
Sep 1, 2020 | News
The ICJ today expressed its concern regarding the 31 August 2020 and 14 August 2020 decisions of the Indian Supreme Court to convict prominent human rights lawyer Prashant Bhushan for criminal contempt of court, on the basis of two twitter posts in which the lawyer criticized the performance of the Indian judiciary.
While the Court only imposed a symbolic fine of one rupee, rather than imprisonment, the ICJ considers that the conviction appears to be inconsistent with international standards on freedom of expression and the role of lawyers.
The ICJ stressed that the ruling risks having a chilling effect on the exercise of protected freedom of expression in India and urged a review of the laws and standards on criminal contempt as applied by the Indian courts.
The two tweets published by Prashant Bhushan referred to the Chief Justice of India riding an expensive motorbike belonging to a BJP leader “when he keeps the SC in Lockdown mode denying citizens their fundamental right to access justice” and asserted that the Supreme Court and the last four Chief Justices of India had contributed to how, in his view, “democracy has been destroyed in India even without a formal Emergency”
The Court in its 31 August judgment held that the tweets were a serious attempt to “denigrate the reputation of the institution of administration of justice” which, it said, is “capable of shaking the very edifice of the judicial administration and also shaking the faith of common man in the administration of justice.”
The Court considered that its ruling was consistent with freedom of speech and expression under Article 19 of the Indian Constitution, saying that it will have to balance its exercise of power to punish for contempt for itself (Article 129) with freedom of speech and expression.
The ICJ is concerned, however, that the conviction appears inconsistent with international law on freedom of expression as guaranteed by the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (Article 19, ICCPR) to which India is a party.
While some restrictions of freedom of expression are permitted by international standards, a particularly wide scope must be preserved for debate and discussion about such matters as the role of the judiciary, access to justice, and democracy, by members of the public, including through public commentary on the courts.
Any restrictions must be strictly necessary and proportionate to meet a legitimate purpose, such as protecting public order or the rights and reputations of others.
“There is a general concern that the protection of freedom of expression is rapidly eroding in India,” said Ian Seiderman, ICJ Legal and Policy Director.
“We have seen this recently around the COVID 19 crisis in relation to the imprisonment of human rights defenders, on draconian charges of sedition, rioting and unlawful assembly for protesting against the Citizenship (Amendment) Act.”
“While the Indian Supreme Court has over the years generally been an institution that has served to advance human rights in India and globally, we fear it now may be perceived as silencing criticism and freedom of expression by invoking outdated criminal contempt laws,” Seiderman added.
The ICJ joins the 1800 Indian lawyers in calling for the Supreme Court “to review the standards of criminal contempt”, emphasizing that the law is overbroad and should be aligned with international law and standards on the limited scope for restrictions on freedom of expression and criminal contempt.
“Prashant Bhushan is a lawyer and lawyers being part of the legal system have a ring-side view and understanding of the state of the court. Convicting a leading lawyer for contempt for expressing his views in this manner may have a chilling effect on lawyers, in particular considering his involvement in many public interest litigation cases,” said Mandira Sharma, ICJ South Asia Senior Legal Adviser.
Contact
Ian Seiderman – ICJ Legal and Policy Director; e: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org , t: +41 22 979 38 00
Matt Pollard – ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, Director, ICJ Centre for the Independence of Judges and Lawyers; e: matt.pollard(a)icj.org, t: +41 79 246 54 75
Download
India-Criminal-Contempt-of-Court-Press-Release-2020-ENG (PDF, with additional background information)

Aug 30, 2020 | Advocacy, News
While commemorating the International Day of the Disappeared 2020, the ICJ and 47 other national and international organizations and groups of victims, in Nepal, call on the responsible authorities to undertake immediate steps towards reinvigoration of the transitional justice (TJ) process, adopting a transparent and consultative process.
On this occasion, the victims’ groups and human rights organizations in Nepal commend the patience and resilience shown by the family members of those subjected to enforced disappearance during the 10-year-long internal armed conflict from 1996-2006. They have worked tirelessly advanced the TJ process (Truth, Justice, Reparation and Institutional Reform) in Nepal for more than a decade through their peaceful struggle, despite many difficult hurdles.
In 2015 the Supreme Court found several sections of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) Act, including the one empowering the commissions to offer amnesty and facilitate mediation/reconciliation between victims and perpetrators, including those involved in gross human rights violations, to be unconstitutional and non compliant with Nepal’s international obligations. More recently, on 26 April 2020 the Court rejected the petitions of the Government to review and revise the 2015 decision.
To date, the Government has not initiated any effort to amend the law as per these decisions. Rather, it has been misusing these Commissions in a manner that has prevented victims from accessing remedies through the regular criminal justice system and has made no efforts to strengthen these Commissions to delivery their mandates effectively. Two years back, Nepal recognized enforced disappearance as a distinct crime for the first time when enacting a new Penal Code. While this step is commendable, these legal provisions have not ensured justice for victims, the police typically refuse to investigate cases from the conflict period,arguing that they come under the jurisdiction of the TJ mechanisms.
Despite civil society’s repeated calls to appoint the Commissioners after amending the TRC Act following wider consultations with victims and civil society, the Government recently appointed Commissioners under the same Act that the SC had deemed flawed five years ago. Moreover, the Government has not addressed the repeated calls and concerns regarding the political interference and lack of transparency in the appointment of the Commissioners and the overall TJ process.
Human rights organizations and many victims groups have lost confidence in and stopped supporting to these Commissions.
The undersigned organizations call upon the Government of Nepal:
- To ensure the Commissions provide for, rather than delay and deny, truth and justice to
victims;
- Start fresh consultations to amend its law in compliance international human rights law
and Supreme Court directives, including by removing of amnesty for the perpetrators
provisions;
- Appoint a new set of commissioners under the revised Act that respects victims basic right
to truth and justice;
- Immediately ensure the social, cultural, economic, psychological and legal support
suffered by the victims and families of enforced disappearance as part of victims’ rights
to reparation;
- Revise the Penal Code to bring it in line with international standards. As a minimum, this
should include:
- amending the definition of enforced disappearances to bring it in line with Nepal’s international obligations and the Convention on the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance
- revising the penalty for enforced disappearance in the Penal Code to make it proportionate to the gravity of the crime
- removal of the statute of limitations for enforced disappearance cases
- Ratify International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearances Punishment.
Download
Full joint-statement with detailed information in English and Nepali. (PDF)
Contact
Ian Seiderman: ICJ Legal and Policy Director, e: ian.seiderman(a)icj.org
Mandira Sharma: ICJ Senior Legal Adviser, e: mandira.sharma(a)icj.org
Aug 22, 2020 | News
On 15 and 22 August 2020, the ICJ, in collaboration with the National Judicial Academy (NJA) of Nepal, organized the National Judicial Dialogue on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women and Enhancing Women’s Access to Justice.
Due to the exigencies caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the judicial dialogue was conducted through virtual means.
Fifteen trial court judges from Kathmandu Valley participated in this judicial dialogue with judicial experts from other countries.
Judge Amy Alabado Avellano, a Regional Trial Court judge from the Philippines, engaged with the judges on the application of the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) in their judicial decisions. Roberta Clarke, ICJ’s Executive Committee Chairperson and UN Women’s OIC for UN Women’s East and Southern Africa Regional Office, spoke on the right to access to justice under international human rights law.
The second day featured a discussion on specific barriers that women in Nepal face when they access justice. The judges discussed their own role and measures available to the judiciary as an institution to enhance access to justice for women in Nepal. Hon. Justice Sapana Pradhan Malla from the Supreme Court of Nepal and Dr. Diwakar Bhatta from the National Judicial Academy of Nepal led these discussions.
At the Dialogue Emerlynne Gil, ICJ Senior International Legal Adviser, remarked that “judges have a responsibility to uphold the fairness and integrity of the justice system by ensuring that proceedings are conducted in a fashion that does not subordinate the fact-finding process to myth and stereotype.” Honorable Top Bahadur Magar, the Executive Director of the National Judicial Academy, stressed that, “Trial court judges play a pivotal role in debunking myths and gender stereotypes.”
Highlighting the importance of continuing the work towards eliminating gender discriminatory practices among frontline justice actors, even during the COVID-19 pandemic, Emerlynne Gil said. “The COVID-19 pandemic is aggravating existing gender inequalities and women are experiencing more violations of their human rights.”
Contact
Laxmi Pokharel, National Legal Advisor, International Commission of Jurists, t: 977 9851047588, e: laxmi.pokharel(a)icj.org
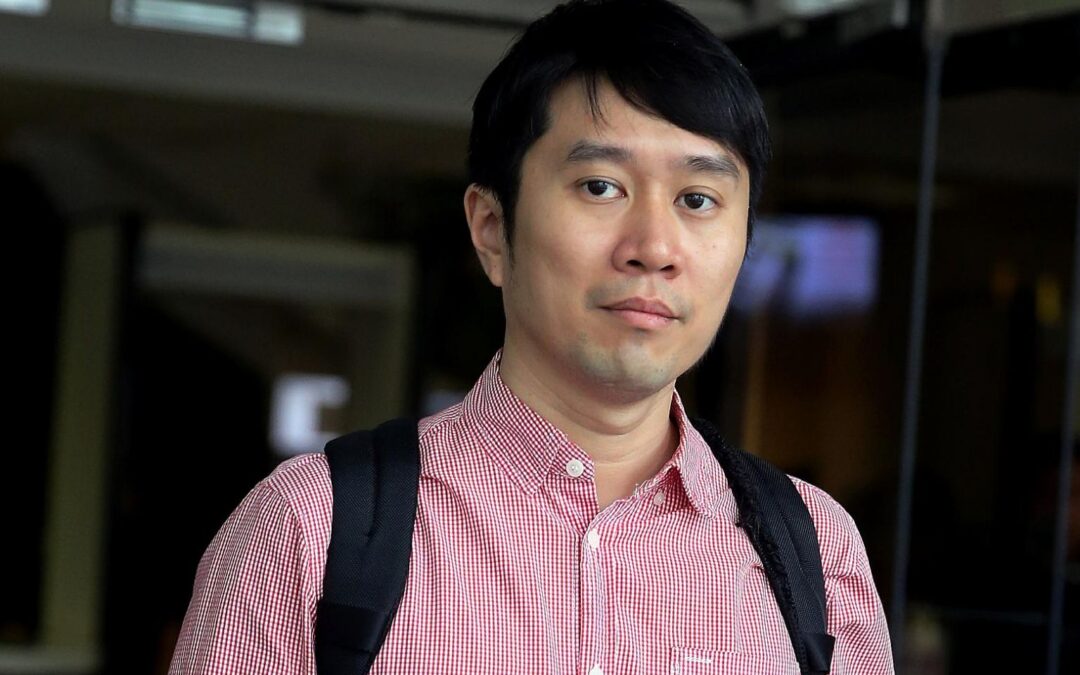

Aug 21, 2020 | News
The ICJ today condemned the conviction and imprisonment of human rights defender Jolovan Wham following the dismissal of his appeal by Singapore’s highest court in connection with a conference he had organized in 2016.
The ICJ urged the Singapore’s authorities to take action to quash the conviction and immediately release Wham from prison.
The ICJ further called on the authorities to refrain from targeting human rights defenders for harassment through unwarranted legal proceedings and to amend the country’s Public Order Act which formed the basis for the charges against Wham.
“Wham will now be in jail for organizing an indoor private discussion, in violation of his rights to free expression and freedom of association and peaceful assembly,” said Ian Seiderman, the ICJ’s Legal and Policy Director.
In November 2016, Wham organized a discussion entitled “Civil Disobedience and Social Movements” for approximately 50 participants in an indoor event venue, which included Hong Kong activist Joshua Wong as a speaker who called in via a video call. Prior to the event, Wham had not applied for a police permit to conduct the discussion, which was required under the Public Order Act (POA) as Wong is not a citizen of Singapore.
In 2019, Wham was convicted of violating section 16(1) of the POA and sentenced to a fine of S$2,000 (approx. USD 1,463) or ten days’ imprisonment in default by the District Court, following which his appeal was dismissed by the High Court. Yesterday, his appeal against the High Court decision was dismissed by Singapore’s apex Court of Appeal. Today, Wham began his prison term of ten days.
“The highly flawed Public Order Act was initially adopted to regulate public assemblies and processions, but has now perversely expanded in its scope of application to cover even private discussions,” said Seiderman.
In January 2019, the UN Special Rapporteurs on the right to freedom of opinion and expression, the situation of human rights defenders and the rights to freedom of peaceful assembly and association issued a joint statement expressing concern that the conviction was “clearly neither a necessary nor a proportional response to the actions of Jolovan Wham.” The Special Rapporteurs noted that the action had wrongly targeted the “legitimate exercise of the right to freedom of expression and freedom of peaceful assembly in Singapore.”
“The conviction and imprisonment of Wham marks a continued trend of abuse of poorly conceived laws to limit free expression, association and peaceful assembly in Singapore and harass individuals who seek to bring human rights violations to light in the country,” said Seiderman.
The ICJ calls on Singapore’s legislators also to act to amend other non-human rights compliant laws, including the Protection from Online Falsehoods and Manipulation Act (POFMA), Administration of Justice (Protection) Act (AJPA), and criminal defamation provisions under its Penal Code.
Wham was previously convicted in 2018 under the AJPA for alleged contempt of court following a comment on Facebook that “Malaysian judges are more independent than Singapore’s in cases with political implications”. He currently has active charges under the POA relating to the organizing of a vigil for a death row inmate and the holding of a silent protest on an MRT train and is being investigated under the POA for holding signs silently in solidarity with other activists.
See also
In a 2019 regional report, the ICJ found that in Singapore, non-human rights compliant provisions in POFMA, AJPA and other contempt of court provisions, civil and criminal defamation laws have been used to curtail freedom of expression and information online.
ICJ, Dictating the Internet: Curtailing Free Expression, Opinion and Information Online in Southeast Asia, December 2019
Similarly, the ICJ and other human rights organizations have called on Singapore authorities to drop investigations of human rights lawyer M Ravi and others under the contempt of court law and cease their harassment of human rights defenders. On 13 August, in relation to a death penalty case M Ravi is defending, the Court of Appeal opined that a statement made by the Attorney-General’s Chambers against the lawyer could have been “reasonably construed as intimidating”, offering a recent glimpse into the trend of legal harassment faced by human rights defenders in the country.
ICJ, ICJ and other groups call on authorities to drop investigations under abusive contempt of court law, March 2020

Aug 13, 2020 | Advocacy, News
Today, the ICJ and 64 civil society organizations jointly called on the Royal Government of Cambodia (“RGC”) to discard the draft Law on Public Order (“draft law”) which, if adopted, would breach Cambodia’s international legal obligations.
The draft law aims to regulate public spaces and public behavior within those spaces, covering aesthetics, sanitation, cleanliness, noise, and social values, all under the broad aim of maintaining “public order”. It sets out a number of specific activities that are prohibited, lists a range of penalties that may be imposed for violations, and grants unfettered enforcement powers to authorities across all levels of government, with the proclaimed objective of creating “a more civilized society”.
The organizations expressed concern that the draft law contains multiple overbroad and arbitrary provisions which violate numerous human rights protections enshrined in the Constitution of the Kingdom of Cambodia and human rights treaties to which Cambodia is party, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
Amidst an ongoing crackdown on fundamental freedoms in Cambodia, a number of existing laws already grant overbroad and unfettered powers to the RGC and are regularly deployed abusively to undermine human rights. Adoption of this draft Law on Public Order would serve to facilitate a further deterioration of the human rights situation in Cambodia.
The joint statement is available in English here.
The joint statement is available in Khmer here.
Contact
Kingsley Abbott, Senior Legal Adviser, ICJ Global Accountability Initiative e: kingsley.abbott(a)icj.org
See also
ICJ, ‘ICJ and 31 organizations jointly urge Governments to call for respect of human rights in Cambodia’, 22 July 2020
ICJ, ‘Cambodia: State of Emergency bill violates the rule of law’, 8 April 2020
ICJ, ‘Misuse of law will do long-term damage to Cambodia’, 26 July 2018
ICJ report, ‘Achieving Justice for Gross Human Rights Violations in Cambodia: Baseline Study’, October 2017







