, 2015 | News
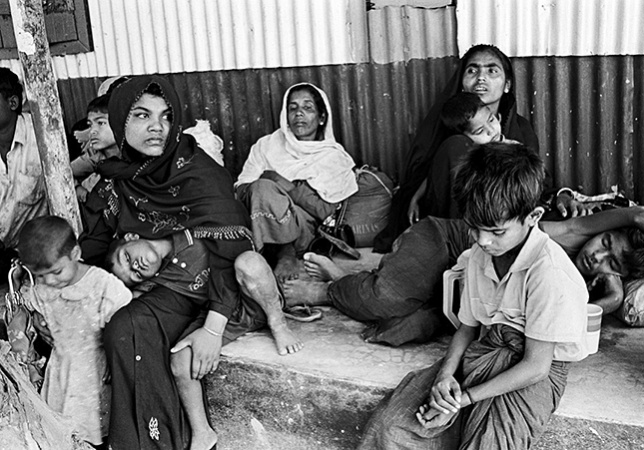
Myanmar’s parliament must reject or extensively revise a series of proposed laws that would entrench already widespread discrimination and risk fuelling further violence against religious minorities, Amnesty International and the ICJ said today.
A package of four laws described as aimed to “protect race and religion” – currently being debated in parliament – include provisions that are deeply discriminatory on religious and gender grounds.
They would force people to seek government approval to convert to a different religion or adopt a new religion and impose a series of discriminatory obligations on non-Buddhist men who marry Buddhist women.
“Myanmar’s parliament must reject these grossly discriminatory laws which should never have been tabled in the first place. They play into harmful stereotypes about women and minorities, in particular Muslims, which are often propagated by extremist nationalist groups,” said Richard Bennett, Amnesty International’s Asia-Pacific Director.
“If these drafts become law, they would not only give the state free rein to further discriminate against women and minorities, but could also ignite further ethnic violence,” he added.
The draft laws have been tabled at a time of a disturbing rise in ethnic and religious tensions, as well as ongoing systematic discrimination against women, in Myanmar.
In this context, where minority groups – and in particular the Rohingya (photo) – face severe discrimination in law, policy and practice, the draft laws could be interpreted to target women and specific communities identified on a discriminatory basis.
“The passage of these laws would not only jeopardize the ability of ethnic and religious minorities in Myanmar to exercise their rights, it could be interpreted as signalling government acquiescence, or even assent, to discriminatory actions,” said Sam Zarifi, ICJ’s Asia Director. “The introduction of these discriminatory bills is distracting from the many serious political and economic issues facing Myanmar today.”
Of the four draft laws, two – the Religious Conversion Bill and the Buddhist Women’s Special Marriage Bill – are inherently flawed and should be rejected completely.
The remaining two – the Monogamy Bill and the Population Control Healthcare Bill – need serious revision and the inclusion of adequate safeguards against all forms of discrimination before being considered, let alone adopted.
These bills do not accord with international human rights law and standards, including Myanmar’s legal obligations as a state party to the UN Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination against Women and the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Amnesty International and the ICJ have conducted a legal analysis of the four laws and have found that:
- The Religious Conversion Bill stipulates that anyone who wants to convert to a different faith will have to apply through a state-governed body, in clear violation of the right to choose one’s own religion. It would establish local “Registration Boards”, made up of government officials and community members who would “approve” applications for conversion. It is unclear whether and how the bill applies to non-citizens, in particular the Rohingya minority, who are denied citizenship in Myanmar. Given the alarming rise of religious tensions in Myanmar, authorities could abuse this law and further harass minorities
- The Buddhist Women’s Special Marriage Bill explicitly and exclusively targets and regulates the marriage of Buddhist women with men from another religion. It blatantly discriminates on both religious and gender grounds, and feeds into widespread stereotypes that Buddhist women are “vulnerable” and that their non-Buddhist husbands will seek to forcibly convert them. The bill discriminates against Buddhist women as well as against non-Buddhist men who face significantly more burdens than Buddhist men should they marry a Buddhist woman.
- The Population Control Healthcare Bill – ostensibly aimed at improving living standards among poor communities – lacks human rights safeguards. The bill establishes a 36-month “birth spacing” interval for women between child births, though it is unclear whether or how women who violate the law would be punished. The lack of essential safeguards to protect women who have children more frequently potentially creates an environment that could lead to forced reproductive control methods, such as coerced contraception, forced sterilization or abortion.
- The Monogamy Bill introduces new provisions that could constitute arbitrary interference with one’s privacy and family – including by criminalizing extra-marital relations – instead of clarifying or consolidating existing marriage and family laws.
Contact
In Bangkok – Sam Zarifi, ICJ Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific, sam.zarifi(a)icj.org; m +66807819002
In London – Olof Blomqvist, Amnesty International Asia-Pacific Press Officer, olof.blomqvist(a)amnesty.org; t: +44 20 7413 5871, m +44 790 4397 956
An extensive legal analysis of the laws by Amnesty International and the ICJ can be found here:
Myanmar-Reject discriminatory race and religion draft laws-Advocacy-2015-ENG (full text in PDF)
Oct 3, 2014 | News
Este communicado sigue una nueva visita a San Juan Sacatepéquez, con el objeto de observar la situación de derechos humanos en dicho municipio.

Sep 15, 2014 | Advocacy, Non-legal submissions
The ICJ supports a joint oral statement, delivered by ARC International, in relation to the Panel on “Protection of the Family”, at the UN Human Rights Council today.
The oral statement emphasised the importance of recognising the diversity of forms of families around the world.
It also noted that familes can be sites for transmissions of values, and that this can on the one hand include the promotion of human rights values, or on the other hand values incompatible with respect for human rights.
Finally, the statement highlighted that a human rights-based approach to family policies must recognise that individuals within families have human rights that require protection. Indeed, while families have the potential to help protect the human rights of their members from violations, families also have the potential to conceal abuses of human rights within the family.
The full statement in PDF format may be downloaded here: Universal-ProtectionofFamily-Advocacy-nonlegalsubmission-2014.EN

Jun 11, 2014 | Events
The ICJ’s Senior Legal Adviser on women’s human rights participated in a panel discussion on ‘Gains, gaps and challenges in addressing violence against women’, convened on 10 June 2014 in the margins of the Human Rights Council’s 26th regular session in Geneva.
The event was co-sponsored by the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the Permanent Missions of Canada and Chile and was moderated by Jane Connors, Chief of the OHCHR Special Procedures Branch. Panelists included Rashida Manjoo, Special Rapporteur on violence against women; Her Excellency Elisa Goldberg, Ambassador of Canada; Her Excellency Marta Maurás Peréz, Ambassador of Chile; and Leah Hoctor, ICJ Senior Legal Adviser.
The ICJ’s intervention focussed on remaining challenges, including the lack of prompt and effective investigations into allegations of violence against women (VAW); systemic failures in some States’ implementation of their due diligence obligations; and a series of disconnects at the international level pertaining to the link between VAW and other forms of discrimination and rights violations that women face, the lack of a holistic conceptualisation and treatment of VAW, and the insufficient integration of legal and normative progress in the discussions and approach of international fora.









