
Aug 19, 2020 | News
Today the ICJ called on the public authorities to refrain from comments or actions that could undermine the integrity of the judicial process and the independence of the judiciary.
On August 4, the Instruction Special Chamber of the Criminal Chamber of the Supreme Court of Justice ordered the pretrial detention, substituted for house arrest, of the former President Álvaro Uribe Velez, relating to allegations of bribery of witnesses and procedural fraud.
In recent days, a number of politicians have made highly inappropriate and inflammatory statements, including some suggesting that judges are making their decisions based on ideological or political biases rather than based on the Constitution and the law.
Colombian president Ivan Duque said in remarks broadcast on television on the 4 of August: “it hurts as a Colombian that many of those who have lacerated the country with barbarism defend themselves at liberty or are even guaranteed to never go to prison, and that an exemplary public servant who has held the highest dignity of the State is not allowed to defend himself in freedom with the presumption of innocence. I am and will always be a believer in the innocence and in the honor of him who, with his example, have earned a place in the history of Colombia.” (unofficial translation).
The ICJ stresses that it is inappropriate for a head-of-State or other executive official to intervene in this manner in a case that is under active judicial proceedings. The UN Basic Principles on the Independence of the Judiciary make clear that “it is the duty of all governmental and other institutions to respect and observe the independence of the judiciary” and this includes refraining from any “improper influences, inducements, pressures, threats or interferences, direct or indirect.”
In reaction to Senator Uribe’s arrest, the political party “Centro Democrático”, of which both President Duque and former President Uribe are members, released a press statement saying that they were planning to propose a National Constituent Assembly with the purpose of “depoliticizing justice”. Also, former President Uribe mentioned on 16 of August that he hoped his political party would initiate a reform of the justice system through a “referendum” to end the “politicization” of the Court.
The ICJ considers that any actions concerning reforms of the justice sector must be based on the standards and best practices that reinforce the independence of the judiciary and the prompt, timely and fair administration of justice, and not on a political reaction based on a single active case.
Lastly, United States Vice President Mike Pence has also made inappropriate remarks related to the Colombian justice system, tweeting on August 14 that he joined the voices that called Colombian authorities to let Alvaro Uribe “defend himself as a free man”.
Contact
Carolina Villadiego Burbano, ICJ Latin America legal and policy adviser, e: carolina.villadiego(a)icj.org

Mar 9, 2020 | News
The ICJ today expressed regret at the death of Judge Khanakorn Pianchana, who committed suicide on 7 March 2020. Judge Khanakorn was widely known after an attempted suicide in October 2019 following the delivery of a verdict which he claimed was interfered by a senior judge.
Judge Khanakorn previously served as Vice Presiding Judge of the Yala Provincial Court in Thailand’s restive southern region. He passed away on 7 March 2020 at his home in Chiang Mai province.
Background
Before the suicide, Judge Khanakorn posted a two-page letter on his Facebook page, in which he claimed that he had been subject to disciplinary proceeding and had criminal charge brought against him after he had publicized his concerns about interference by a superior judge into certain rulings. These involved five individuals detained and interrogated under special security laws in southern Thailand.
In October 2019, Judge Khanakorn claimed in a public letter that he had been ordered by a senior judge to rewrite a ruling in which he exonerated the five individuals charged with murder, for lack of evidence. Following his delivery of the verdict, he shot himself in the chest in a courtroom at Yala Provincial Court.
After his first suicide attempt, according to the Office of the Judiciary’s Press Release dated 18 November 2019, the Judicial Commission initiated an investigation against him for violations of provisions on discipline of judicial officials. He was subsequently transferred to the Court of Appeal Region 5 in Chiang Mai, at which time he was further investigated for committing criminal offences under the Firearms, Ammunition, Explosives, Fireworks and Imitation Firearms Act.
On 7 March 2020, according to the interview gave by Secretary-General of Office of the Judiciary, an initial investigation of the Judicial Commission found that there had been no improper interference, and the disciplinary actions and the criminal charges that are brought against Judge Khanakorn were based on his actions for carrying a gun into court and using the gun to attempt suicide.
Contact
Frederick Rawski, ICJ Asia-Pacific Director, t: +66 64 478 1121; e: frederick.rawski(a)icj.org
Download
To download the statement in Thai, click here.
Jan 24, 2020 | News
Today, the ICJ has conducted a trial observation in disbarment proceedings against lawyer Yerlan Gazymzhanov before the Saryarkyn Court of Nur-Sultan.
Erlan Gazymzhanov is facing disbarment following a lawsuit brought by the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The lawyer is accused of violating court rules by publishing on a social network an archive video from the hearing in a case in which he alleged inappropriate behaviour by the judge.
The case raises issues of the lawyer’s freedom of expression and possible improper interference in his work.
The ICJ will carry out an assessment of the case and its compliance with international standards following its observation of the proceedings.
Another lawyer, Amanzhol Mukhamedyarov is facing a disbarment lawsuit on the same allegations.
Mukhamedyarov’s case will be heard in separate proceedings on 4 February in Esil district court of Nursultan.
Dr Stefan Stobl, a lawyer from Munich (Germany) and a member of the ICJ Section Germany, observed today’s hearing on behalf of the ICJ.
Additional information:
Read ICJ’s trial observation manual
The ICJ has previously expressed concern about increasing restrictions on the independence of lawyers in Kazakhstan:
Kazakhstan: frivolous disbarment proceedings against prominent lawyer Sergey Sizintsev should be immediately dropped, ICJ says
Kazakhstan: ICJ alarmed at government interference in legal profession
Kazakhstan: the ICJ calls to immediately drop prosecution of lawyer Bauyrzhan Azanov

Dec 6, 2019 | News
The ICJ calls on the Polish authorities to put an immediate end to unjustified disciplinary proceedings initiated against judges, including Krystian Markiewicz, Chairperson of the Polish Judges’ Association “Iustitia”.
The ICJ considers that the disciplinary action against Judge Markiewicz’ was initiated because of his questioning of the Polish government’s “reforms” that have severely eroded the independence of the judiciary in Poland.
“The disciplinary action taken against Judge Markiewicz for his criticism of the government’s attack on judicial independence violates international standards on the independence of the judiciary and should be ended immediately”, said Róisín Pillay, Director of the ICJ Europe and Central Asia Programme.
“Judges have a right to freedom of expression and to form and take part in associations of judges. They have a particularly important role in speaking up to defend the rule of law and the independence of the judiciary, which is undermined by arbitrary disciplinary proceedings such as those against Judge Markiewicz”, she added.
By order of the Deputy Disciplinary Commissioner of the ordinary court judges, on 4 December, disciplinary proceedings alleging 55 instances of misconduct were initiated against Judge Krystian Markiewicz. These include: inciting disrespect for Poland’s legal order by questioning the independence and legality of the National Council of the Judiciary (NCJ), and the constitutionality of the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court; and calling for appeals to the Disciplinary Chamber to be suspended.
The disciplinary action against Judge Markiewicz comes within a week of the decision to suspend with immediate effect district Judge Paweł Juszczyszyn, who, in presiding over an appeal, questioned the impartiality of the judge who had delivered the original verdict as a result of being elected by the National Council for the Judiciary. On 1 December 2019, the Polish Judges’ Association Iustitia organized rallies in support of Judge Juszczyszyn.
The ICJ stresses that such actions taken against judges are inconsistent with the duties of all branches of the State to respect and protect the independence of the judiciary. The ICJ calls for Judge Juszczyszyn to be immediately re-instated in his post.
On 4 December 2019, the labour law chamber of the Supreme Court, in implementation of a recent ruling of the Court of Justice of the UE, held that the NCJ is not an impartial and independent body, and that the disciplinary chamber of the Supreme Court is not a “court” under EU or Polish law, thereby confirming the concerns raised by both Judge Juszczyszyn and Judge Markiewicz.
Background
The UN Basic Principles on the Independence of the Judiciary clarify that all governmental and other institutions must respect and observe the independence of the judiciary (Principle 1), and that judges must decide all matters before them impartially, on the basis of facts and in accordance with the law, without any restrictions, improper influences, inducements, pressures, threats or interferences, direct or indirect (Principle 2). Judges can be subject to suspension or removal only following fair procedures (Principle 17) and only for reasons of incapacity or behaviour that renders them unfit to discharge their duties (Principle 18).
In recent years, the Polish executive and legislative authorities have systematically undermined the independence of the judiciary in the country, including through laws that have sought to force the dismissal of judges by lowering the mandatory retirement age. In addition, they have brought the appointment of judges under political control by re-structuring the National Council of the Judiciary (NCJ), with a majority of its members selected by the Polish Parliament. (see ICJ statement)
This move has also politicized the Disciplinary Chamber of the Supreme Court, whose members are selected by the NCJ, and the disciplinary court of first instance. In October 2019, the European Commission referred Poland to the CJEU on the grounds that the new disciplinary regime for judges undermines their independence.
In June 2019, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) held that the Polish Law on the Supreme Court lowering the retirement age of judges of the Supreme Court and providing discretionary power to the President to allow a judge to remain in office following the mandatory retirement date was contrary to the principle of effective judicial protection and therefore in violation of EU law. In November 2019, the CJEU held that Poland violated the independence of the judiciary by lowering in 2017 the pension age of Polish judges and giving the power to maintain them in office to the Minister of Justice.

Dec 3, 2019 | Agendas, Events, News
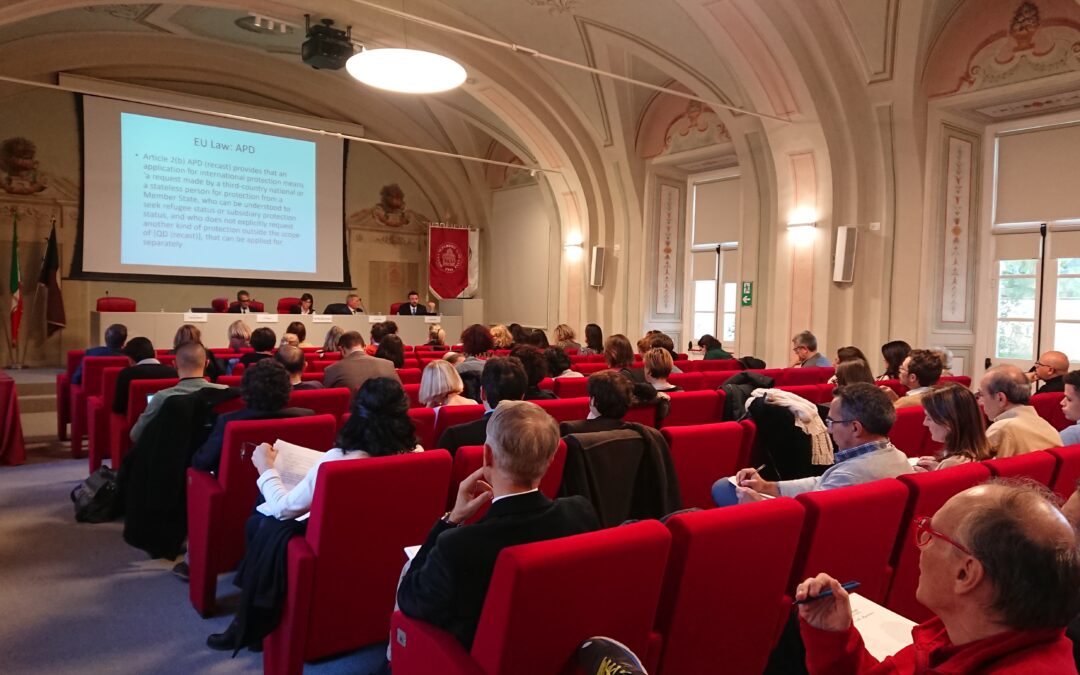
Today, the ICJ together with Scuola Universitaria Sant’Anna and Scuola Superiore de la Magistratura hold a training seminar on access to the asylum procedure and the right to an effective remedy in Pisa, Italy.
The training seminar brings together 65 Italian judges and lawyers specialized in access to international protection. During the two days of training, experts from the CJEU, Italian judiciary and academics, UNHCR and ICJ will deliver the training, bringing international human rights and EU law perspectives to the discussion on Italian law and practice.
Among the issues discussed during the training seminar will be access to the asylum procedure in international and EU law, access to the asylum procedure and accelerated procedures in light of the right to an effective remedy, appeal, legal assistance and legal aid, and interpretation. Further issues including the burden of proof in international protection cases and duties of cooperation with the asylum authority will be examined from the perspectives of judges, of territorial Commissions and lawyers as well as from the international and EU law perspective. Finally, working groups on burden of proof, credibility assessment of asylum seekers and countries of origin of asylum seekers will take place.
See the full agenda here.
This training is a part of FAIR PLUS project. It was carried out with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents are the sole responsibility of ICJ and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Union.









